-
《动手学深度学习 Pytorch版》 6.6 卷积神经网络
import torch from torch import nn from d2l import torch as d2l- 1
- 2
- 3
6.6.1 LeNet
LetNet-5 由两个部分组成:
- 卷积编码器:由两个卷积核组成。 - 全连接层稠密块:由三个全连接层组成。- 1
- 2
模型结构如下流程图(每个卷积块由一个卷积层、一个 sigmoid 激活函数和平均汇聚层组成):
全连接层(10) ↑ \uparrow ↑
全连接层(84) ↑ \uparrow ↑
全连接层(120) ↑ \uparrow ↑
2 × 2 2\times2 2×2平均汇聚层,步幅2 ↑ \uparrow ↑
5 × 5 5\times5 5×5卷积层(16) ↑ \uparrow ↑
2 × 2 2\times2 2×2平均汇聚层,步幅2 ↑ \uparrow ↑
5 × 5 5\times5 5×5卷积层(6),填充2 ↑ \uparrow ↑
输入图像( 28 × 28 28\times28 28×28 单通道) net = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.Linear(120, 84), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.Linear(84, 10))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 28, 28), dtype=torch.float32) # 生成测试数据 for layer in net: X = layer(X) print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape: \t',X.shape) # 确保模型各层数据正确- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 28, 28]) Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 28, 28]) AvgPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 6, 14, 14]) Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 10, 10]) Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 10, 10]) AvgPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 5, 5]) Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 400]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 120]) Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 120]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 84]) Sigmoid output shape: torch.Size([1, 84]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
6.6.2 模型训练
batch_size = 256 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size=batch_size) # 仍使用经典的 Fashion-MNIST 数据集- 1
- 2
def evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, data_iter, device=None): #@save """使用GPU计算模型在数据集上的精度""" if isinstance(net, nn.Module): net.eval() # 设置为评估模式 if not device: device = next(iter(net.parameters())).device metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) # 生成一个有两个元素的列表,使用 add 将会累加到对应的元素上 with torch.no_grad(): for X, y in data_iter: # 为了使用 GPU,需要将数据移动到 GPU 上 if isinstance(X, list): X = [x.to(device) for x in X] else: X = X.to(device) y = y.to(device) metric.add(d2l.accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel()) # 累加(正确预测的数量,总预测的数量) return metric[0] / metric[1] # 正确率- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
#@save def train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, device): """用GPU训练模型(在第六章定义)""" def init_weights(m): # 使用 Xavier 初始化权重 if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d: nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight) net.apply(init_weights) print('training on', device) net.to(device) # 移动数据到GPU optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr) loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc']) timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter) for epoch in range(num_epochs): # 训练损失之和,训练准确率之和,样本数 metric = d2l.Accumulator(3) net.train() for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter): timer.start() optimizer.zero_grad() X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device) y_hat = net(X) l = loss(y_hat, y) l.backward() optimizer.step() with torch.no_grad(): metric.add(l * X.shape[0], d2l.accuracy(y_hat, y), X.shape[0]) timer.stop() train_l = metric[0] / metric[2] train_acc = metric[1] / metric[2] if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1: animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches, (train_l, train_acc, None)) test_acc = evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter) animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc)) print(f'loss {train_l:.3f}, train acc {train_acc:.3f}, ' f'test acc {test_acc:.3f}') print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec ' f'on {str(device)}')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
lr, num_epochs = 0.9, 10 train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())- 1
- 2
loss 0.471, train acc 0.820, test acc 0.815 40056.7 examples/sec on cuda:0- 1
- 2

练习
(1)将平均汇聚层替换为最大汇聚层,会发生什么?
net_Max = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.Linear(120, 84), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.Linear(84, 10)) lr, num_epochs = 0.9, 10 train_ch6(net_Max, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
loss 0.422, train acc 0.844, test acc 0.671 31151.6 examples/sec on cuda:0- 1
- 2

几乎无区别
(2)尝试构建一个基于 LeNet 的更复杂网络,以提高其精准性。
a. 调节卷积窗口的大小。 b. 调整输出通道的数量。 c. 调整激活函数(如 ReLU)。 d. 调整卷积层的数量。 e. 调整全连接层的数量。 f. 调整学习率和其他训练细节(例如,初始化和轮数)。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
net_Best = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 8, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.ReLU(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Conv2d(8, 16, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(32 * 3 * 3, 128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(128, 64), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(64, 32), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(32, 10) )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
lr, num_epochs = 0.4, 10 train_ch6(net_Best, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())- 1
- 2
loss 0.344, train acc 0.869, test acc 0.854 32868.3 examples/sec on cuda:0- 1
- 2
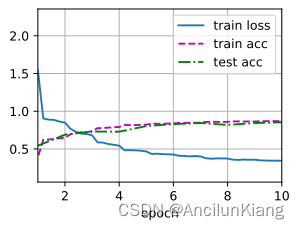
(3)在 MNIST 数据集上尝试以上改进后的网络。
import torchvision from torch.utils import data from torchvision import transforms trans = transforms.ToTensor() mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root="../data", train=True, transform=trans, download=True) mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root="../data", train=False, transform=trans, download=True) train_iter2 = data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=d2l.get_dataloader_workers()) test_iter2 = data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=d2l.get_dataloader_workers()) lr, num_epochs = 0.4, 5 # 大约 6 轮往后直接就爆炸 train_ch6(net_Best, train_iter2, test_iter2, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
loss 0.049, train acc 0.985, test acc 0.986 26531.1 examples/sec on cuda:0- 1
- 2

(4)显示不同输入(例如,毛衣和外套)时 LetNet 第一层和第二层的激活值。
for X, y in test_iter: break x_first_Sigmoid_layer = net[0:2](X)[0:9, 1, :, :] d2l.show_images(x_first_Sigmoid_layer.reshape(9, 28, 28).cpu().detach(), 1, 9) x_second_Sigmoid_layer = net[0:5](X)[0:9, 1, :, :] d2l.show_images(x_second_Sigmoid_layer.reshape(9, 10, 10).cpu().detach(), 1, 9) d2l.plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8


-
相关阅读:
Java中对象引用是什么意思
【activiti】activiti与springboot整合
Java多线程(6):锁与AQS(下)
HTML的段落中怎么样显示出标签要使用的尖括号<>?
js 之reduce 方法实现数组去重原理分布解析
论文阅读笔记 | 三维目标检测——PointRCNN
电子商务平台市场动向的数据分析平台:阿里商品指数,包括淘宝采购指数,淘宝供应指数,1688供应指数。
SpringBoot集成Kafka低版本和高版本
ArcMap安装OSM路网数据编辑插件ArcGIS Editor for OSM的方法
docker默认ip地址修改
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43941037/article/details/132953630
