-
机器学习——决策树与随机森林
机器学习——决策树与随机森林
前言
决策树和随机森林都是常见的机器学习算法,用于分类和回归任务,本文将对这两种算法进行介绍。
一、决策树
1.1. 原理
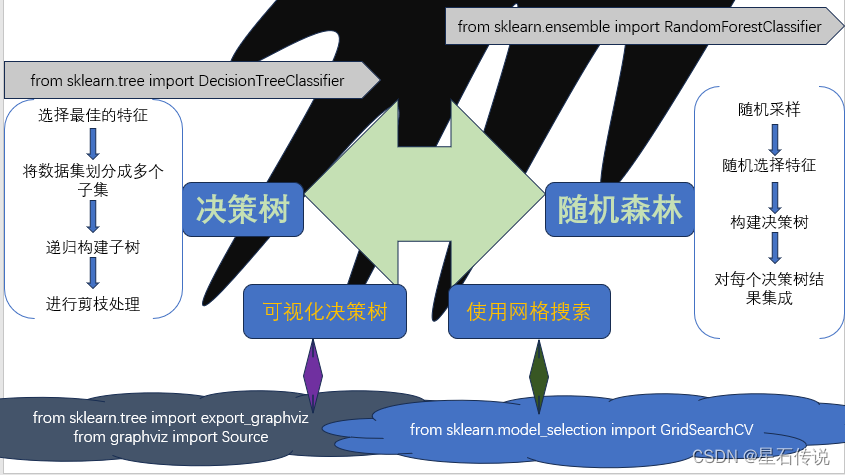
决策树算法是一种基于树结构的分类和回归算法。它通过对数据集进行递归地二分,选择最佳的特征进行划分,直到达到终止条件。
决策树的每个内部节点表示一个特征,根据测试结果进行分类,每个叶子节点表示一个类别或一个回归值。
决策树的构建可以通过以下几个步骤来实现:-
特征选择:根据某个评价指标(如信息增益、基尼不纯度等),选择最佳的特征作为当前节点的划分特征。(即哪个特征带来最多的信息变化幅度,就选择哪一个特征来分类)
-
划分数据集:根据选择的特征,将数据集划分成多个子集,每个子集对应一个分支。对于离散特征,可以根据特征值的不同进行划分;对于连续特征,可以选择一个阈值进行划分。
-
递归构建子树:对每个子集递归地构建子树,直到所有子集被正确分类或满足终止条件。常见的终止条件有:达到最大深度、样本数量小于阈值、节点中的样本属于同一类别等。
-
避免过拟合:对决策树进行剪枝处理。剪枝可以分为前剪枝和后剪枝: 前剪枝是在构建树的过程中进行剪枝,通过设定一个阈值,信息熵减小的数量小于这个值则停止创建分支;后剪枝则是在决策树构建完成后,对节点检查其信息熵的增益来判断是否进行剪枝。
还可以通过控制决策树的最大深度(max_depth)
1.2. 代码实现
import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import make_moons from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier #生成数据集 np.random.seed(41) raw_data = make_moons(n_samples=2000, noise=0.25, random_state=41) data = raw_data[0] target = raw_data[1] # 训练决策树分类模型 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, target) classifer = DecisionTreeClassifier() classifer.fit(x_train, y_train) #计算测试数据集在决策树模型上的准确率得分 print(classifer.score(x_test, y_test)) 0.916 # max_depth 树的最大深度,默认为None classifer = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=6) classifer.fit(x_train, y_train) print(classifer.score(x_test, y_test)) 0.934 # min_samples_leaf 叶节点所需的最小样本数,默认为1 classifer = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=6, min_samples_leaf=6) classifer.fit(x_train, y_train) print(classifer.score(x_test, y_test)) 0.938 # min_impurity_decrease 划分节点时的最小信息增益 def m_score(value): model = DecisionTreeClassifier(min_impurity_decrease=value) model.fit(x_train, y_train) train_score = model.score(x_train, y_train) test_score = model.score(x_test, y_test) return train_score, test_score values = np.linspace(0,0.01,50) score = [m_score(value) for value in values ] train_s = [s[0] for s in score] test_s = [s[1] for s in score] best_index = np.argmax(test_s) print(test_s[best_index]) print(values[best_index]) plt.plot(train_s,label = "train_s") plt.plot(test_s,label = "test_s") plt.legend() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51

从以上代码中可以看出在不同参数的选择情况下,准确率(分类器预测正确的样本数量与总样本数量的比例)得分是不同的,越接近1表示模型的预测性能越好
1.3. 网格搜索
可以使用网格搜索获得最优的模型参数:
# 使用网格搜索获得最优的模型参数 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV classifer = DecisionTreeClassifier() params = { "max_depth": np.arange(1, 10), "min_samples_leaf": np.arange(1, 20), "min_impurity_decrease": np.linspace(0,0.4,50), "criterion" : ("gini","entropy") } grid_searchcv = GridSearchCV(classifer, param_grid=params, scoring="accuracy", cv=5) # scoring指定模型评估指标,例如:'accuracy'表示使用准确率作为评估指标。 grid_searchcv.fit(x_train, y_train) print(grid_searchcv.best_params_) print(grid_searchcv.best_score_) #print(grid_searchcv.cv_results_) print(grid_searchcv.best_index_) print(grid_searchcv.best_estimator_) best_clf = grid_searchcv.best_estimator_ best_clf.fit(x_train,y_train) print(best_clf.score(x_test,y_test)) #结果: {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 8, 'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0, 'min_samples_leaf': 16} 0.9286666666666668 15215 DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy', max_depth=8, min_samples_leaf=16) 0.94- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
1.4. 可视化决策树
得到可视化决策树文件:
df = pd.DataFrame(data = data,columns=["x1","x2"]) from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz from graphviz import Source dot_data = export_graphviz(best_clf, out_file=None, feature_names=df.columns) graph = Source(dot_data) graph.format = 'png'file graph.render(filename='file_image', view=True)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

二、随机森林算法
2.1. 原理
随机森林是一种集成学习方法,它通过构建多个决策树来进行分类或回归,
随机森林的基本原理:-
随机采样:从原始训练集中随机选择一定数量的样本,作为每个决策树的训练集。
-
随机特征选择:对于每个决策树的每个节点,从所有特征中随机选择一部分特征进行评估,选择最佳的特征进行划分。
-
构建决策树:根据随机采样和随机特征选择的方式,构建多个决策树。
-
预测:对于分类问题,通过投票或取平均值的方式,将每个决策树的预测结果进行集成;对于回归问题,将每个决策树的预测结果取平均值。
随机森林函数中的超参数:
-
n_estimators:它表示随机森林中决策树的个数。
-
min_samples_split:内部节点分裂所需的最小样本数
-
min_samples_leaf:叶节点所需的最小样本数
-
max_features:每个决策树考虑的最大特征数量
-
n_jobs :表示允许使用处理器的数量
-
criterion :gini 或者entropy (default = gini)
-
random_state:随机种子
2.2. 代码实现
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.datasets import make_moons from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier #训练随机森林分类模型 np.random.seed(42) raw_data = make_moons(n_samples= 2000,noise= 0.25,random_state=42) data,target = raw_data[0],raw_data[1] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, target,random_state=42) classfier = RandomForestClassifier(random_state= 42) classfier.fit(x_train,y_train) score = classfier.score(x_test,y_test) print(score) 0.93 #网格搜索获取最优参数 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV param_grids = { "criterion": ["gini","entropy"], "max_depth":np.arange(1,10), "min_samples_leaf":np.arange(1,10), "max_features": np.arange(1,3) } grid_search = GridSearchCV(RandomForestClassifier(),param_grid=param_grids,n_jobs= 1,scoring="accuracy",cv=5) grid_search.fit(x_train,y_train) print(grid_search.best_params_) #最优的参数 print(grid_search.best_score_) #最好的得分 best_clf = grid_search.best_estimator_ #最优的模型 print(best_clf) best_clf.fit(x_train,y_train) print(best_clf.score(x_test,y_test)) #查看测试集在最优模型上的得分 #结果: {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 9, 'max_features': 1, 'min_samples_leaf': 7} 0.9506666666666665 RandomForestClassifier(criterion='entropy', max_depth=9, max_features=1, min_samples_leaf=7) 0.932- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
三、补充(过拟合与欠拟合)
过拟合指的是模型在训练集上表现得很好,但在测试集或新数据上表现不佳的情况。
过拟合通常发生在模型过于复杂或训练数据过少的情况下欠拟合指的是模型无法很好地拟合训练集,导致在训练集和测试集上的误差都很高。
欠拟合通常发生在模型过于简单或训练数据过于复杂的情况下
总结
总之,决策树和随机森林都是基于树结构的机器学习算法,具有可解释性和特征选择的能力。随机森林是多个决策树的集成模型,引入了随机性并通过投票或平均来得出最终预测结果,可以有效降低噪声干扰,提高模型的准确性与稳定性,但是增加了计算量。
锦帽貂裘,千骑卷平冈
–2023-9-1 筑基篇
-
-
相关阅读:
Zabbix 5.0部署(centos7+server+MySQL+Apache)
MATLAB算法实战应用案例精讲-【集成算法】集成学习模型Bagging(附Python和R语言代码)
java计算机毕业设计-食材采购平台-源码+数据库+系统+lw文档+mybatis+运行部署
Unity开发之观察者模式(事件中心)
Linux多线程服务端编程:使用muduo C++网络库 学习笔记 第二章 线程同步精要
VoLTE基础自学系列 | VoLTE短消息业务概述暨SMS over IP概述
HTML5学习系列之响应式图像
C语言编程陷阱(一)
springboot+电子族谱信息系统 毕业设计-附源码161714
软件打不开,文件找不到了,如何找到隐藏文件?(windows和mac解决方案)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_78630677/article/details/132545133
