-
无脑014——linux系统,制作coco(json)格式数据集,使用mmdetection训练自己的数据集
电脑,linux,RTX 3090 cuda 11.2
1.制作coco(json)格式数据集

这里我们使用的标注软件是:labelimg
选择voc格式进行标注,标注之后使用以下代码,把voc格式转换成coco格式,注意最后的路径
这个代码只能一次生成一个train.json文件,需要再打标签,生成一个val.json文件,就可以训练了
:import sys import os import json import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET import glob START_BOUNDING_BOX_ID = 1 PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES = {"cat": 1, "person": 2} # If necessary, pre-define category and its id # PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES = {"aeroplane": 1, "bicycle": 2, "bird": 3, "boat": 4, # "bottle":5, "bus": 6, "car": 7, "cat": 8, "chair": 9, # "cow": 10, "diningtable": 11, "dog": 12, "horse": 13, # "motorbike": 14, "person": 15, "pottedplant": 16, # "sheep": 17, "sofa": 18, "train": 19, "tvmonitor": 20} def get(root, name): vars = root.findall(name) return vars def get_and_check(root, name, length): vars = root.findall(name) if len(vars) == 0: raise ValueError("Can not find %s in %s." % (name, root.tag)) if length > 0 and len(vars) != length: raise ValueError( "The size of %s is supposed to be %d, but is %d." % (name, length, len(vars)) ) if length == 1: vars = vars[0] return vars def get_filename_as_int(filename): try: filename = filename.replace("\\", "/") filename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(filename))[0] return int(filename) except: raise ValueError("Filename %s is supposed to be an integer." % (filename)) def get_categories(xml_files): """Generate category name to id mapping from a list of xml files. Arguments: xml_files {list} -- A list of xml file paths. Returns: dict -- category name to id mapping. """ classes_names = [] for xml_file in xml_files: tree = ET.parse(xml_file) root = tree.getroot() for member in root.findall("object"): classes_names.append(member[0].text) classes_names = list(set(classes_names)) classes_names.sort() return {name: i for i, name in enumerate(classes_names)} def convert(xml_files, json_file): json_dict = {"images": [], "type": "instances", "annotations": [], "categories": []} if PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES is not None: categories = PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES else: categories = get_categories(xml_files) bnd_id = START_BOUNDING_BOX_ID for xml_file in xml_files: tree = ET.parse(xml_file) root = tree.getroot() path = get(root, "path") if len(path) == 1: filename = os.path.basename(path[0].text) elif len(path) == 0: filename = get_and_check(root, "filename", 1).text else: raise ValueError("%d paths found in %s" % (len(path), xml_file)) ## The filename must be a number image_id = get_filename_as_int(filename) size = get_and_check(root, "size", 1) width = int(get_and_check(size, "width", 1).text) height = int(get_and_check(size, "height", 1).text) image = { "file_name": filename, "height": height, "width": width, "id": image_id, } json_dict["images"].append(image) ## Currently we do not support segmentation. # segmented = get_and_check(root, 'segmented', 1).text # assert segmented == '0' for obj in get(root, "object"): category = get_and_check(obj, "name", 1).text if category not in categories: new_id = len(categories) categories[category] = new_id category_id = categories[category] bndbox = get_and_check(obj, "bndbox", 1) xmin = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "xmin", 1).text) - 1 ymin = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "ymin", 1).text) - 1 xmax = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "xmax", 1).text) ymax = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "ymax", 1).text) assert xmax > xmin assert ymax > ymin o_width = abs(xmax - xmin) o_height = abs(ymax - ymin) ann = { "area": o_width * o_height, "iscrowd": 0, "image_id": image_id, "bbox": [xmin, ymin, o_width, o_height], "category_id": category_id, "id": bnd_id, "ignore": 0, "segmentation": [], } json_dict["annotations"].append(ann) bnd_id = bnd_id + 1 for cate, cid in categories.items(): cat = {"supercategory": "none", "id": cid, "name": cate} json_dict["categories"].append(cat) os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(json_file), exist_ok=True) json_fp = open(json_file, "w") json_str = json.dumps(json_dict) json_fp.write(json_str) json_fp.close() if __name__ == "__main__": import argparse parser = argparse.ArgumentParser( description="Convert Pascal VOC annotation to COCO format." ) parser.add_argument("xml_dir", nargs='?',default=r'G:\bsh\dataset\dingzi\Annotations',help="Directory path to xml files.", type=str) parser.add_argument("json_file",nargs='?', default=r'G:\bsh\dataset\dingzi\coco_json\train.json',help="Output COCO format json file.", type=str) args = parser.parse_args() xml_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(args.xml_dir, "*.xml")) # If you want to do train/test split, you can pass a subset of xml files to convert function. print("Number of xml files: {}".format(len(xml_files))) convert(xml_files, args.json_file) print("Success: {}".format(args.json_file))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
2.配置mmdet环境
去github mmdet官网下载zip文件,然后解压
https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetectionconda create -n xcb_mmdet31 python=3.8 -y conda activate xcb_mmdet31 conda install pytorch==1.11.0 torchvision==0.12.0 torchaudio==0.11.0 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch pip install -U openmim #最后安装成功 0.3.9 mim install mmengine #最后安装成功 0.7.1 mim install "mmcv>=2.0.0" # 2.0.0rc4 cd mmdetection pip install -v -e . #最后安装成功 3.1.0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
可以使用代码测试环境安装是否成功:
mim download mmdet --config rtmdet_tiny_8xb32-300e_coco --dest . python demo/image_demo.py demo/demo.jpg rtmdet_tiny_8xb32-300e_coco.py --weights rtmdet_tiny_8xb32-300e_coco_20220902_112414-78e30dcc.pth --device cpu- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
然后修改配置文件
此次准备使用的是RTMDet模型3.修改配置文件
3.1 修改文件1
修改configs/rtmdet/rtmdet_l_8xb32-300e_coco.py文件中的32行
num_classes=1,- 1
- 2
3.2 修改文件2
修改configs/base/datasets/coco_detection.py文件中
第3行data_root = 'data/dingzi/'- 1
- 2
第46行47行
ann_file='coco_json/train.json', data_prefix=dict(img='images/train/'),- 1
- 2
- 3
第60行第61行
ann_file='coco_json/val.json', data_prefix=dict(img='images/val/'),- 1
- 2
- 3
第69行
ann_file=data_root + 'coco_json/val.json',- 1
- 2
3.3 修改文件3
修改mmdet/datasets/coco.py文件
第19行('dingzi', 'heidong'),- 1
- 2
3.4 修改文件4
mmdet/evaluation/functional/class_names.py
第75行'dingzi', 'heidong'- 1
- 2
3.5修改完成,重新编译
执行
python setup.py install- 1
4.开始训练
python tools/train.py configs/rtmdet/rtmdet_l_8xb32-300e_coco.py --work-dir output- 1
- 2
训练结束,显示结果:
09/08 17:45:03 - mmengine - INFO - Epoch(val) [300][1/1] coco/bbox_mAP: 0.3930 coco/bbox_mAP_50: 0.8810 coco/bbox_mAP_75: 0.2470 coco/bbox_mAP_s: 0.3030 coco/bbox_mAP_m: 0.4620 coco/bbox_mAP_l: -1.0000 data_time: 0.0520 time: 0.1187- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
因为我只使用了3张图片,所以效果不好,接下来进行推理测试
5.推理测试
python demo/image_demo.py data/dingzi/images/train/ output/rtmdet_l_8xb32-300e_coco.py --weights output/epoch_300.pth- 1
- 2
效果达到预期
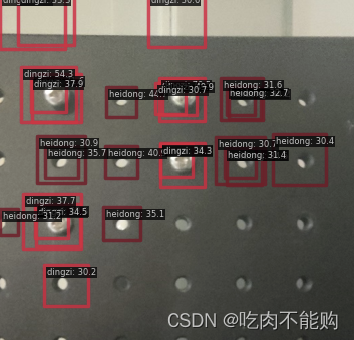 接下来,要继续研究如何使用训练后的模型进行预测标签的保存选项,自动标注
接下来,要继续研究如何使用训练后的模型进行预测标签的保存选项,自动标注
先去吃饭 -
相关阅读:
【前端】Ajax
Android 性能优化—— 启动优化提升60%
tictoc例子理解10-13
Linux C获取本机IP
SpringBoot怎么自定义一个Starter ?
js制作的模拟超逼真下雨效果
EL&JSTL:JSTL总结
脑鸣和耳鸣哪个厉害?
在Springboot项目中使用Redis提供给Lua的脚本
ubuntu:vi 编辑器修改文件的基本操作指令
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44298961/article/details/132755910
