-
负载均衡式在线OJ
文章目录
0 项目展示
- 利用文件的方式进行录题
文件版Oj项目演示视频
- 利用MYSQL数据库的方式录题
负载均衡式在线OJ项目
代码链接
1. 所用技术与开发环境
1.1 所用技术:
- C++ STL 标准库
- Boost 准标准库(字符串切割)
- cpp-httplib 第三方开源网络库
- ctemplate 第三方开源前端网页渲染库
- jsoncpp 第三方开源序列化、反序列化库
- 负载均衡设计
- 多进程、多线程
- MySQL C connect
- Ace前端在线编辑器(了解)
- html/css/js/jquery/ajax (了解)
1.2 开发环境
- Centos 7 云服务器
- vscode
- Mysql Workbench
2 项目基本结构
我们的项目核心是三个模块
模块 功能 comm 公共模块,其它两个共同用到的hpp代码。例如:日志信息LOG compile_server 编译与运行模块 oj_server 获取题目列表,查看题目编写题目界面,负载均衡。 
(来自项目资料)3 CompilerServer模块设计
3.1 整体结构设计
CompilerServer模块: 编译并运行客户端通过网络提交的代码,得到格式化的相关的结果- 1
- compiler模块:只负责代码的编译。拿到待编译代码的文件名,进行编译,并形成对应的临时文件。
- runner模块:只负责运行代码。通过程序替换(execl)—>进行程序的运行—>把运行形成的信息以文件的形式存到temp目录下。
- compiler_run模块:整合编译模块和运行模块。解析用户发来的json串 -->把用户传过来的代码与后台测试用例的代码整合 ----> 编辑一个名字不重复的源文件—>调用编译和运行两个模块完成功能 —> json串构建的结果返回给编译服务模块。
- compiler_server模块:负责搭建http服务,接收客户端发来的请求,后调用compiler_run模块编译运行,并将结果返回给客户端。

- 它们之间的关系

3.2 util.hpp(后面有不认识的函数调用可以来这里看看有没有它的实现方法)
- 代码里有注释
#pragma once #include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include namespace ns_util { class TimeUtil { public: static std::string GetTimeStamp() { struct timeval _time; gettimeofday(&_time, nullptr); return std::to_string(_time.tv_sec); } //获得毫秒时间戳 static std::string GetTimeMs() { struct timeval _time; gettimeofday(&_time, nullptr); return std::to_string(_time.tv_sec * 1000 + _time.tv_usec / 1000); } }; const std::string temp_path = "./temp/"; class PathUtil { public: static std::string AddSuffix(const std::string &file_name, const std::string &suffix) { std::string path_name = temp_path; path_name += file_name; path_name += suffix; return path_name; } // 编译时需要有的临时文件 // 构建源文件路径+后缀的完整文件名 // 1234 -> ./temp/1234.cpp static std::string Src(const std::string &file_name) { return AddSuffix(file_name, ".cpp"); } // 构建可执行程序的完整路径+后缀名 static std::string Exe(const std::string &file_name) { return AddSuffix(file_name, ".exe"); } static std::string CompilerError(const std::string &file_name) { return AddSuffix(file_name, ".compile_error"); } // 运行时需要的临时文件 static std::string Stdin(const std::string &file_name) { return AddSuffix(file_name, ".stdin"); } static std::string Stdout(const std::string &file_name) { return AddSuffix(file_name, ".stdout"); } // 构建该程序对应的标准错误完整的路径+后缀名 static std::string Stderr(const std::string &file_name) { return AddSuffix(file_name, ".stderr"); } }; class FileUtil { public: static bool IsFileExists(const std::string &path_name) { struct stat st; if (stat(path_name.c_str(), &st) == 0) { //获取属性成功,文件已经存在 return true; } return false; } static std::string UniqFileName() { static std::atomic_uint id(0); id++; // 毫秒级时间戳+原子性递增唯一值: 来保证唯一性 std::string ms = TimeUtil::GetTimeMs(); std::string uniq_id = std::to_string(id); return ms + "_" + uniq_id; } static bool WriteFile(const std::string &target, const std::string &content) { std::ofstream out(target); if (!out.is_open()) { return false; } out.write(content.c_str(), content.size()); out.close(); return true; } static bool ReadFile(const std::string &target, std::string *content, bool keep = false) { (*content).clear(); std::ifstream in(target); if (!in.is_open()) { return false; } std::string line; // getline:不保存行分割符,有些时候需要保留\n, // getline内部重载了强制类型转化 while (std::getline(in, line)) { (*content) += line; (*content) += (keep ? "\n" : ""); } in.close(); return true; } }; class StringUtil { public: /************************************* * str: 输入型,目标要切分的字符串 * target: 输出型,保存切分完毕的结果 * sep: 指定的分割符 * **********************************/ static void SplitString(const std::string &str, std::vector<std::string> *target, const std::string &sep) { //boost split boost::split((*target), str, boost::is_any_of(sep), boost::algorithm::token_compress_on); } }; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
3.1.1 添加日志功能(comm模块)
#pragma once #include#include #include "util.hpp" namespace ns_log { using namespace ns_util; /*日志设计为五个等级 NORMAL:正常 DEBUG:dubug WARNING:警告 ERROR:错误 DEADLY:致命*/ // 日志等级 enum { INFO, //就是整数 DEBUG, WARNING, ERROR, FATAL }; inline std::ostream &Log(const std::string &level, const std::string &file_name, int line) { // 添加日志等级 std::string message = "["; message += level; message += "]"; // 添加报错文件名称 message += "["; message += file_name; message += "]"; // 添加报错行 message += "["; message += std::to_string(line); message += "]"; // 日志时间戳 message += "["; message += TimeUtil::GetTimeStamp(); message += "]"; // cout 本质 内部是包含缓冲区的 std::cout << message; //不要endl进行刷新 return std::cout; } // LOG(INFo) << "message" << "\n"; // 开放式日志 #define LOG(level) Log(#level, __FILE__, __LINE__) } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
3.1.2 获取日期时间格式的时间戳(comm模块)
获取当前时间:系统调用gettimeofday接口获取当前的时间戳
namespace ns_util { class TimeUtil { public: static std::string GetTimeStamp() { struct timeval _time; gettimeofday(&_time, nullptr); return std::to_string(_time.tv_sec); } //获得毫秒时间戳 static std::string GetTimeMs() { struct timeval _time; gettimeofday(&_time, nullptr); return std::to_string(_time.tv_sec * 1000 + _time.tv_usec / 1000); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
3.2 compiler编译模块
- 子进程进行编译(需要进行程序替换)
- 父进程等待子进程编译后的结果
具体实现的流程图如下:

当然这里就需要公共模块util.cpp里的代码(把无后缀的filename文件通过Pathutile类中的静态函数形成·所需要的相关后缀文件、例如—.Cpp文件)#pragma once #include#include #include #include #include #include #include "../comm/util.hpp" #include "../comm/log.hpp" // 只负责进行代码的编译 namespace ns_compiler { // 引入路径拼接功能 using namespace ns_util; using namespace ns_log; class Compiler { public: Compiler() {} ~Compiler() {} // 返回值:编译成功:true,否则:false // 输入参数:编译的文件名 // file_name: 1234 // 1234 -> ./temp/1234.cpp // 1234 -> ./temp/1234.exe // 1234 -> ./temp/1234.stderr static bool Compile(const std::string &file_name) { pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid < 0) { // 内部错误,创建子进程失败 LOG(ERROR) << "内部错误,创建子进程失败" << "\n"; return false; } else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程 umask(0); int _stderr = open(PathUtil::CompilerError(file_name).c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644); if (_stderr < 0) { // 没有成功形成stderr文件 LOG(WARNING) << "没有成功形成stderr文件" << "\n"; exit(1); } // 重定向标准错误到_stderr dup2(_stderr, 2); // 程序替换,并不影响进程的文件描述符表 // 子进程: 调用编译器,完成对代码的编译工作 // g++ -o target src -std=c++11 execlp("g++", "g++", "-o", PathUtil::Exe(file_name).c_str(), PathUtil::Src(file_name).c_str(), "-D", "COMPILER_ONLINE", "-std=c++11", nullptr); LOG(ERROR) << "启动编译器g++失败,可能是参数错误" << "\n"; exit(2); } else { // 父进程 waitpid(pid, nullptr, 0); //阻塞等待子进程完成编译 // 编译是否成功,就看有没有形成对应的可执行程序 if (FileUtil::IsFileExists(PathUtil::Exe(file_name))) { // 编译成功! LOG(INFO) << PathUtil::Src(file_name) << " 编译成功!" << "\n"; return true; } } LOG(ERROR) << "编译失败,没有形成可执行程序" << "\n"; return false; } }; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
3.3 runner运行模块
运行实现的功能可以分三种情况:
- 代码跑完,结果正确
- 代码跑完,结果不正确
- 代码没跑完,异常了
把结果通过返回值的不同交给compliler_run模块处理。
3.4 compliler_run模块
3.4.1 功能实现概述
这里就涉及到网络服务,用户的代码会以json串的方式传给compliler_run模块。首先每次用户提交的代码都是唯一性的源文件,然后调用编译模块和运行模块编译并运行该源文件,然后通过编译与运行的结果构建相关的json串返回给上层,两个参数,一个输入形的json串,一个输出形的json串。
-
json串的body内容如下:
* 输入: * code: 用户提交的代码 * input: 用户给自己提交的代码对应的输入,不做处理 * cpu_limit: 时间要求 * mem_limit: 空间要求 * * 输出: * 必填 * status: 状态码 * reason: 请求结果 * 选填: * stdout: 我的程序运行完的结果 * stderr: 我的程序运行完的错误结果 * * 参数: * in_json: {"code": "#include...", "input": "","cpu_limit":1, "mem_limit":10240} * out_json: {"status":"0", "reason":"","stdout":"","stderr":"",}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
3.5 compiler_server模块
把整个模块打包成一个网络服务,用户使用POST方法请求服务器上的compiler_run服务,请求的正文就是我们编译运行模块需要的json串。服务器用过json串调用编译运行模块,得到返回的json串后见响应返回给用户。

4 OJServer模块设计
4.1 各个模块功能介绍
- 基于MVC 结构的oj 服务设计本质:建立一个小型网站
OJ模块实现如下三个部分
- 获取首页,用题目列表充当
- 编辑区域页面
- 提交判题功能(编译并运行)
- 整个模块采用的是MVC的设计模式进行设计
M: Model,通常是和数据交互的模块,比如,对题库进行增删改查(文件版,MySQL)
V: view, 通常是拿到数据之后,要进行构建网页,渲染网页内容,展示给用户的(谷歌浏览器)
C: control, 控制器,就是我们的核心业务逻辑

整个模块可分为四个部分:
oj_model模块:负责模块前两个功能的数据部分,通过与题库交互,得到题目的信息。
oj_view模块:负责渲染用户得到网页。
oj_control模块:负责整个OJServer模块的业务逻辑控制。对下负责选择不同的主机请求编译服务,对上根据用户的三种请求,配合上面两个模块,完成对应的功能。
oj_server模块:搭建http服务,根据用户的请求,完成功能。4.2 oj_server模块
- 用户请求的服务路由功能
#include#include "../comm/httplib.h" #include "oj_control.hpp" using namespace httplib; using namespace ns_control; static Control *ctrl_ptr = nullptr; void Recovery(int signo) { ctrl_ptr->RecoveryMachine(); } int main() { signal(SIGQUIT, Recovery); // 用户请求的服务器功能 Server svr; Control ctrl; ctrl_ptr = &ctrl; // 获取所有的题目列表 svr.Get("/all_questions", [&ctrl](const Request &req, Response &resp) { // 返回一张包含所有题目的网页 std::string html; ctrl.ALLQuestions(&html); resp.set_content(html, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); // resp.set_content("这是所有题目列表", "Text/plain; charset=utf-8"); }); // 用户要根据题目编号,获取题目的内容 // /question/100 -> 正则匹配 // R"()", 原始字符串raw string,保持字符串内容的原貌,不用做相关的转义 svr.Get(R"(/qustion/(\d+))", [&ctrl](const Request &req, Response &resp) { std::string number = req.matches[1]; std::string html; ctrl.Questions(number, &html); resp.set_content(html, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); }); // 用户提交代码,使用我们的判题功能(1. 每道题的测试用例 2. compile_and_run) svr.Post(R"(/judge/(\d+))", [&ctrl](const Request &req, Response &resp) { std::string number = req.matches[1]; std::string result_json; ctrl.Judge(number, req.body, &result_json); resp.set_content(result_json, "application/json;charset=utf-8"); // resp.set_content("指定题目判题" + number, "Text/plain; charset=utf-8"); }); svr.set_base_dir("./wwwroot"); svr.listen("0.0.0.0", 8080); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
4.3 oj_model模块
- model功能,提供对数据的操作。主要是为了得到题库中对应的题目信息。
因此我们设计的类的成员属性如下(结构化):
- 文件版:
struct Question { std::string number; // 题目编号,唯一 std::string title; // 题目的标题 std::string star; // 难度: 简单 中等 困难 int cpu_limit; // 题目的时间要求(S) int mem_limit; // 题目的空间要去(KB) std::string desc; // 题目的描述 std::string header; // 题目预设给用户在线编辑器的代码 std::string tail; // 题目的测试用例,需要和header拼接,形成完整代码 };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
注意:文件需要指明路径。

- MYSQL版:
struct Question { std::string number; // 题目编号,唯一 std::string title; // 题目的标题 std::string star; // 难度: 简单 中等 困难 std::string desc; // 题目的描述 std::string header; // 题目预设给用户在线编辑器的代码 std::string tail; // 题目的测试用例,需要和header拼接,形成完整代码 int cpu_limit; // 题目的时间要求(S) int mem_limit; // 题目的空间要去(KB) };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

4.4 oj_view模块
渲染的意思就是把网页中的代码相关的关键字替换了,就相当与c语言的宏替代(我说的不准,只是类比一下)具体做法就需要在Linux上下载ctemplate

4.5 oj_control模块
- control,逻辑控制模块
- oj_control模块负责整个OJServer模块的业务逻辑控制。对下负责选择不同的主机请求编译服务,对上根据用户的三种请求,配合model和control两个模块,完成对应的功能。
- 它需要能够提供三个功能,即:一个可以构建好题目列表网页,一个可以根据题目编号构建好单个题目网页,还有一个判题功能。
- 要实现它的功能就需要前面那些模块的配合,网页获取题目列表的两个功能肯定需要model模块和view模块实现。判题功能需要调用compile_server模块,使用它的编译与运行的结果帮我完成判题。(当然服务器的选择需要计数来实现负载均衡;而普通数字肯定不行,我们需要加锁保护。)
5. 前端页面设计
前端的内容大家看一下,感兴趣的话可以去菜鸟教程看看。
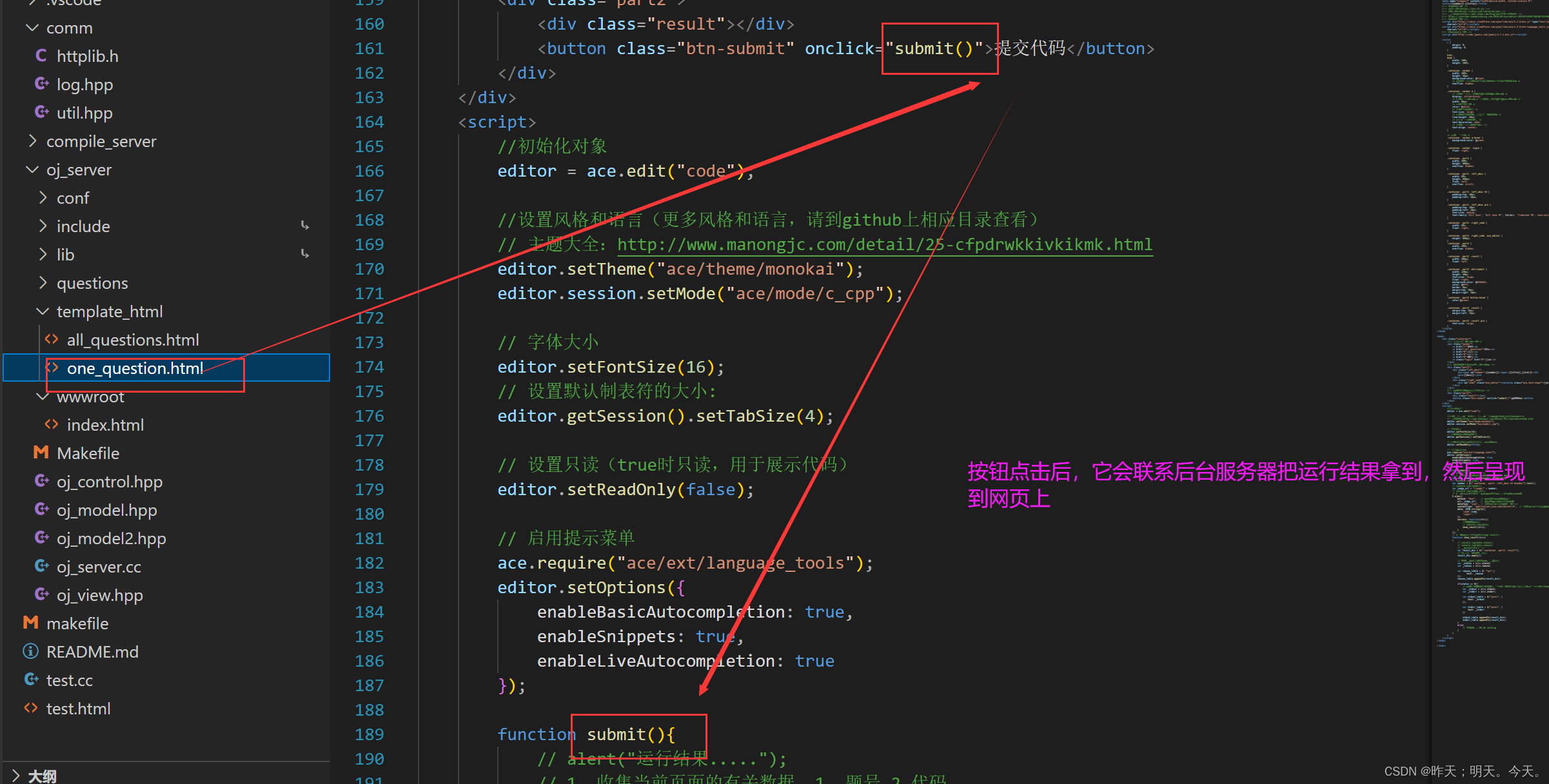
6 顶层项目部署Makefile
在顶层新建一个Makefile文件,该文件的功能是make时可以同时编译CompilerServer服务和OJServer服务,当输入make output时会自动形成一个output文件,里面包含了compiler_server和oj_server的应用程序和一些运行程序必须的文件。输入make clean不光会清理掉创建的可执行程序,还会清理掉output。

output的内容就可以发布出去了。7 项目组件的安装与使用
7.1 jsoncpp
7.2 httplib
7.3 boost库
7.4 ctemplate
-
相关阅读:
docker 开启 tcp 端口
http接口自动化测试框架实现
数据库中间MyCat最新硬核教程,主从复制,分库分表
【原创】MQTT开发笔记(三)Win10上部署Mosquitto
任务流程----
Java 面试题
2022/11/20[指针] 通过函数,利用指针将数组a中前n个元素按相反顺序存放
使用electron ipcRenderer接收通信消息多次触发
【MATLAB教程案例17】基于NSGAII多目标优化算法的matlab仿真及应用
【RHCE】作业:配置NFS开发目录&配置DNS正向解析域名
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Dingyuan0/article/details/133377936
