-
栈与队列经典题目——用队列实现栈
本篇文章讲解栈和队列这一部分知识点的经典题目:用栈实现队列、用队列实现栈。对应的题号分别为:Leetcode.225——用队列实现栈,。
在对两个题目进行解释之前,先回顾以下栈和队列的特点与不同:
栈是一种特殊的线性表,并且只能在尾部进行插入、删除的操作。对于栈的实现,可以通过顺序表或者链表的思路来达成。但是,参考栈只能在尾部进行插入、删除操作的特点。一般采用顺序表进行实现。
队列也是一种特殊的线性表,只能在队尾进行插入操作,在队头进行删除操作。鉴于队列的这一性质,一般采用链表来实现队列。
1.Leetcode.225——用队列实现栈:
题目如下:

1.1 思路分析:
给出下列一个栈:

在栈中,遵从后进先出的原则。但是,本题要求是利用队列来实现栈。对于队列来说,出数据只能从队头进行。题目中要求利用两个队列来实现栈的功能,对于本功能,思路如下:
给定下面两个队列,分别命名为 ,
,

按照题目中的要求,需要移除元素
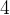 。对于队列来说,移除元素只能从队头进行。所以,先把
。对于队列来说,移除元素只能从队头进行。所以,先把 中的元素
中的元素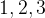 都移动到
都移动到 中。此时效果如下:
中。此时效果如下:
此时,再对
 进行一次取队头元素的操作即可。 下面为了方便表达,将
进行一次取队头元素的操作即可。 下面为了方便表达,将 简称为
简称为 ,
, 简称为
简称为
由上述分析可知。解决本题的关键就是在使用两个队列时,需要让一个队列中存储元素,另一个队列保持为空。当需要进行返回栈顶元素的操作时,再让为空的队列保存另一个队列中的前
 项元素。所以,
项元素。所以, 一个队列用于存储元素,一个用于保持空状态为了方便表达。下面,会默认创建两个结构体指针:
一个队列用于存储元素,一个用于保持空状态为了方便表达。下面,会默认创建两个结构体指针: ,来存储
,来存储 的地址,
的地址, 来存储
来存储 的地址。并在后续会针对二者谁为空进行判断。
的地址。并在后续会针对二者谁为空进行判断。(注:下面只给出各种给定功能的实现方法,在进行解题时,需要预先将编写好的xiami码复制到题目上方,本文采用一起学数据结构(6)——栈和队列_起床写代码啦!的博客-CSDN博客
中的队列)
1.2 各功能的实现:
1.2.1 栈的创建及初始化
 :
:前面说到,需要一个用于存储元素的队列,一个保持空状态的队列。但是对于二者谁为空,在后续的操作
 中进行判断即可。在本功能中不需要进行判断。代码如下:
中进行判断即可。在本功能中不需要进行判断。代码如下:- //创建队列
- typedef struct {
- Que q1;
- Que q2;
- } MyStack;
- //初始化队列,注意,返回值返回地址,需要采用malloc返回以保证返回时不会因为变量的局部性成为野指针
- MyStack* myStackCreate() {
- MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
- QueueInit(&obj->q1);
- QueueInit(&obj->q2);
- return obj;
- }
1.2.2 向栈中插入元素myStackPush:
为了保证
 为空,
为空, 不为空,所以,在向栈中插入元素时,需要向
不为空,所以,在向栈中插入元素时,需要向 中插入。在初始化这一步骤中,并没有分辨哪个队列为空,在本步骤并不需要明确知道哪个队列为空,只需要利用
中插入。在初始化这一步骤中,并没有分辨哪个队列为空,在本步骤并不需要明确知道哪个队列为空,只需要利用 函数判断队列
函数判断队列 是否为空,如果
是否为空,如果 为空,此时
为空,此时 为
为 ,直接向
,直接向 中进行插入,反之则向
中进行插入,反之则向 中插入,代码如下:
中插入,代码如下:- void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- {
- QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
- }
- else
- {
- QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
- }
- }
1.2.3 移除并返回栈顶元素 myStackPop:
在思路分析中,已经给出了该功能的实现方法。即,让
 指向的队列中的前
指向的队列中的前 项元素移动到
项元素移动到 所对应的元素。在移动元素之前,需要先判断
所对应的元素。在移动元素之前,需要先判断 哪个队列为空。方法如下:
哪个队列为空。方法如下:首先创建结构体指针
 ,
, 。让二者分别指向队列
。让二者分别指向队列 。利用
。利用 函数判断此时的
函数判断此时的 是否为空,若为空,则不做改变。若不为空,则令
是否为空,若为空,则不做改变。若不为空,则令 ,
, 中存储的地址交换。
中存储的地址交换。代码如下:
- int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
- Que* noempty = &obj->q1;
- Que* empty = &obj->q2;
- if(!QueueEmpty(empty))
- {
- noempty = &obj->q2;
- empty = &obj->q1;
- }
- }
再判断出
 哪个队列为
哪个队列为 ,哪个队列为
,哪个队列为 后,进行下一步。首先,利用
后,进行下一步。首先,利用 函数取出
函数取出 中的队头元素,再利用
中的队头元素,再利用 函数将
函数将 取出的元素插入到
取出的元素插入到 中。
中。题目要求,移除并且返回。所以需要额外创建一个变量
 用于存储栈顶元素。之后再利用
用于存储栈顶元素。之后再利用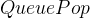 函数移除栈顶元素,最后返回
函数移除栈顶元素,最后返回 即可。代码如下:
即可。代码如下:
- int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
- Que* noempty = &obj->q1;
- Que* empty = &obj->q2;
- if(!QueueEmpty(empty))
- {
- noempty = &obj->q2;
- empty = &obj->q1;
- }
- while( QueueSize(noempty) > 1)
- {
- QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(noempty));
- QueuePop(noempty);
- }
- int Top = QueueFront(noempty);
- QueuePop(noempty);
- return Top;
- }
1.2.4 返回栈顶元素myStackTop:
栈顶元素所对应的位置就是队列的队尾。所以,只需要采用向栈中插入元素的方法,通过
 函数,对不满足
函数,对不满足 的队列(即非空队列)调用
的队列(即非空队列)调用 函数,返回函数的返回值即可。代码如下:
函数,返回函数的返回值即可。代码如下:- int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- {
- return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
- }
- else
- {
- return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
- }
- }
1.2.5 探空myStackEmpty:
原理较为简单,只给出代码:
- bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
- return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
- }
1.2.6 释放动态开辟的空间myStackFree:
代码如下:- void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
- QueueDestory(&obj->q1);
- QueueDestory(&obj->q2);
- free(obj);
- }
2.结果展示及题解代码总览:
2.1 结果展示:

2.2 题解代码总览:
- typedef int QDataType;
- typedef struct QueueNode
- {
- struct QueueNode* next;
- QDataType data;
- }QNode;
- typedef struct Queue
- {
- QNode* phead;
- QNode* tail;
- int size;
- }Que;
- //初始化
- void QueueInit(Que* ps);
- //销毁
- void QueueDestory(Que* ps);
- //插入元素
- void QueuePush(Que* ps, QDataType x);
- //删除元素
- void QueuePop(Que* ps);
- //取头部元素
- QDataType QueueFront(Que* ps);
- //取尾部元素
- QDataType QueueBack(Que* ps);
- //探空
- bool QueueEmpty(Que* ps);
- //求长度
- int QueueSize(Que* ps);
- void QueueInit(Que* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->phead = ps->tail = 0;
- ps->size = 0;
- }
- void QueuePush(Que* ps, QDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc");
- exit(-1);
- }
- newnode->next = NULL;
- newnode->data = x;
- if (ps->tail == NULL)
- {
- ps->phead = ps->tail = newnode;
- }
- else
- {
- ps->tail->next = newnode;
- ps->tail = newnode;
- }
- ps->size++;
- }
- void QueuePop(Que* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
- if (ps->phead->next == NULL)
- {
- free(ps->phead);
- ps->phead = ps->tail = NULL;
- }
- else
- {
- QNode* next = ps->phead->next;
- free(ps->phead);
- ps->phead = next;
- }
- ps->size--;
- }
- QDataType QueueFront(Que* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
- return ps->phead->data;
- }
- QDataType QueueBack(Que* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
- return ps->tail->data;
- }
- bool QueueEmpty(Que* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->phead == NULL;
- }
- int QueueSize(Que* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->size;
- }
- void QueueDestory(Que* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- QNode* cur = ps->phead;
- while (cur)
- {
- QNode* next = cur->next;
- free(cur);
- cur = next;
- }
- ps->phead = ps->tail = NULL;
- ps->size = 0;
- }
- //创建队列
- typedef struct {
- Que q1;
- Que q2;
- } MyStack;
- //初始化队列,注意,返回值返回地址,需要采用malloc返回以保证返回时不会因为变量的局部性成为野指针
- MyStack* myStackCreate() {
- MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
- QueueInit(&obj->q1);
- QueueInit(&obj->q2);
- return obj;
- }
- void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- {
- QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
- }
- else
- {
- QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
- }
- }
- //思路:将非空队列中前N-1项元素移到空队列中
- int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
- Que* noempty = &obj->q1;
- Que* empty = &obj->q2;
- if(!QueueEmpty(empty))
- {
- noempty = &obj->q2;
- empty = &obj->q1;
- }
- while( QueueSize(noempty) > 1)
- {
- QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(noempty));
- QueuePop(noempty);
- }
- int Top = QueueFront(noempty);
- QueuePop(noempty);
- return Top;
- }
- int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- {
- return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
- }
- else
- {
- return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
- }
- }
- bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
- return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
- }
- void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
- QueueDestory(&obj->q1);
- QueueDestory(&obj->q2);
- free(obj);
- }
-
相关阅读:
组合总和 (递归回溯+剪枝)
基于springboot+vue的前后端分离房屋租赁信息网站
CompletableFuture原理与实践-外卖商家端API的异步化
ubuntu20.04安装MySQL8、MySQL服务管理、mysql8卸载
wifi指纹室内定位系统 计算机竞赛
TI AM3352/54/59 工业核心板硬件说明书
Linux用户管理常用命令及对应配置文件
Linux:【1】Linux中的文件权限概念和相关命令
数据治理-数据管理角色
大模型Prompt-Tuning技术入门
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_76836325/article/details/132888836
