-
MySQL基础—从零开始学习MySQL
1、MySQL安装
以管理员身份运行cmd
- net start mysql80
- net stop mysql80
客户端连接
1). 方式一:使用MySQL提供的客户端命令行工具

2). 方式二:使用系统自带的命令行工具执行指令
- mysql [-h 127.0.0.1] [-P 3306] -u root -p
- 参数:
- -h : MySQL服务所在的主机IP
- -P : MySQL服务端口号, 默认3306
- -u : MySQL数据库用户名
- -p : MySQL数据库用户名对应的密码
[ ] 内为可选参数,如果需要连接远程的 MySQL ,需要加上这两个参数来指定远程主机 IP 、端口,如果连接本地的MySQL ,则无需指定这两个参数。mysql -u root -p2. SQL
2.1 SQL通用语法
语言的统一语法。1). SQL 语句可以单行或多行书写,以分号结尾。2). SQL 语句可以使用空格 / 缩进来增强语句的可读性。3). MySQL 数据库的 SQL 语句不区分大小写,关键字建议使用大写。4). 注释:- 单行注释:-- 注释内容 或 # 注释内容
- 多行注释:/* 注释内容 */
2.2 SQL分类
SQL 语句,根据其功能,主要分为四类: DDL 、 DML 、 DQL 、 DCL 。
2.3 DDL
Data Definition Language ,数据定义语言,用来定义数据库对象 ( 数据库,表,字段 ) 。2.3.1 数据库操作
1). 查询所有数据库
show databases;2). 查询当前数据库
select database();3). 创建数据库
create database [ if not exists ] 数据库名 [ default charset 字符集 ] [ collate 排序规则 ] ;create database itcast;4). 删除数据库
drop database [ if exists ] 数据库名;5). 切换数据库
use 数据库名;2.3.2 表操作
2.3.2.1 表操作-查询创建
1). 查询当前数据库所有表
show tables;2). 查看指定表结构desc 表名;通过这条指令,我们可以查看到指定表的字段,字段的类型、是否可以为 NULL ,是否存在默认值等信息。3). 查询指定表的建表语句show create table 表名; 4). 创建表结构
4). 创建表结构- CREATE TABLE 表名(
- 字段1 字段1类型 [ COMMENT 字段1注释 ],
- 字段2 字段2类型 [COMMENT 字段2注释 ],
- 字段3 字段3类型 [COMMENT 字段3注释 ],
- ......
- 字段n 字段n类型 [COMMENT 字段n注释 ]
- ) [ COMMENT 表注释 ] ;
注意: [...] 内为可选参数,最后一个字段后面没有逗号
2.3.2.2 表操作-数据类型
数值类型
分类 类型 大小 有符号(SIGNED)范围 无符号(UNSIGNED)范围 描述 数值类型 TINYINT 1 byte (-128,127) (0,255) 小整数值 SMALLINT 2 bytes (-32768,32767) (0,65535) 大整数值 MEDIUMINT 3 bytes (-8388608,8388607) (0,16777215) 大整数值 INT或INTEGER 4 bytes (-2147483648,2147483647) (0,4294967295) 大整数值 BIGINT 8 bytes (-2^63,2^63-1) (0,2^64-1) 极大整数值 FLOAT 4 bytes (-3.402823466 E+38,3.402823466351 E+38) 0 和 (1.175494351 E-38,3.402823466 E+38) 单精度浮点数值 DOUBLE 8 bytes (-1.7976931348623157 E+308,1.7976931348623157 E+308) 0 和 (2.2250738585072014 E-308,1.7976931348623157 E+308) 双精度浮点数值 DECIMAL 依赖于M(精度)和D(标度)的值 依赖于M(精度)和D(标度)的值 小数值(精确定点数) 日期时间类型
分类 类型 大小 范围 格式 描述 日期类型 DATE 3 1000-01-01 至 9999-12-31 YYYY-MM-DD 日期值 TIME 3 -838:59:59 至 838:59:59 HH:MM:SS 时间值或持续时间 YEAR 1 1901 至 2155 YYYY 年份值 DATETIME 8 1000-01-01 00:00:00 至 9999-12-31 23:59:59 YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS 混合日期和时间值 TIMESTAMP 4 1970-01-01 00:00:01 至 2038-01-19 03:14:07 YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS 混合日期和时间值,时间戳 2.3.2.4 表操作-修改
1). 添加字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型 (长度) [ comment 注释 ] [ 约束 ];2). 修改数据类型
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 新数据类型 (长度); 13). 修改字段名和字段类型
alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名 类型 (长度) [ comment 注释 ] [ 约束 ];2.5.1 添加数据
1). 给指定字段添加数据
insert into 表名 (字段名1, 字段名2, ...) values (值1, 值2, ...);2). 给全部字段添加数据insert into 表名 values (值1, 值2, ...);3). 批量添加数据
- INSERT INTO 表名 (字段名1, 字段名2, ...) VALUES (值1, 值2, ...), (值1, 值2, ...), (值
- 1, 值2, ...) ;
insert into 表名 values (值1, 值2, ...), (值1, 值2, ...), (值1, 值2, ...);2.5.2 修改数据
修改数据的具体语法为 :update 表名 set 字段名1 = 值1 , 字段名2 = 值2 , .... [ where 条件 ];注意事项 :修改语句的条件可以有,也可以没有,如果没有条件,则会修改整张表的所有数据。2.5.3 删除数据
delete from 表名 [ where 条件 ];注意事项 :- DELETE 语句的条件可以有,也可以没有,如果没有条件,则会删除整张表的所有数据。
- DELETE 语句不能删除某一个字段的值(可以使用UPDATE,将该字段值置为NULL即可)。
2.6 DQL
2.6.1 基本语法
- SELECT
- 字段列表
- FROM
- 表名列表
- WHERE
- 条件列表
- GROUP BY
- 分组字段列表
- HAVING
- 分组后条件列表
- ORDER BY
- 排序字段列表
- LIMIT
- 分页参数
2.6.2 基础查询
1). 查询多个字段
- select 字段1, 字段2, 字段3 ... from 表名;
- select * from 表名;
- 注意 : * 号代表查询所有字段,在实际开发中尽量少用(不直观、影响效率)。
2). 字段设置别名
- select 字段1 [ as 别名1 ] , 字段2 [ as 别名2 ] ... from 表名;
- select 字段1 [ 别名1 ] , 字段2 [ 别名2 ] ... from 表名;
1). 常见的聚合函数

2). 语法
select 聚合函数(字段列表) from 表名;2.6.5 分组查询
1). 语法
- select 字段列表 from 表名 [ where 条件 ] group by 分组字段名 [ having 分组
- 后过滤条件 ];
2). where 与 having 区别执行时机不同: where 是分组之前进行过滤,不满足 where 条件,不参与分组;而 having 是分组之后对结果进行过滤。判断条件不同: where 不能对聚合函数进行判断,而 having 可以。2.6.6 排序查询
1). 语法
select 字段列表 from 表名 order by 字段1 排序方式1 , 字段2 排序方式2 ;2). 排序方式ASC : 升序 ( 默认值 )DESC: 降序2.6.7 分页查询
1). 语法
select 字段列表 from 表名 limit 起始索引, 查询记录数 ;注意事项 :- 起始索引从0开始,起始索引 = (查询页码 - 1)* 每页显示记录数。
- 分页查询是数据库的方言,不同的数据库有不同的实现,MySQL中是limit。
- 如果查询的是第一页数据,起始索引可以省略,直接简写为 limit 10。
2.6.8 执行顺序

2.7 DCL
2.7.1 管理用户
1). 查询用户
select * from mysql.user;2). 创建用户
create user'用户名'@'主机名' identified by '密码';3). 修改用户密码
alter user '用户名'@'主机名' identified with mysql_native_password by '新密码' ;4). 删除用户
drop user '用户名'@'主机名' ;- 在MySQL中需要通过用户名@主机名的方式,来唯一标识一个用户。
- 主机名可以使用 % 通配。
2.7.2 权限控制
MySQL中定义了很多种权限,但是常用的就以下几种:

1). 查询权限
show grants for'用户名'@'主机名' ;2). 授予权限
grant 权限列表 on 数据库名.表名 to '用户名'@'主机名';3). 撤销权限
revoke 权限列表 on 数据库名.表名 from '用户名'@'主机名'3. 函数
3.1 字符串函数
MySQL中内置了很多字符串函数,常用的几个如下:

A. concat : 字符串拼接
select concat('Hello' , ' MySQL');B. lower : 全部转小写
select lower('Hello');C. upper : 全部转大写
select upper('Hello');D. lpad : 左填充
- select lpad('01', 5, '-');
- # ---01
E. rpad : 右填充
- select rpad('01', 5, '-');
- # 01---
F. trim : 去除空格
- select trim(' Hello MySQL ') ;
- #Hello MySQL
- #去除前后空格
G. substring : 截取子字符串
- select substring('Hello MySQL',1,5);
- #Hello
示例
由于业务需求变更,企业员工的工号,统一为5位数,目前不足5位数的全部在前面补0。比如: 1号员 工的工号应该为00001。
update emp set workno = lpad(workno, 5, '0');3.2 数值函数

A. ceil:向上取整
select ceil(1.1);B. floor:向下取整
select floor(1.9);C. mod:取模
select mod(7,4);D. rand:获取随机数
select rand();E. round:四舍五入
select round(2.344,2);示例
获取随机数可以通过rand()函数,但是获取出来的随机数是在0-1之间的,所以可以在其基础 上乘以1000000,然后舍弃小数部分,如果长度不足6位,补0
select lpad(round(rand()*1000000 , 0), 6, '0');3.3 日期函数

A. curdate:当前日期
select curdate();B. curtime:当前时间
select curtime();C. now:当前日期和时间
select now();D. YEAR , MONTH , DAY:当前年、月、日
- select YEAR(now());
- select MONTH(now());
- select DAY(now());
E. date_add:增加指定的时间间隔
select date_add(now(), INTERVAL 70 YEAR );示例
查询所有员工的入职天数,并根据入职天数倒序排序。 思路: 入职天数,就是通过当前日期 - 入职日期,所以需要使用datediff函数来完成。
select name, datediff(curdate(), entrydate) as 'entrydays' from emp order by entrydays desc;3.4 流程函数
流程函数也是很常用的一类函数,可以在SQL语句中实现条件筛选,从而提高语句的效率。

A. if
- select if(false, 'Ok', 'Error');
- #Error
B. ifnull
- select ifnull('Ok','Default'); #OK
- select ifnull('','Default'); #
- select ifnull(null,'Default');# Default
C. case when then else end
需求: 查询emp表的员工姓名和工作地址 (北京/上海 ----> 一线城市 , 其他 ----> 二线城市) 案例: 具体的SQL语句如下:
- select name,
- (case workaddress when '北京' then '一线城市' when '上海' then '一线城市' else
- '二线城市' end ) as '工作地址' from emp
示例
- create table score(
- id int comment 'ID',
- name varchar(20) comment '姓名',
- math int comment '数学',
- english int comment '英语',
- chinese int comment '语文'
- ) comment '学员成绩表';
- insert into score(id, name, math, english, chinese) VALUES (1, 'Tom', 67, 88, 95
- ), (2, 'Rose' , 23, 66, 90),(3, 'Jack', 56, 98, 76);
- select id,name,
- (case when math >= 85 then '优秀' when math >=60 then '及格' else '不及格' end ) '数学',
- (case when english >= 85 then '优秀' when english >=60 then '及格' else '不及格' end ) '英语',
- (case when chinese >= 85 then '优秀' when chinese >=60 then '及格' else '不及格' end ) '语文'
- from score;
4. 约束
4.1 概述
概念:约束是作用于表中字段上的规则,用于限制存储在表中的数据。
目的:保证数据库中数据的正确、有效性和完整性。

注意:约束是作用于表中字段上的,可以在创建表/修改表的时候添加约束。
4.2 约束演示
根据需求,完成表结构的创建。需求如下:

- create table tb_user(
- id int auto_increment primary key comment 'ID唯一标识',
- name varchar(10) not null unique comment '姓名' ,
- age int check (age > 0 && age <= 120) comment '年龄' ,
- status char(1) default '1' comment '状态',
- gender char(1) comment '性别'
- )comment '用户表';
insert into tb_user (name,age,status,gender) values('Tom1',19,'1','男'),('Tom2',20,'0','男');4.3 外键约束
4.3.1 介绍
外键:用来让两张表的数据之间建立连接,从而保证数据的一致性和完整性。

左侧的emp表是员工表,里面存储员工的基本信息,在员工的信息中存储的是部门的ID dept_id,而这个部门的ID是关联的 部门表dept的主键id,那emp表的dept_id就是外键,关联的是另一张表的主键。
4.3.2 语法
1). 添加外键
- create table 表名(
- 字段名 数据类型,
- ...
- [constraint] [外键名称] foreign key (外键字段名) references 主表 (主表列名)
- );
alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key (外键字段名) references 主表 (主表列名) ;2). 删除外键
alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称;4.3.3 删除/更新行为
添加了外键之后,再删除父表数据时产生的约束行为,我们就称为删除/更新行为。具体的删除/更新行 为有以下几种:

alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key (外键字段) references 主表名 (主表字段名) on update cascade on delete cascade;1). CASCADE
- alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references
- dept(id) on update cascade on delete cascade ;
2). SET NULL
- alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references
- dept(id) on update set null on delete set null ;
5. 多表查询
5.1 多表关系
项目开发中,在进行数据库表结构设计时,会根据业务需求及业务模块之间的关系,分析并设计表结 构,由于业务之间相互关联,所以各个表结构之间也存在着各种联系,基本上分为三种:
- 一对多(多对一)
- 多对多
- 一对一
5.1.1 一对多
在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主
5.1.2 多对多
建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键
5.1.3 一对一
在任意一方加入外键,关联另外一方的主键,并且设置外键为唯一的(UNIQUE)
5.2 多表查询概述
5.2.1 数据准备
- -- 创建dept表,并插入数据
- create table dept(
- id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,
- name varchar(50) not null comment '部门名称'
- )comment '部门表';
- -- 创建emp表,并插入数据
- INSERT INTO dept (id, name) VALUES (1, '研发部'), (2, '市场部'),(3, '财务部'), (4,'销售部'), (5, '总经办'), (6, '人事部');
- create table emp(
- id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,
- name varchar(50) not null comment '姓名',
- age int comment '年龄',
- job varchar(20) comment '职位',
- salary int comment '薪资',
- entrydate date comment '入职时间',
- managerid int comment '直属领导ID',
- dept_id int comment '部门ID'
- )comment '员工表';
- -- 添加外键
- alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id);
- INSERT INTO emp (id, name, age, job,salary, entrydate, managerid, dept_id)
- VALUES
- (1, '金庸', 66, '总裁',20000, '2000-01-01', null,5),
- (2, '张无忌', 20, '项目经理',12500, '2005-12-05', 1,1),
- (3, '杨逍', 33, '开发', 8400,'2000-11-03', 2,1),
- (4, '韦一笑', 48, '开发',11000, '2002-02-05', 2,1),
- (5, '常遇春', 43, '开发',10500, '2004-09-07', 3,1),
- (6, '小昭', 19, '程序员鼓励师',6600, '2004-10-12', 2,1),
- (7, '灭绝', 60, '财务总监',8500, '2002-09-12', 1,3),
- (8, '周芷若', 19, '会计',48000, '2006-06-02', 7,3),
- (9, '丁敏君', 23, '出纳',5250, '2009-05-13', 7,3),
- (10, '赵敏', 20, '市场部总监',12500, '2004-10-12', 1,2),
- (11, '鹿杖客', 56, '职员',3750, '2006-10-03', 10,2),
- (12, '鹤笔翁', 19, '职员',3750, '2007-05-09', 10,2),
- (13, '方东白', 19, '职员',5500, '2009-02-12', 10,2),
- (14, '张三丰', 88, '销售总监',14000, '2004-10-12', 1,4),
- (15, '俞莲舟', 38, '销售',4600, '2004-10-12', 14,4),
- (16, '宋远桥', 40, '销售',4600, '2004-10-12', 14,4),
- (17, '陈友谅', 42, null,2000, '2011-10-12', 1,null);
5.2.2 分类
- 连接查询
- 内连接:相当于查询A、B交集部分数据
- 外连接:
- 左外连接:查询左表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分数据
- 右外连接:查询右表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分数据
- 自连接:当前表与自身的连接查询,自连接必须使用表别名
- 子查询
5.3 内连接
内连接查询的是两张表交集部分的数据。
1). 隐式内连接
select 字段列表 from表1 , 表2 where 条件 ... ;2). 显式内连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 [inner] join 表2 on 连接条件 ... ;示例
查询每一个员工的姓名 , 及关联的部门的名称
- --隐式内连接实现
- select emp.name , dept.name from emp , dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id;
- -- 为每一张表起别名,简化SQL编写
- select e.name,d.name from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;
- --显式内连接实现
- select e.name, d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
5.4 外连接

1). 左外连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 left [ outer] join 表2 on 条件 ... ;左外连接相当于查询表1(左表)的所有数据,当然也包含表1和表2交集部分的数据。
2). 右外连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 right [ outer] join 表2 on 条件 ... ;右外连接相当于查询表2(右表)的所有数据,当然也包含表1和表2交集部分的数据。
示例
- --查询emp表的所有数据, 和对应的部门信息
- select e.*, d.name from emp e left outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
- select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
- --查询dept表的所有数据, 和对应的员工信息(右外连接)
- select d.*, e.* from emp e right outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
- select d.*, e.* from dept d left outer join emp e on e.dept_id = d.id;
5.5 自连接
5.5.1 自连接查询
select 字段列表 from 表A 别名A join 表A 别名B on 条件 ... ;示例
查询员工 及其 所属领导的名字
select a.name , b.name from emp a , emp b where a.managerid = b.id;查询所有员工 emp 及其领导的名字 emp , 如果员工没有领导, 也需要查询出来
select a.name '员工', b.name '领导' from emp a left join emp b on a.managerid = b.id;5.5.2 联合查询
对于union查询,就是把多次查询的结果合并起来,形成一个新的查询结果集。
- select 字段列表 from 表A ...
- union [ all ]
- select 字段列表 from 表B ...;
对于联合查询的多张表的列数必须保持一致,字段类型也需要保持一致。
union all 会将全部的数据直接合并在一起,union 会对合并之后的数据去重。
示例
将薪资低于 5000 的员工 , 和 年龄大于 50 岁的员工全部查询出来.
- --全部
- select * from emp where salary < 5000
- union all
- select * from emp where age > 50;
- --去重
- select * from emp where salary < 5000
- union
- select * from emp where age > 50;
5.6 子查询
5.6.1 概述
1). 概念
SQL语句中嵌套SELECT语句,称为嵌套查询,又称子查询。
select * from t1 where column1 = ( select column1 from t2 );子查询外部的语句可以是INSERT / UPDATE / DELETE / SELECT 的任何一个。
2). 分类
根据子查询结果不同,分为:
- 标量子查询(子查询结果为单个值)
- 列子查询(子查询结果为一列)
- 行子查询(子查询结果为一行)
- 表子查询(子查询结果为多行多列)
根据子查询位置,分为:
- WHERE之后
- FROM之后
- SELECT之后
5.6.2 标量子查询
子查询返回的结果是单个值(数字、字符串、日期等),最简单的形式,这种子查询称为标量子查询。
常用的操作符:= <> > >= < <=
- --查询 "销售部" 的所有员工信息
- select * from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '销售部');
- --查询在 "方东白" 入职之后的员工信息
- select * from emp where entrydate > (select entrydate from emp where name = '方东白');
5.6.3 列子查询
子查询返回的结果是一列(可以是多行),这种子查询称为列子查询。 常用的操作符:IN 、NOT IN 、 ANY 、SOME 、 ALL

- --查询 "销售部" 和 "市场部" 的所有员工信息
- select * from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name = '销售部' or name = '市场部');
- --查询比 财务部 所有人工资都高的员工信息
- select * from emp where salary > all ( select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '财务部') );
- --查询比研发部其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
- select * from emp where salary > any ( select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部') );
- select * from emp where salary > some ( select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部') );
5.6.4 行子查询
子查询返回的结果是一行(可以是多列),这种子查询称为行子查询。
常用的操作符:= 、<> 、IN 、NOT IN
- --查询与 "张无忌" 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息;
- select * from emp where (salary,managerid) = (select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌');
5.6.5 表子查询
子查询返回的结果是多行多列,这种子查询称为表子查询。 常用的操作符:IN
- --查询与 "鹿杖客" , "宋远桥" 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
- select * from emp where (job,salary) in ( select job, salary from emp where name = '鹿杖客' or name = '宋远桥' );
- --查询入职日期是 "2006-01-01" 之后的员工信息 , 及其部门信息
- select e.*, d.* from (select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01') e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
5.7 多表查询案例
数据环境准备:
- create table salgrade(
- grade int,
- losal int,
- hisal int
- ) comment '薪资等级表';
- insert into salgrade values (1,0,3000);
- insert into salgrade values (2,3001,5000);
- insert into salgrade values (3,5001,8000);
- insert into salgrade values (4,8001,10000);
- insert into salgrade values (5,10001,15000);
- insert into salgrade values (6,15001,20000);
- insert into salgrade values (7,20001,25000);
- insert into salgrade values (8,25001,30000);
三张表:emp员工表、dept部门表、salgrade薪资等级表 。
1). 查询员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息 (隐式内连接)
select e.name,e.age,e.job,d.name from emp e,dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;2). 查询年龄小于30岁的员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(显式内连接)
select e.name , e.age , e.job , d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age < 30;3). 查询拥有员工的部门ID、部门名称
select distinct d.id , d.name from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;4). 查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工, 及其归属的部门名称; 如果员工没有分配部门, 也需要展示出 来(外连接)
select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age > 40 ;5). 查询所有员工的工资等级
- -- 方式一
- select e.* , s.grade , s.losal, s.hisal from emp e , salgrade s where e.salary >= s.losal and e.salary <= s.hisal;
- -- 方式二
- select e.* , s.grade , s.losal, s.hisal from emp e , salgrade s where e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal;
6). 查询 "研发部" 所有员工的信息及 工资等级
select e.* , s.grade from emp e , dept d , salgrade s where e.dept_id = d.id and (e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal ) and d.name = '研发部';7). 查询 "研发部" 员工的平均工资
select avg(e.salary) from emp e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id and d.name = '研发部';8). 查询工资比 "灭绝" 高的员工信息。
select * from emp where salary > ( select salary from emp where name = '灭绝' );9). 查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > ( select avg(salary) from emp );10). 查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
- select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = 1;
- select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = 2;
- select * from emp e2 where e2.salary < ( select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = e2.dept_id );
11). 查询所有的部门信息, 并统计部门的员工人数
select d.id, d.name , ( select count(*) from emp e where e.dept_id = d.id ) '人数' from dept d;12). 查询所有学生的选课情况, 展示出学生名称, 学号, 课程名称
select s.name , s.no , c.name from student s , student_course sc , course c where s.id = sc.studentid and sc.courseid = c.id ;6. 事务
6.1 事务简介
事务 是一组操作的集合,它是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务会把所有的操作作为一个整体一起向系统提交或撤销操作请求,即这些操作要么同时成功,要么同时失败。6.2 事务操作
数据准备
- drop table if exists account;
- create table account(
- id int primary key AUTO_INCREMENT comment 'ID',
- name varchar(10) comment '姓名',
- money double(10,2) comment '余额'
- ) comment '账户表';
- insert into account(name, money) VALUES ('张三',2000), ('李四',2000);
6.2.1 未控制事务
1). 测试正常情况
- select * from account where name = '张三';
- update account set money = money - 1000 where name = '张三';
- update account set money = money + 1000 where name = '李四';
2). 测试异常情况- -- 1. 查询张三余额
- select * from account where name = '张三';
- -- 2. 张三的余额减少1000
- update account set money = money - 1000 where name = '张三';
- 出错了....
- -- 3. 李四的余额增加1000
- update account set money = money + 1000 where name = '李四';
6.2.2 控制事务一
1). 查看/设置事务提交方式
- select @@autocommit;
- --手动提交
- set @@autocommit = 0;
2). 提交事务
commit;3). 回滚事务
rollback;注意:上述的这种方式,我们是修改了事务的自动提交行为 , 把默认的自动提交修改为了手动提交, 此时我们执行的 DML 语句都不会提交 , 需要手动的执行 commit 进行提交。6.2.3 控制事务二
1). 开启事务
start transaction 或 begin;2). 提交事务commit;3). 回滚事务rollback;6.3 事务四大特性
- 原子性(Atomicity):事务是不可分割的最小操作单元,要么全部成功,要么全部失败。
- 一致性(Consistency):事务完成时,必须使所有的数据都保持一致状态。
- 隔离性(Isolation):数据库系统提供的隔离机制,保证事务在不受外部并发操作影响的独立环境下运行。
- 持久性(Durability):事务一旦提交或回滚,它对数据库中的数据的改变就是永久的。
6.4 并发事务问题
1). 赃读:一个事务读到另外一个事务还没有提交的数据

2). 不可重复读:一个事务先后读取同一条记录,但两次读取的数据不同,称之为不可重复读。
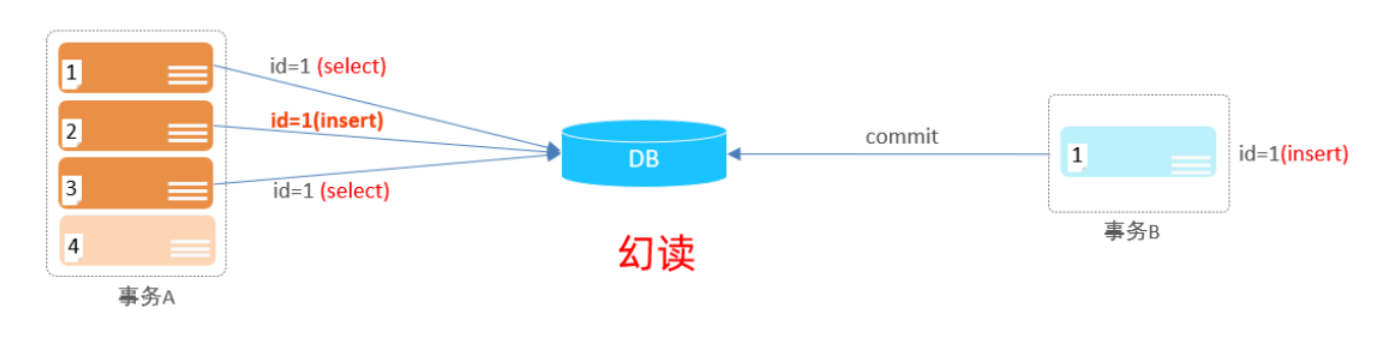
 3). 幻读:一个事务按照条件查询数据时,没有对应的数据行,但是在插入数据时,又发现这行数据已经存在,好像出现了 "幻影 " 。
3). 幻读:一个事务按照条件查询数据时,没有对应的数据行,但是在插入数据时,又发现这行数据已经存在,好像出现了 "幻影 " 。1). 查看事务隔离级别
select @@transaction_isolation;2). 设置事务隔离级别
- SET [ SESSION | GLOBAL ] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL { READ UNCOMMITTED |
- READ COMMITTED | REPEATABLE READ | SERIALIZABLE }
注意:事务隔离级别越高,数据越安全,但是性能越低。
-
相关阅读:
curl: (56) Recv failure: Connection reset by peer
pod原理
mysql自动备份脚本开发,包含自动清理备份文件机制
HM VNISEdit2.0.3修正版
每章一篇博客带你拿下吉林大学JAVAEE期末(六:EJB)
QT两个类之间使用信号槽
概率论_复习_第7章:参数估计
什么是ArchiMate?有优缺点和运用场景?
AUTOSAR规范与ECU软件开发(实践篇)10.5、Adaptive AUTOSAR平台新概念介绍
25. K个一组翻转链表
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45699456/article/details/132924705