-
【C# Programming】值类型、良构类型
值类型
1、值类型
值类型的变量直接包含值。换言之, 变量引用的位置就是值内存中实际存储的位置。

2、引用类型
引用类型的变量存储的是对一个对象实例的引用(通常为内存地址)。
复制引用类型的值时,复制的只是引用。这个引用非常小(32位机器时4 字节引用)
3、结构
除string 和object 是引用类型,所有C# 内建类型都是值类型。C#也 允许用户自定义值类型。
结构是一种自定义的值类型,它使用关键字struct。 例如:
- struct Angle
- {
- public Angle(int degrees, int minutes, int seconds)
- {
- Degrees = degrees;
- Minutes = minutes;
- Seconds = seconds;
- }
- // Using C# 6.0 read-only, automatically implememted properties.
- public int Degrees { get; }
- public int Minutes { get; }
- public int Seconds { get; }
- public Angle Move(int degrees, int minutes, int seconds)
- {
- return new Angle(Degrees + degrees, Minutes + minutes, Seconds + seconds);
- }
- }
3.1 结构的初始化
- 除了属性和字段,结构还可包含方法和构造器。结构不允许包含用户定义的默认构造器。在没有提供默认的构造器时, C# 编译器会自动生成一个默认构造器将所有字段初始化为各自的默认值。
- 为了确保值类型的局部变量能完全初始化,结构的每个构造器都必须初始化结构中所有字段。如果对结构的所有数据初始化失败,会造成编译错误。
- C# 禁止结构中的字段初始化器,例如:
- struct Angle
- {
- //……
- // ERROR: Fields cannot be initialized at declaration time
- // private int _Degrees = 42;
- }
- 为值类型使用new 操作符,会造成“运行时”在临时存储池中创建对象的新实例,并将所有字段初始化为默认值。
4、default 操作符的使用
所有值类型都有自定义的无参构造器将值类型的实例初始化成默认状态。所以总可以合法使用new操作符创建值类型的变量。除此之外,还可使用default操作符生成结构的默认值。例如:
- struct Angle
- {
- public Angle(int hours, int minutes)
- : this(hours, minutes, default(int))
- {}
- public Angle(int degrees, int minutes, int seconds)
- {
- Degrees = degrees;
- Minutes = minutes;
- Seconds = seconds;
- }
- public int Degrees { get; }
- public int Minutes { get; }
- public int Seconds { get; }
- public Angle Move(int degrees, int minutes, int seconds)
- {
- return new Angle(Degrees + degrees, Minutes + minutes, Seconds + seconds);
- }
- }
5、值类型的继承和接口
- 所有值类型都隐式密封
- 除枚举外,所有值类型都派生自 System.ValueType
- 值类型也能实现接口
6、装箱
6.1 将值类型转换为一个引用类型称为装箱(boxing) 转换。 转换的结果时对一个存储位置的引用。
转换的步骤如下:
- 在堆上分配内存, 它将用于存放值类型数据以及少许额外开销。
- 接着发生一次内存复制,当前存储位置的值类型数据被复制到堆上分配好的位置。
- 转换的结果是对堆上新存储位置的引用
6.2 相反的过程称为拆箱(unboxing).拆箱转换先检查已经装箱的值的类型兼容于要拆箱成的值类型,然后复制堆中存储的值
6.3 装箱/拆箱的CIL 代码
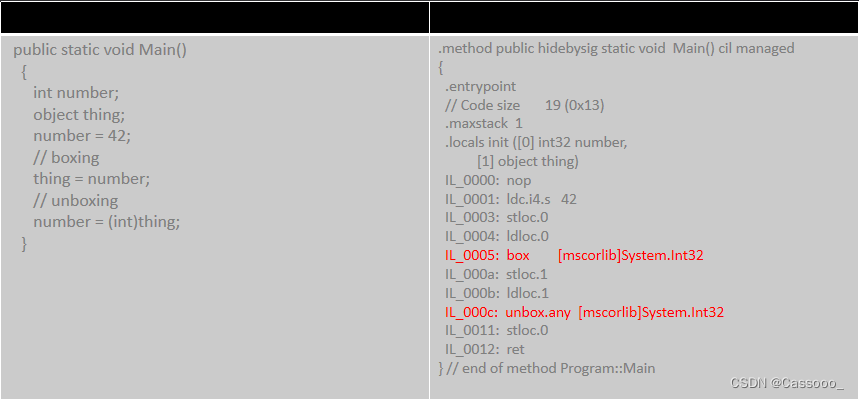
6.4 如果装箱和拆箱进行的不是很频繁,那么实现它们的性能问题不大。但有的时候,装箱会频繁发生,这就可能大幅影响性能。例如:
- static void Main()
- {
- int totalCount;
- System.Collections.ArrayList list = new System.Collections.ArrayList();
- Console.Write("Enter a number between 2 and 1000:");
- totalCount = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
- // Execution-time error:
- // list.Add(0); // Cast to double or 'D' suffix required. Whether cast or using 'D' suffix,
- list.Add((double)0); // boxing
- list.Add((double)1); // boxing
- for(int count = 2; count < totalCount; count++)
- {
- list.Add(
- ((double)list[count - 1] + // unboxing
- (double)list[count - 2])); // unboxing
- }
- foreach(double count in list) // unboxing
- Console.Write("{0}, ", count);//boxing
- }
6.5 另一个装箱/拆箱例子 (接口要求被调用者为引用类型):
- class Program
- {
- static void Main()
- {
- Angle angle = new Angle(25, 58, 23);
- object objectAngle = angle; // Box
- Console.Write(((Angle)objectAngle).Degrees);
- ((Angle)objectAngle).MoveTo(26, 58, 23); // Unbox, modify unboxed value, and discard value
- Console.Write(", " + ((Angle)objectAngle).Degrees);
- ((IAngle)angle).MoveTo(26, 58, 23); // Box, modify boxed value, and discard reference to box
- Console.Write(", " + ((Angle)angle).Degrees);
- ((IAngle)objectAngle).MoveTo(26, 58, 23); // Modify boxed value directly
- Console.WriteLine(", " + ((Angle)objectAngle).Degrees);
- }
- }
- interface IAngle
- {
- void MoveTo(int hours, int minutes, int seconds);
- }
- struct Angle : IAngle
- {
- public Angle(int degrees, int minutes, int seconds)
- {
- Degrees = degrees;
- Minutes = minutes;
- Seconds = seconds;
- }
- // NOTE: This makes Angle mutable, against the general guideline
- public void MoveTo(int degrees, int minutes, int seconds)
- {
- Degrees = degrees;
- Minutes = minutes;
- Seconds = seconds;
- }
- public int Degrees {get; set;}
- public int Minutes {get; set;}
- public int Seconds {get; set;}
- }
6.6 如果将值类型的实例作为接收者来调用object 声明的虚方法时
- 如果接收者已拆箱,而且结构重写了该方法,将直接调用重写的方法。因为所有值类型都是密封的。
- 如果接收者已拆箱,而且结构没有重写该方法,就必须调用基类的实现。该实现预期的接收者是一个对象引用。所以接收者被装箱。
- 如果接收者已装箱,而且结构重写了该方法,就将箱子的存储位置传给重写的方法,不对其拆箱。
- 如果接收者已装箱,而且结构没有重写该方法,就将箱子的引用传给基类的实现,该实现预期正是一个引用。
7、枚举
- 枚举是由开发者声明的值类型。枚举的关键特征是在编译时声明了一组可以通过名称来引用的常量值。例如:
- enum ConnectionState
- {
- Disconnected,
- Connecting,
- Connected,
- Disconnecting
- }
- 想要使用枚举值需要为其附加枚举名称前缀。 例如:ConnectionState. Connecting
- 枚举值实际是作为整数常量实现的,第一个枚举值默认为0, 后续每项都递增1, 然而可以显式为枚举赋值。例如:
- enum ConnectionState : short
- {
- Disconnected,
- Connecting = 10,
- Connected,
- Joined = Connected,
- Disconnecting
- }
- 所有的枚举基类都是System.enum. 后者从System.ValueType 派生。除此之外,不能从现有枚举类型派生以添加额外成员
- 对于枚举类型,它的值并不限于限于声明中命名的值。 只要值能转换成基础类型,就能转换枚举值。
8、枚举和字符串之间的转换
- 枚举的一个好处是ToString() 方法会输出枚举值的标识符。
- 使用Enum.Parse可以将字符串转换为枚举
- public static void Main()
- {
- ThreadPriorityLevel priority = (ThreadPriorityLevel)Enum.Parse(
- typeof(ThreadPriorityLevel), "Idle");
- Console.WriteLine(priority);
- }
- 为了避免抛出异常,C#4.0 后提供了TryParse 方法。
- public static void Main()
- {
- System.Diagnostics.ThreadPriorityLevel priority;
- if(Enum.TryParse("Idle", out priority))
- {
- Console.WriteLine(priority);
- }
- }
9、枚举作为标志使用
- 枚举值还可以组合以表示复合值。 此时,枚举声明应使用 Flags 属性进行标记以表示枚举值可以组合, 例如:
- [Flags]
- public enum FileAttributes
- {
- None = 0, // 000000000000000
- ReadOnly = 1 << 0, // 000000000000001
- Hidden = 1 << 1, // 000000000000010
- System = 1 << 2, // 000000000000100
- Directory = 1 << 4, // 000000000010000
- Archive = 1 << 5, // 000000000100000
- Device = 1 << 6, // 000000001000000
- Normal = 1 << 7, // 000000010000000
- Temporary = 1 << 8, // 000000100000000
- SparseFile = 1 << 9, // 000001000000000
- ReparsePoint = 1 << 10, // 000010000000000
- Compressed = 1 << 11, // 000100000000000
- Offline = 1 << 12, // 001000000000000
- NotContentIndexed = 1 << 13, // 010000000000000
- Encrypted = 1 << 14, // 100000000000000
- }
- 可以使用按位OR 操作符联结枚举值,使用按位AND操作符测试特定位是否存在
- public static void ChapterMain()
- {
- string fileName = @"enumtest.txt";
- System.IO.FileInfo file = new System.IO.FileInfo(fileName);
- file.Attributes = FileAttributes.Hidden | FileAttributes.ReadOnly;
- Console.WriteLine(“{0} | {1} = {2}”, FileAttributes.Hidden, FileAttributes.ReadOnly, (int)file.Attributes);
- if((file.Attributes & FileAttributes.Hidden) != FileAttributes.Hidden)
- throw new Exception("File is not hidden.");
- if((file.Attributes & FileAttributes.ReadOnly) != FileAttributes.ReadOnly)
- throw new Exception("File is not read-only.");
- }
- 枚举声明中也可以用标志组合定义额外的枚举值
- [Flags]
- enum DistributedChannel
- {
- None = 0,
- Transacted = 1,
- Queued = 2,
- Encrypted = 4,
- Persisted = 16,
- FaultTolerant = Transacted | Queued | Persisted
- }
良构类型
1、重写ToString
- 默认情况下,在任何对象上调用ToString() 将返回类的完全限定名称 。例如:在一个Sytem.IO.FileStream对象上调用ToString() 方法将返回字符串 System.IO.FileStream
- Console.WriteLine() 和System.Diagnostics.Trace.Write 等方法会调用对象的ToString 方法。 因此,重写ToString 输出比默认值更有意义的信息
- public struct Coordinate
- {
- public Coordinate(Longitude longitude, Latitude latitude)
- {
- Longitude = longitude;
- Latitude = latitude;
- }
- public Longitude Longitude { get; }
- public Latitude Latitude { get; }
- public override string ToString() =>$"{ Longitude } { Latitude }";
- }
- public struct Longitude { }
- public struct Latitude { }
- 由于缺乏本地化和其他高级格式化功能,所以它不太适合一般性用户文本显示
2、重写GetHashCode
散列码的作用是生成与对象值对应的数字,从而高效地平衡散列表。 为了获得良好的GetHashCode() 的实现,请参照以下原则
- 必须:相等的对象必须有相等的散列值。(若a.Equals(b)),则 a.GetHashCode ()== b.GetHashCode()
- 必须:在特定对象的生存期内,GetHashCode() 始终返回相同的值,即使对象数据发生了变化。
- 必须: GetHashCode() 不应引发任何异常。它总是成功返回一个值
- 性能: 散列码应尽可能唯一
- 性能: 可能的散列码的值应当尽可能在int 范围内平均分布
- 性能: GetHashCode() 的性能应该优化,它通常在Equals 中实现用于“短路”一次完整的相等性比较。所以当类型作为字典集合中的key 使用时,会频繁调用该方法
- 性能:两个对象的细微差别应造成散列码的极大差异。 理想情况下,1位的差异应造成散列码平均16位的差异,这有助于保持散列的平衡性
- 安全性: 攻击者应该难以伪造具有特定散列值的对象
在重写Equals或者将类作为散列表集合的键时,需要重写GetHashCode。(如:Collections.HashTable 和 Collections.Generic.Dictionary)
- public struct Coordinate
- {
- public Coordinate(Longitude longitude, Latitude latitude)
- {
- Longitude = longitude;
- Latitude = latitude;
- }
- public Longitude Longitude { get; }
- public Latitude Latitude { get; }
- public override int GetHashCode()
- {
- int hashCode = Longitude.GetHashCode();
- // As long as the hash codes are not equal
- if(Longitude.GetHashCode() != Latitude.GetHashCode())
- {
- hashCode ^= Latitude.GetHashCode(); // eXclusive OR
- }
- return hashCode;
- }
- public override string ToString() => string.Format("{0} {1}", Longitude, Latitude);
- }
- public struct Longitude { }
- public struct Latitude { }
通常采用的方法是像相关类型的散列码应用XOR 操作符,并确保XOR的操作数不相近或相等。否则结果全为零。在操作数相近或相等的情况下,考虑改为使用移位和加法的操作。
为了进行更细致的控制,应该使用移位操作符来分解比int 大的类型。 例如,对于一个名为value 的long类型,int GetHashCode() {return ((int)value ^ (int)(value >>32))} ;
如果基类不是object, 应该在XOR 赋值中包含base.GetHashCode()
假如计算得到的值可能改变,或者哉将值缓存之后能显著优化性能,就应该对散列值进行缓存。
3、重写Equals
对象同一性 和相等的对象值
- 两个引用如果引用同一个对象,就说它们是同一的。object 包含名为ReferenceEquals() 的静态方法,它能显式检查对象的同一性
- 两个对象实例的成员值部分或全部相等,也可以说它们相等
实现Equals
- 检查是否为null
- 如果是引用类型,就检查引用是否相等
- 检查数据类型是否相同
- 一个指定了具体类型的辅助方法,它能将操作数视为要比较的类型,而不是将其视为对象
- 可能要检查散列码是否相等。
- 如果基类重写了Equals,就检查base.Equals()
- 比较每一个标识字段,判断是否相等
- 重写GetHashCode
- 重写== 和!= 操作符
重写Equals 例子:
- //例1:
- public sealed class ProductSerialNumber
- {
- public ProductSerialNumber(string productSeries, int model, long id)
- {
- ProductSeries = productSeries;
- Model = model;
- Id = id;
- }
- public string ProductSeries { get; }
- public int Model { get; }
- public long Id { get; }
- public override int GetHashCode()
- {
- int hashCode = ProductSeries.GetHashCode();
- hashCode ^= Model; // Xor (eXclusive OR)
- hashCode ^= Id.GetHashCode(); // Xor (eXclusive OR)
- return hashCode;
- }
- public override bool Equals(object obj)
- {
- if(obj == null )
- return false;
- if(ReferenceEquals(this, obj))
- return true;
- if(this.GetType() != obj.GetType())
- return false;
- return Equals((ProductSerialNumber)obj);
- }
- public bool Equals(ProductSerialNumber obj)
- {
- return ((obj != null) && (ProductSeries == obj.ProductSeries) &&
- (Model == obj.Model) && (Id == obj.Id));
- }
- //....
- }
- //例2:
- public static void Main()
- {
- ProductSerialNumber serialNumber1 =new ProductSerialNumber("PV", 1000, 09187234);
- ProductSerialNumber serialNumber2 = serialNumber1;
- ProductSerialNumber serialNumber3 = new ProductSerialNumber("PV", 1000, 09187234);
- // These serial numbers ARE the same object identity.
- if(!ProductSerialNumber.ReferenceEquals(serialNumber1, serialNumber2))
- throw new Exception("serialNumber1 does NOT " + "reference equal serialNumber2");
- // And, therefore, they are equal.
- else if(!serialNumber1.Equals(serialNumber2))
- throw new Exception("serialNumber1 does NOT equal serialNumber2");
- else {
- Console.WriteLine("serialNumber1 reference equals serialNumber2");
- Console.WriteLine("serialNumber1 equals serialNumber2");
- }
- // These serial numbers are NOT the same object identity.
- if(ProductSerialNumber.ReferenceEquals(serialNumber1, serialNumber3))
- throw new Exception("serialNumber1 DOES reference " + "equal serialNumber3");
- // But they are equal (assuming Equals is overloaded).
- else if(!serialNumber1.Equals(serialNumber3) || serialNumber1 != serialNumber3)
- throw new Exception("serialNumber1 does NOT equal serialNumber3");
- Console.WriteLine("serialNumber1 equals serialNumber3");
- }
4、比较操作符重载
实现操作符的过程称为操作符重载. C# 支持重载所有操作符,除了x.y、 f(x)、 new、 typeof、default、checked、unchecked、delegate、is、as、= 和=> 之外
一旦重写了Equals, 就可能出现不一致情况,对两个对象执行Equals()可能返回true,但 ==操作符返回false. 因为==默认也是执行引用相等性检查。因此需要重载相等(==)和不相等操作符(!=)
- public sealed class ProductSerialNumber
- {
- //...
- public static bool operator ==(ProductSerialNumber leftHandSide, ProductSerialNumber rightHandSide)
- {
- // Check if leftHandSide is null. (operator== would be recursive)
- if(ReferenceEquals(leftHandSide, null))
- {
- return ReferenceEquals(rightHandSide, null); // Return true if rightHandSide is also nulland false otherwise.
- }
- return (leftHandSide.Equals(rightHandSide));
- }
- public static bool operator !=(ProductSerialNumber leftHandSide, ProductSerialNumber rightHandSide)
- {
- return !(leftHandSide == rightHandSide);
- }
- }
5、二元操作符重载
+、-、* 、/ 、%、|、^、<<和>> 操作符都被实现为二元静态方法。其中至少一个参数的类型是包容类型。方法名由operator 加操作名构成。
- public struct Arc
- {
- public Arc(Longitude longitudeDifference, Latitude latitudeDifference)
- {
- LongitudeDifference = longitudeDifference;
- LatitudeDifference = latitudeDifference;
- }
- public Longitude LongitudeDifference { get; }
- public Latitude LatitudeDifference { get; }
- }
- public struct Coordinate
- {
- //....
- public static Coordinate operator +(Coordinate source, Arc arc)
- {
- Coordinate result = new Coordinate( new Longitude( source.Longitude + arc.LongitudeDifference),
- new Latitude(source.Latitude + arc.LatitudeDifference));
- return result;
- }
- }
6、 赋值与二元操作符的结合
只要重载了二元操作符,就自动重载了赋值操作符和二元操作符的结合(+=、-=、/=、%=、&=、|=、^=、<<=和>>=. 所以可以直接使用下列代码 coordinate += arc;
它等价于: coordinate = coordinate + arc;
7、一元操作符
- 一元操作符的重载类似于二元操作符的重载,只是它们只获取一个参数 该参数必须是包容类型。
- public struct Latitude
- {
- //……
- // UNARY
- public static Latitude operator -(Latitude latitude)
- {
- return new Latitude(-latitude.Degrees);
- }
- public static Latitude operator +(Latitude latitude)
- {
- return latitude;
- }
- }
- 重载 true 和 false 时,必须同时重载两个操作符。它们的签名和其他操作符重载必须相同,但是返回值必须时一个bool 值。
- public struct Example
- {
- //public static bool operator false(object item)
- //{
- // return true;
- // // ...
- //}
- //public static bool operator true(object item)
- //{
- // return true;
- // // ...
- //}
- }
- 重载true和false 的操作符类型可以在 if、do、while 和for 语句的控制表达 式中使用
8、引用程序集
开发者可以将程序的不同部分转移到单独的编译单元中,这些单元称为类库,或者简称库。 然后程序可以引用和依赖类库来提供自己的一部分功能。
更改程序集目标:
编译器允许通过/target 选项创建下面4种不同的程序集类型
- 控制台程序: 省略target 或者指定 /target:exe
- 类库:/target: library
- Window 可执行程序:/target: winexe
- 模块:/target : module
引用程序集:
C# 允许开发者在命令行上引用程序集。方法是使用 /reference (/r)。
例如:csc.exe /R:Coordinates.dll Program.cs
9、类型封装

-
相关阅读:
ptp协议相关术语
Python二级 每周练习题19
Linux centos安装SQL Server数据库,结合cpolar内网穿透实现公网访问
VMware 网络模式
Mysql 学习(十 三)InnoDB的BufferPool
P2320 [HNOI2006] 鬼谷子的钱袋
学生会学习部部长竞选稿
OAuth2.0第三方授权原理与实战
uniapp使用vue3和ts开发小程序自定义tab栏,实现自定义凸出tabbar效果
记一次事故看 Redis 开发规范
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44906102/article/details/133142720
