-
LeetCode //C - 129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
You are given the root of a binary tree containing digits from 0 to 9 only.
Each root-to-leaf path in the tree represents a number.
For example, the root-to-leaf path 1 -> 2 -> 3 represents the number 123.
Return the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers. Test cases are generated so that the answer will fit in a 32-bit integer.A leaf node is a node with no children.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 25
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.Example 2:
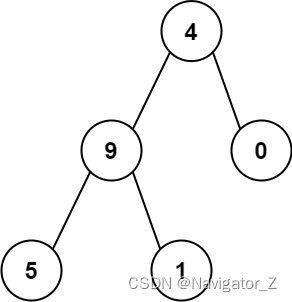
Input: root = [4,9,0,5,1]
Output: 1026
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495.
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491.
The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40.
Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 1000].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 9
- The depth of the tree will not exceed 10.
From: LeetCode
Link: 129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
Solution:
Ideas:
-
Use a recursive helper function to traverse the tree.
-
In the helper function:
- If the current node is null, return 0.
- Compute the current number by multiplying the parent’s number by 10 and adding the current node’s value.
- If the current node is a leaf node (both left and right children are null), return the current number.
- Otherwise, return the sum of the helper function’s results for the left and right children.
Code:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ int helper(struct TreeNode* root, int currentNumber) { if (!root) { return 0; } // Compute the current number currentNumber = currentNumber * 10 + root->val; // If it's a leaf node if (!root->left && !root->right) { return currentNumber; } return helper(root->left, currentNumber) + helper(root->right, currentNumber); } int sumNumbers(struct TreeNode* root) { return helper(root, 0); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
-
相关阅读:
C语言之预处理,头文件
Docker常用命令
2535. 数组元素和与数字和的绝对差
Java final关键字具有什么功能呢?
【机器学习 & PCA】未完成(Bug || 问题 待解决)...
【k8s】kube-proxy 工作模式
linux部署校园网绕过53端口服务脚本
【错误记录】Uncaught TypeError: m.nodeName.toLowerCase is not a function
JSP技术基础(1)(标准语法)
Cobbler 服务搭建及Cobbler api 使用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/navicheung/article/details/132787816
