-
MySQL高级语句(第一部分)
MySQL高级语句(第一部分)
一、MySQL进阶查询
先建立www数据库,再建立location 表和Store_Info 表,用于测试和演示
create database www; use www; create table location (Region char(20),Store_Name char(20)); insert into location values('East','Boston'); insert into location values('East','New York'); insert into location values('West','Los Angeles'); insert into location values('West','Houston');- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
create table store_info (Store_Name char(20),Sales int(10),Date char(10)); insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','1500','2020-12-05'); insert into store_info values('Houston','250','2020-12-07'); insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','300','2020-12-08'); insert into store_info values('Boston','700','2020-12-08');- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
1、select ----显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名";- 1
举例- 1
select * from store_info;- 1

select store_name from store_info;- 1

2、distinct ----不显示重复的数据记录
语法:select distinct "字段" from "表名";- 1
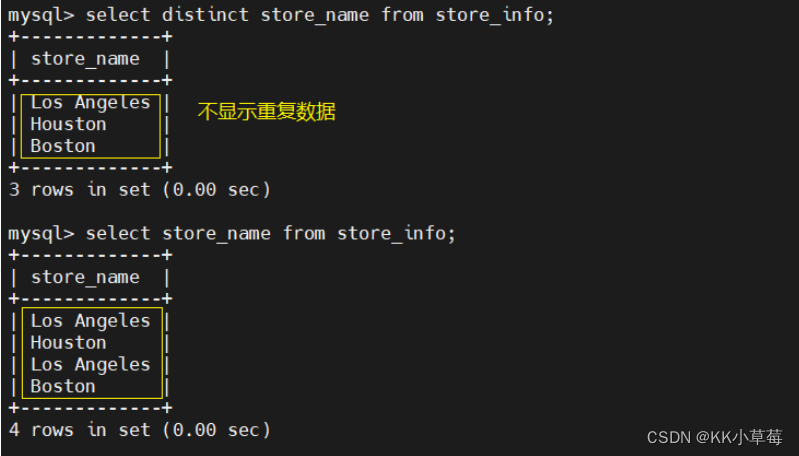
举例: select distinct store_name from store_info;- 1
- 2
3、where ----有条件查询
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "条件";- 1
举例- 1
select * from store_info where store_name='Los Angeles';- 1

select * from store_info where sales <= 1000;- 1

select * from store_info where sales != 1500; # !=不等于- 1
- 2

4、and or ----且 或
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "条件1" {[and|or] "条件2"}+ ;- 1
举例- 1
select * from store_info where sales > 1000 or (sales > 200 and sales < 500); #sales>1000或sales>200且sales<500- 1
- 2

5、in ----显示已知的值的数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" in ('值1', '值2', ...);- 1
举例- 1
select * from store_info where store_name in ('Houston','Boston'); #显示指定项的数据记录- 1
- 2

select * from store_info where store_name not in ('Houston','Boston');- 1

6、between ----显示两个值范围内的数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" between '值1' and '值2';- 1
举例- 1
select * from store_info where sales between 300 and 1000;- 1

7、通配符
----通常通配符都是跟 like 一起使用的
% :百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符 _ :下划线表示单个字符 'A_Z':所有以 'A' 起头,另一个任何值的字符,且以 'Z' 为结尾的字符串。例如,'ABZ' 和 'A2Z' 都符合这一个模式,而 'AKKZ' 并不符合 (因为在 A 和 Z 之间有两个字符,而不是一个字符)。 'ABC%': 所有以 'ABC' 起头的字符串。例如,'ABCD' 和 'ABCABC' 都符合这个模式。 '%XYZ': 所有以 'XYZ' 结尾的字符串。例如,'WXYZ' 和 'ZZXYZ' 都符合这个模式。 '%AN%': 所有含有 'AN'这个模式的字符串。例如,'LOS ANGELES' 和 'SAN FRANCISCO' 都符合这个模式。 '_AN%':所有第二个字母为 'A' 和第三个字母为 'N' 的字符串。例如,'SAN FRANCISCO' 符合这个模式,而 'LOS ANGELES' 则不符合这个模式。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
8、like ----模糊匹配
----匹配一个模式来找出我们要的数据记录
模糊匹配默认会扫描全表,索引不生效
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" like {模式};- 1
举例- 1
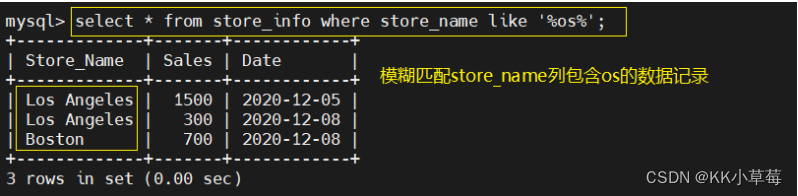
select * from store_info where store_name like '%os%'; #模糊匹配store_name列包含os的数据记录- 1
- 2
9、order by
----按关键字排序
语法:select "字段" from "表名" [where "条件"] order by "字段" [asc, desc]; #ASC 是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式。 #DESC 是按降序方式进行排序。- 1
- 2
- 3
#举例 select * from store_info order by sales asc; #升序排序 select * from store_info order by sales desc; #降序排序- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

10、group by----汇总分组
----对GROUP BY后面的字段的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的
GROUP BY 有一个原则,凡是在 GROUP BY 后面出现的字段,必须在 SELECT 后面出现;
凡是在 SELECT 后面出现的、且未在聚合函数中出现的字段,必须出现在 GROUP BY 后面语法:select "字段1", sum("字段2") from "表名" group by "字段1";- 1
select store_name, sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name order by sales desc; #汇总销售总额然后排序- 1
- 2

11、having
----用来过滤由 GROUP BY 语句返回的记录集,通常与 GROUP BY 语句联合使用
HAVING 语句的存在弥补了 WHERE 关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。
语法:select "字段1", sum("字段2") from "表格名" group by "字段1" having (函数条件);- 1
select store_name, sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name having sum(sales) > 1500; #返回sales>1500的数据- 1
- 2

12、别名 ----字段別名 表格別名
语法:select "表格別名"."字段1" [as] "字段別名" from "表格名" [as] "表格別名";- 1
#举个例子 select a.store_name store, sum(a.sales) as "total sales" from store_info as a group by a.store_name; #sum函数别名定义为total sales,as可省略,store_info表,别名定义为a,别名定义后,当前SQL语句中所有用到store_info表的地方,都能用a代替- 1
- 2
- 3

13、子查询
----连接表格,在WHERE 子句或 HAVING 子句中插入另一个 SQL 语句
语法:select "字段1" from "表格1" where "字段2" [比较运算符] (select "字段1" from "表格2" where "条件"); #外查询 (#内查询) #内查询的结果,作为外查询的参数 [比较运算符] #可以是符号的运算符,例如 =、>、<、>=、<= #也可以是文字的运算符,例如 like、in、between- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
#举例1 select sum(sales) from store_info where store_name in (select store_name from location where region = 'West'); #外查询返回符合的数据记录的销售总额 #内查询的结果作为外查询的参数- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

#举例2 select sum(A.sales) from store_info as A where A.store_name in (select store_name from location as B where B.store_name = A.store_name); #store_info表 别名为A表,在当前语句中,可以直接用a代替store_info使用 #location表 别名为B表- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

14、exists
用来测试内查询有没有产生任何结果,类似布尔值是否为真
如果有的话,系统就会执行外查询中的SQL语句。若是没有的话,那整个 SQL 语句就不会产生任何结果
语法:select "字段1" from "表格1" where exists (select * from "表格2" where "条件";- 1
#举个例子 select sum(sales) from store_info where exists (select * from location where region = 'West'); #存在region为West的数据记录继续执行外查询 select sum(sales) from store_info where exists (select store_name from location where region ='Westt'); #不存在region为Westt的数据记录不会继续执行外查询,返回Null- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

15、练习

group by store_name having count(store_name) >=2; select store_name from store_info group by store_name having count(store_name) >=2; select store_name,count(store_name) from store_info group by store_name having count(store_name) >=2;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

二、MySQL数据库函数
1、数学函数
数字函数 功能 abs(x) 返回 x 的绝对值 rand() 返回 0 到 1 的随机数 mod(x,y) 返回 x 除以 y 以后的余数 power(x,y) 返回 x 的 y 次方 round(x) 返回离 x 最近的整数 round(x,y) 保留 x 的 y 位小数四舍五入后的值 sqrt(x) 返回 x 的平方根 truncate(x,y) 返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值 ceil(x) 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数 floor(x) 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数 greatest(x1,x2…) 返回集合中最大的值,也可以返回多个字段的最大的值 least(x1,x2…) 返回集合中最小的值,也可以返回多个字段的最小的值 select abs(-1), rand(), mod(5,3), power(2,3), round(1.89); #-1的绝对值,随机数,5 3取余数,2的3次方,1.89四舍五入- 1
- 2

select round(1.8937,3), truncate(1.235,2), ceil(5.2), floor(2.1), least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1); #1.8937第三位四舍五入,1.235取2位小数,大于或者等于5.2的整数,<=2.1的整数,合集中的最小值- 1
- 2

2、聚合函数
聚合函数 功能 avg() 返回指定列的平均值 count() 返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数 min() 返回指定列的最小值 max() 返回指定列的最大值 sum(x) 返回指定列的所有值之和 avg- 1
select avg(sales) from store_info; #求平均值- 1
- 2

count- 1
#count(*) 包括了所有的列的行数,在统计结果的时候,不会忽略列值为 NULL
#count(列名) 只包括列名那一列的行数,在统计结果的时候,会忽略列值为 NULL 的行select count(store_name) from store_info; #非null行数,重复的单独计数 select count(distinct store_name) from store_info; #去重 select count(*) from store_info; #统计所有列的行数,包括null行- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

max和min- 1
select max(sales) from store_info; #返回最大值 select min(sales) from store_info; #返回最小值- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

sum- 1
select sum(sales) from store_info; #sales列的数据记录的和- 1
- 2

3、字符串函数
字符串函数 功能 trim() 返回去除指定格式的值 concat(x,y) 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串 substr(x,y) 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同 substr(x,y,z) 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串 length(x) 返回字符串 x 的长度 replace(x,y,z) 将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y upper(x) 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母 lower(x) 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母 left(x,y) 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符 right(x,y) 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符 repeat(x,y) 将字符串 x 重复 y 次 space(x) 返回 x 个空格 strcmp(x,y) 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1 reverse(x) 将字符串 x 反转 3.1 trim
select trim ([ [位置] [要移除的字符串] from ] 字符串); #[位置]:的值可以为 leading (起头), trailing (结尾), both (起头及结尾)。 #[要移除的字符串]:从字串的起头、结尾,或起头及结尾移除的字符串。缺省时为空格。- 1
- 2
- 3
select trim(leading 'Los' from (select store_name from location where store_name='Los Angeles')); #去除store_name字段中Los Angeles的Los ,只提取Angeles select trim(trailing 'York' from (select store_name from location where store_name='New York')); #去除store_name字段中New York的York ,只提取New- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

3.2 concat
字段名 不要加
' '字符串 要加
' 'select concat (region ,' ',store_name) from location; #拼接region和store_name字段,并且在中间加上空格- 1
- 2

select region || ' ' store_name from location;- 1

3.3 substr
select substr(store_name,5) from location where store_name ='Los Angeles'; #Los Angeles第5个位置开始的字符串 select substr(store_name,5,6) from location where store_name ='Los Angeles'; #第5个位置开始,长度为6的字符- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

3.4 length
select store_name,length(store_name) from location; #返回字段store_name中字符串的长度- 1
- 2

3.5 replace
select replace (region,'st','stern') from location; #把region字段,st结尾替换成stern结尾- 1
- 2

三、连接查询
1、表连接
表连接 概述 inner join 内连接 只返回两个表中联结字段相等的行记录 left join 左连接 返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录,不相等的部分返回NULL right join 右连接 返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中联结字段相等的记录,不相等的部分返回NULL 修改表数据 update store_info set store_name='Washington' where sales=300;- 1
- 2

内连接一: select * from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name; 内连接二: select * from location A, store_info B where A.store_name = B.store_name; #通过多表查询实现- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

右连接: select * from location A right join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name;- 1
- 2

左连接: select * from location A left join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name;- 1
- 2

2、union语句
联集,将两个SQL语句的结果合并起来,两个SQL语句所产生的字段需要是同样的数据记录种类
union:生成结果的数据记录值将没有重复,且按照字段的顺序进行排序
语法:[select 语句 1] union [select 语句 2];- 1
select store_name from location union select store_name from store_info; #合并store_info表和location表中的store_name字段,去重- 1
- 2

union all :将生成结果的数据记录值都列出来,无论有无重复
语法:[select 语句 1] union all [select 语句 2];- 1
select store_name from location union all select store_name from store_info; #合并,不去重,所以会有重复的数据记录- 1
- 2

3、多表查询之求交集值
取两个SQL语句结果的交集
基本语法 select A.字段 from 左表 A inner join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段; select A.字段 from 左表 A inner join 右表 B using(同名字段); select A.字段 from 左表 A, 右表 B where A.字段 = B.字段; #多表查询 select A.字段 from 左表 A where A.字段 in (select B.字段 from 右表 B); #子查询 select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is not null; select B.字段 from 左表 A right join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is not null;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
举例- 1
#方式一 select A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name; #返回两表中字段相等的记录- 1
- 2
- 3

#方式二 select A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B using (store_name); #字段相同时,可以直接使用using(字段)- 1
- 2
- 3

#取两个SQL语句结果的交集,且没有重复 select distinct A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name; #inner join返回两表中相等的部分,distinct去重- 1
- 2
- 3

select distinct A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B using (store_name) where B.store_name is not NULL; #增加了条件判断,非null的数据记录- 1
- 2

select A.store_name from (select B.store_name from location B inner join store_info C on B.store_name = C.store_name) A group by A.store_name; #通过子查询+内连接查询+group by排序,返回store_name中相等的行记录- 1
- 2

select A.store_name from (select distinct store_name from location union all select distinct store_name from store_info) A group by A.store_name having count( *) > 1; #首先,子查询`select distinct store_name from location`从“location”表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。 #然后,子查询`select distinct store_name from store_info`从“store_info”表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。 #使用`union all`将两个子查询的结果合并,并作为临时表A。 #最后,对临时表A按照店铺名称进行分组,使用`having count(*) > 1`筛选出出现次数大于1的店铺名称。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

4、多表查询之求无交集值
显示第一个SQL语句的结果,且与第二个SQL语句没有交集的结果,且没有重复
求左表无交集 select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is null; select 字段 from 左表 where 字段 not in (select 字段 from 右表); 求右表无交集 select B.字段 from 左表 A right join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is null; select 字段 from 右表 where 字段 not in (select 字段 from 左表); 求多表的无交集 select A.字段 from (select distinct 字段 from 左表 union all select distinct 字段 from 右表) A group by A.字段 having count(A.字段)=1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
举例- 1
select distinct store_name from location where (store_name) not in ( select store_name from store_info); #返回所有在"location"表中出现但在"store_info"表中不存在的店铺名称,即无交集值 #子查询`select store_name from store_info`从"store_info"表中选择所有的店铺名称。 #主查询`select distinct store_name from location`从"location"表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。 #使用`where (store_name) not in`条件将主查询中的店铺名称过滤掉那些在子查询结果中出现的店铺名称。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

select distinct A.store_name from location A left join store_info B using (store_name) where B.store_name is NULL; #返回在"location"表中出现但在"store_info"表中不存在的店铺名称 #使用`left join`将"location"表(作为左表,记为A)和"store_info"表(作为右表,记为B)按照店铺名称进行连接。 #使用`using (store_name)`条件指定以店铺名称为连接的字段。 #使用`where B.store_name is NULL`条件过滤掉在连接结果中,店铺名称在"location"表中出现但在"store_info"表中没有匹配的记录。 #最后,使用`distinct`关键字来返回不重复的店铺名称。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

select A.store_name from (select distinct store_name from location union all select distinct store_name from store_info) as A group by A.store_name having count(*)=1; #返回只在"location"表或"store_info"表中出现一次的店铺名称,即只出现在其中一个表中但没有重复出现的店铺名称 #子查询`select distinct store_name from location`从"location"表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。 #子查询`select distinct store_name from store_info`从"store_info"表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。 #使用`union all`将两个子查询的结果合并。 #将合并结果作为临时表A,并使用`as A`来给临时表起一个别名。 #在临时表A的基础上,使用`group by A.store_name`对店铺名称进行分组。 #使用`having count(*) = 1`筛选出出现次数为1的店铺名称。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

四、SQL语句执行顺序
FROM <left table> ON <join_condition> <join_type> JOIN <right_table> WHERE <where condition> GROUP BY <group_by_list> HAVING <having_condition> SELECT DISTINCT <select list> ORDER BY <order_by_condition> LIMIT <limit number> ######################################################################################################## 在SQL中,一般而言,SQL查询语句的执行顺序如下: 1. FROM:指定要查询的数据表或视图。 2. JOIN:根据指定的条件连接多个表。 3. WHERE:基于指定的条件筛选出符合要求的行。 4. GROUP BY:按照指定的列进行分组。 5. HAVING:对分组后的结果进行条件筛选。 6. SELECT:选择要返回的列。 7. DISTINCT:去除重复的行。 8. ORDER BY:按照指定的列进行排序。 9. LIMIT/OFFSET:限制返回的结果数量和起始位置。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
-
相关阅读:
OpenCV视频防抖技术解析
【无标题】
期末前端web大作业——名侦探柯南网页制作 Hbuiderx制作网页 静态HTML网页单页制作 dreamweaver网页设计与制作代码 web前端期末大作业
uniapp——第3篇:自定义组件、组件间传数据
【App自动化测试】(六)移动端自动化中常用的元素定位方式
web基础与HTTP协议
Word处理控件Aspose.Words功能演示:在 Python 中从 Word 文档中提取图像
1230天,百度再见!!!
【面试普通人VS高手系列】HashMap是怎么解决哈希冲突的?
不要小看了积分商城,它的作用可以很大
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_71593537/article/details/133250790
