-
【初阶数据结构】二叉树全面知识总结
二叉树详解
铁汁们,今天给大家分享一篇二叉树全面知识总结,来吧,开造⛳️树的概念及其结构
树的概念
树的概念:是一种非线性的数据结构,它由n个有限的节点组成的一个具有层次关系的集合。树的结构类似于真实世界中的树,它看起来就像一颗倒挂着的树,即:它的根是朝上的,而叶子是朝下的。


说明:1.有一个特殊的节点,根节点,该节点没有父节点(前驱节点);
2.根节点除外,其他节点被分成了M个互不相交的集合{a1, a2, a3…},每个集合又是一颗结构类似的子树(每个子树又可以被分成根节点、左子树、右子树)——》递归思想,把大事化小,树是递归定义的;
3.其他节点都有一个父节点(前驱节点),并且可以有零个或多个子节点(后继节点)。一个节点可以有一个或多个子节点,但每个节点最多只能有一个父节点 ——》说明子树是不相交的。

注意:树形结构中,子树之间不能有交集,否则就不是树形结构。
树的相关概念

树的表示方法
树形结构的线性表:树在进行存储时,既要保存值域,也要保存各个节点之间的关系。
树的表示方法:双亲表示法、孩纸兄弟表示法、孩纸表示法、孩纸双亲表示法等(多叉树)。
孩纸兄弟表示法
孩纸兄弟表示法:让根节点指向第一个节点,让第一个节点指向靠的最近的兄弟节点,依次往后,直到无兄弟节点和兄弟节点无第一个节点。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #includetypedef int DataType; typedef struct Node //孩纸兄弟表示法 { struct Node* firstchild; struct Node* secondchild; DataType val; //值域 }Node; int main() { Node* parent; //从根节点开始 Node* child = parent->firstchild; //让根节点指向第一个节点 while (child) { printf("%d ", child->val); child = child->secondchild; //第一个节点指向靠的最近的兄弟节点 } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24

双亲表示法(并查集)

//c++实现代码: #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include//合并查集(最基本版:用来1.合并两个集合, 2.查找两个数是否在一个集合内) using namespace std; const int N = 1e5 + 10; //每个集合都用一个树来表示,树的编号就是整个集合的编号,每个数都有个树根。每个节点用来存储其父节点,p[x]表示节点x的父节点 //判断每个集合的树根,p[x] == x //求x的集合编号,while(p[x] != x) x = p[x]; //将两个集合编号合并,因px是x的集合编号,py是y的集合编号,p[x] = y(让x所在的集合变为y所在集合的儿子)或者p[y] = x(让y所在的集合变为x所在集合的儿子) int p[N]; int find(int x) //查找每个数的树根(集合编号)+路径压缩(因每个节点均向上找树根,当一个节点找到了树根,则该节点所在的路径上所有的点父节点直接等于树根) { if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x]; } int main() { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i; //因每个数都在不同的集合中,让集合的编号的本身(p[x] == x,树根) while (m--) { char op[2]; int a, b; cin >> op >> a >> b; if (*op == 'I') p[find(a)] = find(b); //两个集合的合并 else //判断两数所在的集合是否相同,即:判断树根值是否向他 { if (find(a) == find(b)) printf("YES\n"); //相同 else printf("NO\n"); //不相同 } } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
树的实际应用
树的应用:用于表示文件系统的目录,表示方法为孩子兄弟法。



二叉树
二叉树的概念
二叉树定义:是由有限节点组成的集合,该集合可能为空(空树),或不为空(由一个根节点加上左子树和右子树组成)。
注意:
1.二叉树度小于等于2。
2.二叉树不存在度大于2的节点。
3.二叉树有左、右子树之分,次序不能颠倒,所以二叉树也为有序树。二叉树都是由以下几种情况的树复合而成的:

二叉树的种类
特殊的二叉树:满二叉树、完全二叉树。
1.满二叉树:
一个二叉树,每一层节点达到了最大值(度等于2),则这个二叉树为满二叉树。

注意:满二叉树高度为h,满二叉树总结点树为2^n-1个。
现实生活中的满二叉树:

2.完全二叉树:
二叉树深度为n,1.我是文本 红色red前n-1层结点数都要达到最大值(度为2),最后一层结点数不一定达到最大值,但最后一层节点一定是从左到右排布的。完全二叉树是一种特殊的满二叉树。

注意:完全二叉树的总结点个数范围为[ 2^(n-1), 2^n-1]。
二叉树的性质

题目:

二叉树的存储结构
二叉树一般可分为两种结构存储,一种为顺序存储,一种为链式存储。
1.顺序存储
顺序结构存储数据实质就是用数组来存储,一般数组只适用于存储满二叉树、完全二叉树,若存储普通的二叉树则会造成空间浪费,堆、栈、顺序表均为顺序存储结构,均用数组来存储数据。二叉树顺序存储在逻辑结构上是一颗二叉树(想象出来的结构),在 color = red>物理结构上是一个数组(实际存在的)。

2.链式存储二叉树链式存储:
用链表来表示二叉树节点之间的逻辑关系,通常链表中每个节点由三个域组成,数据域和左、右指针域,左、右指针域分别存储该节点的左、右孩子的地址,根节点通过其左右子节点指针连接到左右子树,子节点可以依次连接到它们的子树。链式结构又可以分为二叉链、三叉链。二叉链:
每个节点包含数据元素和指向左右子节点的指针。通过这个指针,可以实现从子节点到父节点的访问。二叉链结构使得在树中的任意节点上,能够直接访问其父节点,方便进行反向操作。但要注意,根节点的父节点指针为空。三叉链:
每个节点除了包含数据元素和指向左右子节点的指针之外,还包含一个指向父节点的指针。三叉链结构使得在树中的任意节点上,能够同时访问其父节点和子节点,方便进行各种树的操作。二叉树顺序结构的实现
堆的概念及结构
堆:堆中所有的元素按完全二叉树的顺序全部存储到一维数组中,当根节点的值<=左、右子树的根节点的值,任意父亲节点值<=左、右孩纸节点的值,则该堆为小堆;当根节点的值>=左、右子树的根节点的值,任意父亲节点值>=左、右孩纸节点的值,则该堆为大堆。
注意:堆的性质:
1.任意父亲节点值<=(或者>=)左、右孩纸节点的值。
2.堆的逻辑结构为完全二叉树(堆是一颗完全二叉树),物理结构为数组。
堆向上、向下调整法
给出一个数组,就可以画出其对应得完全二叉树,通过向上或向下调整法可以将其调整为一个小堆。
向上、向下调整法使用前提:左、右子树必须都为堆。
向上调整法:从根节点的左结点开始,从左到右依次调整每一层的所有节点形成堆。
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child) //(使用前提:左、右子树均为堆)向上调整,从根节点的左结点开始,数据从上往下依次向上调整形成堆 { int parent = (child - 1) / 2; //父亲节点(找父亲节点) while (child > 0) // { if (a[child] < a[parent]) //该节点与父节点值进行比较 swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); //交换,形成小堆 child = parent; //递归 parent = (child - 1) / 2; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

向下调整法:从最后一个非叶子节点开始,数据从下往上依次向下调整每个节点形成堆。
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent) //(使用前提:根的左、右子树均为堆)向下调整,从最后一个非叶子节点开始,数据从下往上依次向下调整形成堆 { int child = parent * 2 + 1; //孩纸节点,初始化左孩子值比右孩纸值小(找孩纸节点) while (child < n) // { if (child + 1 < n && a[child] > a[child + 1]) //左、右孩纸值进行比较,确保右孩纸存在,且左孩子值比右孩纸值大 swap(&a[child], &a[child + 1]); //交换,此时child节点中的值为孩纸节点的最小值 if (a[child] < a[parent]) //左孩子值与父节点值进行比较 swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); //交换,形成小堆 parent = child; //递归 child = parent * 2 + 1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

堆的插入
思路:将数据直接插入到最后一个位置,新插入的元素在向上调整。
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x) //向堆中插入一个元素 { assert(hp); //断言,不能对空指针进行加、减、解引用操作 if (hp->size == hp->capacity) //空间满了,不能进行插入数据,如需插入数据,需要realloc进行扩容 { int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2; //新容量 HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity); if (tmp == NULL) //realloc开辟失败 { perror("realloc failed"); exit(-1); } hp->a = tmp; //realloc开辟成功 hp->capacity = newcapacity; //容量进行更新为新容量 } hp->a[hp->size] = x; //在末尾插入一个元素 hp->size++; AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1); //在将新插入的元素进行向上调整形成堆 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
堆的删除
思路:将堆中最后一个元素覆盖堆顶元素,堆顶元素在向下调整。
void HeapPop(Heap* hp) //删除堆顶元素 { assert(hp); //断言,不能对空指针进行加、减、解引用操作 hp->a[0] = hp->a[hp->size-1]; //将最后一个元素覆盖堆顶元素 hp->size--; AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0); //在将堆顶元素进行向下调整形成堆 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
堆的创建
void HeapCreat(Heap* hp, int* b, int n) //建堆(堆的创建) { assert(hp && b); //断言,不能对空指针进行加、减、解引用操作 hp->a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n); //malloc动态开辟数组空间 if (hp->a == NULL) //malloc动态开辟失败 { perror("malloc failed"); exit(-1); //异常退出,终止程序,(非0值表示不正常退出,0表示正常退出) } memcpy(hp->a, b, sizeof(HPDataType) * n); //此处需要将已知的数组建成堆,将数组中所有值拷贝给动态开辟的数组 hp->size = hp->capacity = n; for (int i = (n-2)/2; i >= 0; i--) //向下调整法建堆,从倒数第一个非叶子节点开始调整,层数依次向上,每层从右到左遍历每个节点,每个节点都向下调整 AdjustDown(hp->a, n, i); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
堆实现总代码
Heap.h- 1
#pragma once //用数组来模拟实现堆(顺序表实现) #include#include //malloc #include //assert #include //memcpy typedef int HPDataType; typedef struct HeapNode //动态版 { HPDataType* a; //malloc动态开辟数组空间,存储每个节点的值 int size; //表示堆中实际有效节点的总个数 int capacity; //容量 }Heap; //传址调用,此处只需要改变结构体中的成员变量,只需要传结构体的地址,形参为一级指针(顺序表),若需要改变结构体的地址,则形参为二级指针(单链表)。 void HeapCreat(Heap* hp, int* b, int n); //建堆(堆的创建) void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x); //向堆中插入一个元素 void HeapDestory(Heap* hp); //销毁 void HeapPop(Heap* hp); //删除堆顶元素 HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp); //获取堆顶元素 int HeapSize(Heap* hp); //获取堆中有效节点的总个数 int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp); //判断堆是否为空 void HeapPrint(Heap* hp); //打印堆中节点的值 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
Heap.c- 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include"Heap.h" void swap(int* p1, int* p2) //交换两元素的值,传址调用,传值调用(形参的改变不会影响实参的改变) { int tmp = *p1; *p1 = *p2; *p2 = tmp; } void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent) //(使用前提:根的左、右子树均为堆)向下调整,从最后一个非叶子节点开始,数据从下往上依次向下调整形成堆 { int child = parent * 2 + 1; //孩纸节点,初始化左孩子值比右孩纸值小 while (child < n) // { if (child + 1 < n && a[child] > a[child + 1]) //左、右孩纸值进行比较,确保右孩纸存在,且左孩子值比右孩纸值大 swap(&a[child], &a[child + 1]); //交换,此时child节点中的值为孩纸节点的最小值 if (a[child] < a[parent]) //左孩子值与父节点值进行比较 swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); //交换,形成小堆 parent = child; //递归 child = parent * 2 + 1; } } void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child) //(使用前提:左、右子树均为堆)向上调整,从根节点的左结点开始,数据从上往下依次向上调整形成堆 { int parent = (child - 1) / 2; //父亲节点 while (child > 0) // { if (a[child] < a[parent]) //该节点与父节点值进行比较 swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); //交换,形成小堆 child = parent; //递归 parent = (child - 1) / 2; } } void HeapCreat(Heap* hp, int* b, int n) //建堆(堆的创建) { assert(hp && b); //断言,不能对空指针进行加、减、解引用操作 hp->a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n); //malloc动态开辟数组空间 if (hp->a == NULL) //malloc动态开辟失败 { perror("malloc failed"); exit(-1); //异常退出,终止程序,(非0值表示不正常退出,0表示正常退出) } memcpy(hp->a, b, sizeof(HPDataType) * n); //此处需要将已知的数组建成堆,将数组中所有值拷贝给动态开辟的数组 hp->size = hp->capacity = n; for (int i = (n-2)/2; i >= 0; i--) //向下调整法建堆,从倒数第一个非叶子节点开始调整,层数依次向上,每层从右到左遍历每个节点,每个节点都向下调整 AdjustDown(hp->a, n, i); } void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x) //向堆中插入一个元素 { assert(hp); //断言,不能对空指针进行加、减、解引用操作 if (hp->size == hp->capacity) //空间满了,不能进行插入数据,如需插入数据,需要realloc进行扩容 { int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2; //新容量 HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity); if (tmp == NULL) //realloc开辟失败 { perror("realloc failed"); exit(-1); } hp->a = tmp; //realloc开辟成功 hp->capacity = newcapacity; //容量进行更新为新容量 } hp->a[hp->size] = x; //在末尾插入一个元素 hp->size++; AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1); //在将新插入的元素进行向上调整形成堆 } void HeapDestory(Heap* hp) //销毁 { assert(hp);//断言,不能对空指针进行加、减、解引用操作 free(hp->a); //释放malloc动态开辟的空间 hp->a = NULL; //防止该空间被其他变量存储了该地址,通过该地址访问此空间,不能访问已经释放的空间,会造成野指针 hp->size = hp->capacity = 0; } void HeapPop(Heap* hp) //删除堆顶元素 { assert(hp); //断言,不能对空指针进行加、减、解引用操作 hp->a[0] = hp->a[hp->size-1]; //将最后一个元素覆盖堆顶元素 hp->size--; AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0); //在将堆顶元素进行向下调整形成堆 } HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp) //获取堆顶元素 { return hp->a[0]; } int HeapSize(Heap* hp) //获取堆中有效节点的总个数 { return hp->size; } int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp) //判断堆是否为空,为空,则为true,不为空,则为false { if (hp->size > 0) return 0; else return 1; } void HeapPrint(Heap* hp) //打印堆中节点的值 { assert(hp); for (int i = 0; i < hp->size; i++) //遍历堆中元素(通过数组的下标来遍历完全二叉树中的每个节点) printf("%d ", hp->a[i]); printf("\n"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
Test.c- 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #pragma once #include"Heap.h" int main() { Heap hp; int b[4] = { 3, 2, 1 ,4}; int n = sizeof(b) / sizeof(int); HeapCreat(&hp, b, n); HeapPrint(&hp); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { int x; scanf("%d", &x); HeapPush(&hp, x); } HeapPrint(&hp); HeapPop(&hp); HeapPrint(&hp); printf("%d\n", HeapTop(&hp)); printf("%d\n", HeapSize(&hp)); if (HeapEmpty(&hp)) printf("YES\n"); else printf("NO\n"); HeapDestory(&hp); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34

建堆时间复杂度的证明

堆排序
注意:在进行堆排序建堆时:升序,建大堆、 降序,建小堆。
原因:堆排序是为了对数组进行排序,不是进行打印数组,便于进行其他一系列操作。
排升序,如果建小堆,只可以第一次获得最小的数,若要将剩余的元素进行排升序,只能将剩余的元素看成个堆,但各个元素对应的节点之间的关系已全部打乱,需要将剩余的元素重新建成堆,代价太大,时间复杂度为O(n*longn)。
排升序,建大堆,将第一个最大的数与最后一个元素进行交换,个数减1,在从剩余的n-1个找出次大的数,在与最后一个元素交换,个数减1,如此反复,时间复杂度为O(nlong)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #includevoid swap(int* p1, int* p2) //传址调用,形参的改变会影响实参的改变 { int tmp = *p1; *p1 = *p2; *p2 = tmp; } void down(int* a, int n, int parent) //向下调整法建堆,建大堆 { int child = parent * 2 + 1; //左孩纸节点 while (child < n) //边界 { if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1])//找到左孩纸与右孩纸节点中的最大值 swap(&a[child], &a[child + 1]); if(a[parent] < a[child]) //建大堆 swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); parent = child; //循环处理 child = parent * 2 + 1; } } void Heapsort(int* a, int n) //堆排序,对数组进行排序,升序,建大堆 { for (int i = (n - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--) //向下调整法建堆,从下标为(i-1-1)/2的节点开始 down(a, n, i); int end = n - 1; //最后一个元素所对应的下标值 while (end > 0) { swap(&a[0], &a[end]); //堆中最大的树与最后一个树进行交换 down(a, end, 0); //将剩余的n-1个元素建大堆 end--; } for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]); } int main() { int a[6]; for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]); Heapsort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(int)); //堆排序 return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55

TopK问题
TopK问题:
求数据中的前k个大的数或者前k个小的数,该数据个数的范围非常的大,一般情况是建个堆,但在内存中不能一次性将所有数据全部加载到内存中,此时考虑将数据存入文件中,即:在文件中找TopK问题,实际应用场景:世界前500名富豪,游戏中前100名活跃的玩家等。
在文件中找前K个大的数:
1.将所有数据先存入文件中去,在从文件中读取,建成前K个数小堆。
2.在依次将文件中剩余的数据读取,每读取一个数,分别与堆中第一个树进行比较,比它大,两数据值进行交换,该数往下沉建成小堆,如此反复,最终堆中的K个数为文件中最大的前K个数。#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include#include //malloc, srand #include //time(时间戳) void swap(int* p1, int* p2) //传址调用 { int tmp = *p1; *p1 = *p2; *p2 = tmp; } void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent) //(使用前提:根的左、右子树均为堆)向下调整,从最后一个非叶子节点开始,数据从下往上依次向下调整形成堆 { int child = parent * 2 + 1; //孩纸节点,初始化左孩子值比右孩纸值小 while (child < n) // { if (child + 1 < n && a[child] > a[child + 1]) //左、右孩纸值进行比较,确保右孩纸存在,且左孩子值比右孩纸值大 swap(&a[child], &a[child + 1]); //交换,此时child节点中的值为孩纸节点的最小值 if (a[child] < a[parent]) //左孩子值与父节点值进行比较 swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); ///交换,形成小堆 parent = child; //递归 child = parent * 2 + 1; } } void CreatNData() //在文件中创造数据 { int n = 100000; const char* file = "data.txt"; FILE* fin = fopen(file, "w"); //以写的方式将文件打开 if (fin == NULL) //文件打开失败 { perror("fopen failed"); exit(-1); //异常退出,终止程序(负数) } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) //创造n个随机数 { int x = rand() % 10000; //数据值得范围为0~9999 fprintf(fin, "%d\n", x); //将n个树写到文件中("%d\n",每个数据占一行) } fclose(fin); //关闭文件 } /*思路:一、从文件中读出k个数据放在数组中(fscanf,有格式),将k个数建成小堆(不可以是大堆,最大的数据会堵在堆顶不下去) * 二、依次将文件中剩余的n-k个数据读取过来,与堆顶进行比较,大于,则往下沉 * 此时堆中剩余的k个数为最大的前k个数(且为升序) */ void HeapTopK(int k) //topk { const char* file = "data.txt"; FILE* fout = fopen(file, "r"); //以读的方式将文件打开 if (file == NULL) //文件打开失败 { perror("fopen failed"); exit(-1); //异常退出,终止程序(负数) } //一、从文件中读出k个数据放在数组中(fscanf,有格式),将k个数建成小堆(不可以是大堆,最大的数据会堵在堆顶不下去) int* mink = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k); //malloc创造一个动态数组用来存储文件中的前k个数 if (mink == NULL) //malloc开辟失败 { perror("malloc failed"); exit(-1);//异常退出,终止程序(负数) } for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) //从文件中读出k个数据 fscanf(fout, "%d", &mink[i]); for (int i = (k-2)/2; i >= 0; i--)//将k个数建成小堆 AdjustDown(mink, k, i); // 二、依次将文件中剩余的n - k个数据读取过来,与堆顶进行比较,大于,则往下沉 int x = 0; while (fscanf(fout, "%d", &x) != EOF)//将文件中剩余的n - k个数据读取 { //fscanf返回值为读取的个数,读取失败或者读取为NULL,则返回EOF(~EOF(-1)== 0) if (x > mink[0]) //与堆顶进行比较,大于,则往下沉 mink[0] = x; AdjustDown(mink, k, 0); } for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) printf("%d ", mink[i]); free(mink); //释放malloc动态开辟的空间 mink = NULL; fclose(fout); //关闭文件 } int main() { srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); //生成随机数srand~time~rand //CreatNData(); //创造数据 int k; scanf("%d", &k); //topk HeapTopK(k); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99




二叉树链式结构的实现
创建二叉树
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int n, int* i) //由前序遍历将数组中的值创建二叉树 { if (a[*i] == '#') // '#'代表空节点 { (*i)++; //数组向后走一位,构建下一个节点 return NULL; } BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode)); //malloc动态开辟内存,创建新节点 if (root == NULL) //malloc动态开辟失败 { perror("malloc failed"); exit(-1); //终止程序,异常退出,0表示正常退出,非0表示异常退出 } root->val = a[*i]; //数组中值不为空,将该值赋给新节点 (*i)++; //数组向后走一位,构建下一个节点 //该节点的左、右节点均创建完成,该节点在其左、右节点进行链接 root->left = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, i); //递归处理创建左节点,左节点遇到空,递归结束 root->right = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, i); //递归处理创建右节点,右节点遇到空,递归结束 return root; //返回树的根节点 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
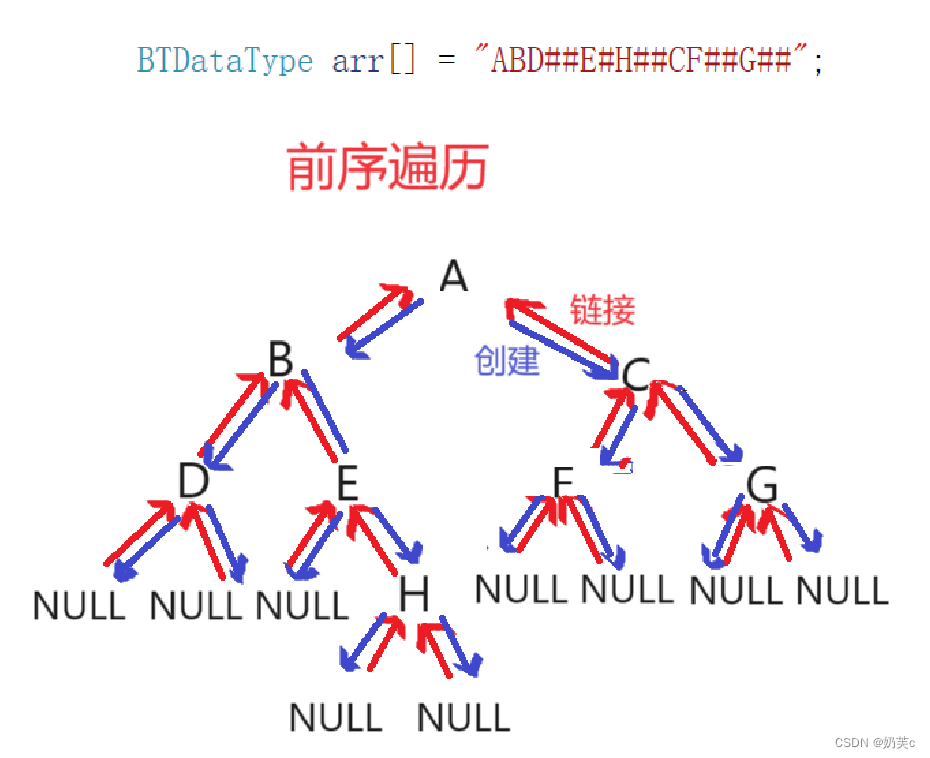
前序遍历及其实现
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root) //前序遍历,根、左、右 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return ; printf("%c ", root->val); //根 BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->left); //递归处理左 BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->right); //递归处理右 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

中序遍历及其实现
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root) //中序遍历,左、根、右 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return; BinaryTreeInOrder(root->left); //递归处理左 printf("%c ", root->val); //根 BinaryTreeInOrder(root->right); //递归处理右 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

后序遍历及其实现
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root) //后序遍历,左、右、根 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return; BinaryTreePostOrder(root->left); //递归处理左 BinaryTreePostOrder(root->right); //递归处理右 printf("%c ", root->val); //根 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
销毁二叉树
/*采用后序遍历,不可采用前序遍历,原因:销毁根节点之前需要存储左子树的根,便于可以找到左子树,也需要存储右子树的根,便于可以找到右子树*/ void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root) //销毁,后序遍历 { if (root == NULL) //空树,未动态开辟任何节点 return; BinaryTreeDestory(root->left); //递归处理左 BinaryTreeDestory(root->right); //递归处理右 free(root); //销毁根 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
求二叉树的高度
int BinaryTreeHeight(BTNode* root) //树的高度 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; int leftheight = BinaryTreeHeight(root->left); //左子树的高度 int rightheight = BinaryTreeHeight(root->right); //右子树的高度 return leftheight > rightheight ? leftheight + 1 : rightheight + 1; //找出左、右子树高度大的树+根(+1) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
求二叉树总节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root) //树的总节点个数,分治法、递归法(将其分为根、左子树、右子树,对应的子树又可以分成根、左、右子树) { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; return BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1; //左子树的节点+右子树的节点+根节点(+1) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
求二叉树叶子节点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root) //树中叶子节点的个数,分治法、递归法(将其分为根、左子树、右子树,对应的子树又可以分成根、左、右子树) { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) //叶子节点的特征,该左、右节点均为空,则该节点为叶子节点 return 1; return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right); //左子树叶子节点个数+右子树叶子节点个数 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
求二叉树第k层节点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k) //树中第k层节点的总个数,将第k层转换为1层,将k-1层转换为第2层..直到k==1,则为第k层 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; if (k == 1) //第k层 return 1; return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x) //在树中查找是否存在值为x的节点 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; if (root->val == x) //找到了 return root; BTNode* ret = NULL; ret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x); //递归左子树 if (ret) //若左子树找到了直接返回 return ret; ret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x); //左子树找不到,在找右子树 if (ret) //右子树找到了直接返回 return ret; return NULL; //找不到 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
二叉树总代码实现
BinaryTree.h- 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include#include //malloc #include //strlen typedef char BTDataType; //二叉树节点值的类型,适用于任意数据类型 typedef struct BinaryTreeNode //树中的节点 { struct BinaryTreeNode* left; //指针域:左孩纸 struct BinaryTreeNode* right; //右孩纸 BTDataType val; //数据域 }BTNode; BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int n, int* i); //由前序遍历将数组中的值创建二叉树 void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root);//前序遍历,根、左、右 void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root); //中序遍历,左、根、右 void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root); //后序遍历,左、右、根 void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode *root); //销毁 int BinaryTreeHeight(BTNode* root); //树的高度 int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root); //树的总节点个数 int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root); //树中叶子节点的个数 int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k); //树中第k层节点的总个数 BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x); //在树中查找是否存在值为x的节点 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
BinaryTree.c- 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include"BinaryTree.h" BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int n, int* i) //由前序遍历将数组中的值创建二叉树 { if (a[*i] == '#') // '#'代表空节点 { (*i)++; //数组向后走一位,构建下一个节点 return NULL; } BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode)); //malloc动态开辟内存,创建新节点 if (root == NULL) //malloc动态开辟失败 { perror("malloc failed"); exit(-1); //终止程序,异常退出,0表示正常退出,非0表示异常退出 } root->val = a[*i]; //数组中值不为空,将该值赋给新节点 (*i)++; //数组向后走一位,构建下一个节点 //该节点的左、右节点均创建完成,该节点在其左、右节点进行链接 root->left = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, i); //递归处理创建左节点,左节点遇到空,递归结束 root->right = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, i); //递归处理创建右节点,右节点遇到空,递归结束 return root; //返回树的根节点 } void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root) //前序遍历,根、左、右 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return ; printf("%c ", root->val); //根 BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->left); //递归处理左 BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->right); //递归处理右 } void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root) //中序遍历,左、根、右 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return; BinaryTreeInOrder(root->left); //递归处理左 printf("%c ", root->val); //根 BinaryTreeInOrder(root->right); //递归处理右 } void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root) //后序遍历,左、右、根 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return; BinaryTreePostOrder(root->left); //递归处理左 BinaryTreePostOrder(root->right); //递归处理右 printf("%c ", root->val); //根 } /*采用后序遍历,不可采用前序遍历,原因:销毁根节点之前需要存储左子树的根,便于可以找到左子树,也需要存储右子树的根,便于可以找到右子树*/ void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root) //销毁,后序遍历 { if (root == NULL) //空树,未动态开辟任何节点 return; BinaryTreeDestory(root->left); //递归处理左 BinaryTreeDestory(root->right); //递归处理右 free(root); //销毁根 } int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root) //树的总节点个数,分治法、递归法(将其分为根、左子树、右子树,对应的子树又可以分成根、左、右子树) { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; return BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1; //左子树的节点+右子树的节点+根节点(+1) } int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root) //树中叶子节点的个数,分治法、递归法(将其分为根、左子树、右子树,对应的子树又可以分成根、左、右子树) { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) //叶子节点的特征,该左、右节点均为空,则该节点为叶子节点 return 1; return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right); //左子树叶子节点个数+右子树叶子节点个数 } int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k) //树中第k层节点的总个数,将第k层转换为1层,将k-1层转换为第2层..直到k==1,则为第k层 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; if (k == 1) //第k层 return 1; return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1); } BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x) //在树中查找是否存在值为x的节点 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; if (root->val == x) //找到了 return root; BTNode* ret = NULL; ret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x); //递归左子树 if (ret) //若左子树找到了直接返回 return ret; ret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x); //左子树找不到,在找右子树 if (ret) //右子树找到了直接返回 return ret; return NULL; //找不到 } int BinaryTreeHeight(BTNode* root) //树的高度 { if (root == NULL) //空树 return 0; int leftheight = BinaryTreeHeight(root->left); //左子树的高度 int rightheight = BinaryTreeHeight(root->right); //右子树的高度 return leftheight > rightheight ? leftheight + 1 : rightheight + 1; //找出左、右子树高度大的树+根(+1) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
Test.c- 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include"BinaryTree.h" int main() { BTDataType arr[] = "ABD##E#H##CF##G##"; int n = strlen(arr); int j = 0; BTNode* root = BinaryTreeCreate(arr, n, &j); //由前序遍历将数组中的值创建二叉树 BinaryTreePrevOrder(root); //前序遍历 printf("\n"); BinaryTreeInOrder(root); //中序遍历 printf("\n"); BinaryTreePostOrder(root); //后序遍历 printf("\n"); printf("%d\n", BinaryTreeHeight(root)); //树的高度 printf("%d\n",BinaryTreeSize(root)); //树的总节点个数 printf("%d\n", BinaryTreeLeafSize(root)); //树中叶子节点的个数 printf("%d\n", BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root, 3)); //树中第k层节点的总个数 BTNode* ret = BinaryTreeFind(root, 'F'); //在树中查找是否存在值为x的节点 if (ret != NULL) printf("找到了\n"); else printf("找不到\n"); BinaryTreeDestory(root); //销毁 return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29

层序遍历

void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root) //层次遍历,用队列实现,上一层带下一层,当上一层节点全部出队,则下一层所有节点均入队了 { Queue plist; QueueInit(&plist); //初始化队列,队列中用于存储树中的节点 if (root == NULL) //空树 return; QueuePush(&plist, root); //将根插入队列中 while (!QueueEmpty(&plist)) // { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&plist); //获取队头元素 printf("%d ", front->val); //打印树中节点的值 if (front->left) //左孩纸不为空,空节点不能入队 QueuePush(&plist, front->left); //将该节点的左孩子入队 if (front->right) //右孩纸不为空,空节点不能入队 QueuePush(&plist, front->right); //将该节点的右孩子入队 QueuePop(&plist); //删除队头元素 } printf("\n"); QueueDestroy(&plist); //二叉树的销毁 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
判断是否为二叉树

int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root) //判断其是否为二叉树,最后一层非空节点从左到右连续分布 { Queue plist; QueueInit(&plist); //初始化队列,队列中用于存储树中的节点 if (root == NULL) //空树 return; QueuePush(&plist, root); //将根插入队列中 while (!QueueEmpty(&plist)) // { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&plist); //获取队头元素 if (front == NULL) //队头为空节点 break; QueuePush(&plist, front->left); //左孩纸入队,空节点也需入队 QueuePush(&plist, front->right); //右孩纸入队,空节点也需入队 QueuePop(&plist); //删除非空节点 } while (!QueueEmpty(&plist)) // { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&plist); //获取队头元素 QueuePop(&plist); //删除队头节点 if (front != NULL) //队头为非空节点 { QueueDestroy(&plist); return false; //不是完全二叉树 } QueuePop(&plist); //删除队头节点 } QueueDestroy(&plist); //销毁 return true; //是完全二叉树 printf("\n"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
总代码
Tset.c- 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include"Queue.h" /*void test() { Queue plist; QueueInit(&plist); QueuePush(&plist, 1); QueuePush(&plist, 2); QueuePush(&plist, 3); QueuePush(&plist, 4); QueuePush(&plist, 5); QueuePush(&plist, 6); while (!QueueEmpty(&plist)) { printf("%d ", QueueFront(&plist)); QueuePop(&plist); } printf("\n"); QueueDestroy(&plist); } int main() { test(); //测试队列,先进先出 return 0; } */ BTNode* BuyNode(int x) { BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode)); root->left = NULL; root->right = NULL; root->val = x; return root; } void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root) { Queue plist; QueueInit(&plist); if (root == NULL) return; QueuePush(&plist, root); while (!QueueEmpty(&plist)) { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&plist); printf("%d ", front->val); if (front->left) QueuePush(&plist, front->left); if (front->right) QueuePush(&plist, front->right); QueuePop(&plist); } printf("\n"); QueueDestroy(&plist); } int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root) { Queue plist; QueueInit(&plist); if (root == NULL) return; QueuePush(&plist, root); while (!QueueEmpty(&plist)) { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&plist); if (front == NULL) break; QueuePush(&plist, front->left); QueuePush(&plist, front->right); QueuePop(&plist); } while (!QueueEmpty(&plist)) { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&plist); QueuePop(&plist); // if (front != NULL) { QueueDestroy(&plist); return false; } QueuePop(&plist); } QueueDestroy(&plist); return true; printf("\n"); } int main() { BTNode* n1 = BuyNode(1); BTNode* n2 = BuyNode(6); BTNode* n3 = BuyNode(7); BTNode* n4 = BuyNode(2); BTNode* n5 = BuyNode(3); BTNode* n6 = BuyNode(4); BTNode* n7 = BuyNode(5); n1->left = n2; n1->right = n3; n2->left = n4; n2->right = n5; n3->left = n6; n3->right = n7; BinaryTreeLevelOrder(n1); if (BinaryTreeComplete(n1)) printf("是完全二叉树\n"); else printf("不是完全二叉树\n"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
Queue.c- 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include"Queue.h" void QueueInit(Queue* p) //初始化 { assert(p); //断言,检查指针的有效性,防止对空指针进行解引用,加减操作 p->front = NULL; p->rear = NULL; p->size = 0; } void QueuePush(Queue* p, QDataType x) //入队 { assert(p); //断言,检查指针的有效性,防止对空指针进行解引用,加减操作 QNode* newnode=(QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); //malloc动态开辟新的节点 if (newnode == NULL) //开辟空间失败 { perror("malloc"); //报错原因 exit(-1); //终止程序,异常结束 } newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (p->rear == NULL) //注意:头插(特殊处理),链表为空 { p->front = p->rear = newnode; } else //尾插 ,需要找尾节点 { p->rear->next = newnode; p->rear=p->rear->next; } p->size++; //链表中有效元素个数加+ } bool QueueEmpty(Queue* p) //判断队列是否为空 { assert(p); //断言,检查指针的有效性,防止对空指针进行解引用,加减操作 return p->front == NULL; //为空,则为真,返回非0值,若不为空,为假,则返回0 } void QueuePop(Queue* p) //出队 { assert(p); //断言,检查指针的有效性,防止对空指针进行解引用,加减操作 assert(!QueueEmpty(p)); //断言,链表为空,则不能进行删除 if (p->front->next == NULL) //注意:当链表中只剩一个元素,因为尾指针、头指针同时指向该节点,释放该节点,需要将尾指针、头指针都置成NULL,否则会造成野指针(指向已经被释放的空间) { free(p->front); p->front = p->rear = NULL; } else //链表中剩余至少有1个元素 { QNode* next = p->front->next; free(p->front); p->front = next; } p->size--; //链表中有效元素个数加- } QDataType QueueFront(Queue* p) //获取队头元素 { assert(p); //断言,检查指针的有效性,防止对空指针进行解引用,加减操作 assert(!QueueEmpty(p)); //断言,链表为空,则不能获取到队头的元素 return p->front->data; } QDataType QueueBack(Queue* p) //获取队尾元素 { assert(p); //断言,检查指针的有效性,防止对空指针进行解引用,加减操作 assert(!QueueEmpty(p)); //断言,链表为空,则不能获取到队尾的元素 return p->rear->data; } int QueueSize(Queue* p) //获取队列中有效元素的个数 { assert(p); //断言,检查指针的有效性,防止对空指针进行解引用,加减操作 assert(!QueueEmpty(p)); //断言,链表为空,则不能获取到有效元素的总个数 return p->size; } void QueueDestroy(Queue* p) //销毁 { assert(p); //断言,检查指针的有效性,防止对空指针进行解引用,加减操作 while (p->front) //遍历链表 { QNode* next = p->front->next; free(p->front); p->front = next; } p->front = p->rear = NULL; p->size = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
Queue.h- 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include#include //malloc #include //assert #include //bool类型 typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType; typedef int BTDataType; typedef struct BinaryTreeNode { struct BinaryTreeNode* left; struct BinaryTreeNode* right; BTDataType val; }BTNode; typedef struct QueueNode //链式结构:表示队列 { QDataType data; struct QueueNode* next; }QNode; typedef struct Queue //队列结构 { QNode* front; //队头 QNode* rear; //队尾 int size; //有效元素个数 }Queue; void QueueInit(Queue* p); //初始化 void QueuePush(Queue* p, QDataType x); //入队 void QueuePop(Queue* p); //出队 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* p); //获取队头元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* p); //获取队尾元素 int QueueSize(Queue* p); //获取队列中有效元素的个数 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* p); //判断队列是否为空 void QueueDestroy(Queue* p); //销毁 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39

铁铁们,二叉数全面知识总结就到此结束啦,若博主有不好的地方,请指正,欢迎铁铁们留言,请动动你们的手给作者点个👍鼓励吧,你们的鼓励就是我的动力✨ -
相关阅读:
【JavaEE】Java的前世今身
Centos7 Shell编程之正则表达式、文本处理工具
C++面试题其一
ZooKeeper设置ACL权限控制,删除权限
centos7 安装 RabbitMq
在Linux环境下从源码构建并安装GCC
京东数据分析:2023年9月京东打印机行业品牌销售排行榜
iOS CGRect CGPoint NSRange等结构体的NSLog打印输出
C++ std::default_random_engine的使用
技术应用:使用Spring Boot、MyBatis Plus和Dynamic DataSource实现多数据源
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74808907/article/details/132853109
