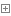
论文信息 论文标题:Generalized Domain Adaptation with Covariate and Label Shift CO-ALignment 论文作者:Shuhan Tan, Xingchao Peng, Kate Saenko 1 摘要 提出问题:标签偏移;
解决方法:
原型分类器模拟类特征分布,并使用 Minimax Entropy 实现条件特征对齐;
使用高置信度目标样本伪标签实现标签分布修正;
2 介绍 2.1 当前工作 假设条件标签分布不变 p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) " role="presentation">p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) " role="presentation">p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) " role="presentation">p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) p ( y ) ≠ q ( y )
假设不成立的原因:
场景不同,标签跨域转移 p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) " role="presentation">p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) 如果存在标签偏移,则当前的 UDA 工作性能显著下降; 一个合适的 UDA 方法应该能同时处理协变量偏移和标签偏移;
2.2 本文工作 本文提出类不平衡域适应 (CDA),需要同时处理 条件特征转移 和 标签转移 。
具体来说,除了协变量偏移假设 p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) " role="presentation">p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) " role="presentation">p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) p ( x ∣ y ) ≠ q ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">p ( x ∣ y ) ≠ q ( x ∣ y ) p ( x ∣ y ) ≠ q ( x ∣ y ) p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) " role="presentation">p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) p ( y ) ≠ q ( y )
CDA 的主要挑战:
标签偏移阻碍了主流领域自适应方法的有效性,这些方法只能边缘对齐特征分布; 在存在标签偏移的情况下,对齐条件特征分布 p ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">p ( x ∣ y ) p ( x ∣ y ) q ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">q ( x ∣ y ) q ( x ∣ y ) 当一个或两个域中的数据在不同类别中分布不均时,很难训练无偏分类器;
CDA 概述:
3 问题定义 In Class-imbalanced Domain Adaptation, we are given a source domain D S = { ( x i s , y i s ) i = 1 N s } D S = { ( x s i , y s i ) N s i = 1 } D S = { ( x i s , y i s ) i = 1 N s } N s N s N s D T = { ( x i t ) i = 1 N t } D T = { ( x t i ) N t i = 1 } D T = { ( x i t ) i = 1 N t } N t N t N t p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) " role="presentation">p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) p ( y ∣ x ) = q ( y ∣ x ) p ( x ∣ y ) ≠ q ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">p ( x ∣ y ) ≠ q ( x ∣ y ) p ( x ∣ y ) ≠ q ( x ∣ y ) p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) " role="presentation">p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) p ( x ) ≠ q ( x ) p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) " role="presentation">p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) p ( y ) ≠ q ( y ) D S D S D S D T D T D T y = θ ( x ) " role="presentation">y = θ ( x ) y = θ ( x ) ϵ T ( θ ) = Pr ( x , y ) ∼ q [ θ ( x ) ≠ y ] " role="presentation">ϵ T ( θ ) = Pr ( x , y ) ∼ q [ θ ( x ) ≠ y ] ϵ T ( θ ) = Pr ( x , y ) ∼ q [ θ ( x ) ≠ y ]
4 方法 4.1 整体框架
4.2 用于特征转移的基于原型的条件对齐 目的:对齐 p ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">p ( x ∣ y ) p ( x ∣ y ) q ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">q ( x ∣ y ) q ( x ∣ y )
步骤:首先使用原型分类器(基于相似度)估计 p ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">p ( x ∣ y ) p ( x ∣ y ) minimax entropy " role="presentation">minimax entropy minimax entropy q ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">q ( x ∣ y ) q ( x ∣ y )
4.2.1 原型分类器 原因:基于原型的分类器在少样本学习设置中表现良好,因为在标签偏移的假设下中,某些类别的设置频率可能较低;
python
class Predictor_deep_latent (nn.Module ):def __init__ (self, in_dim = 1208 , num_class = 2 , temp = 0.05 ):super (Predictor_deep_latent, self).__init__()
512
False )
def forward (self, x, reverse=False , eta=0.1 ):if reverse:
return feat, logit
View Code 源域上的样本使用交叉熵做监督训练:
L S C = E ( x , y ) ∈ D S L c e ( h ( x ) , y ) ( 1 ) " role="presentation">L S C = E ( x , y ) ∈ D S L c e ( h ( x ) , y ) ( 1 ) L S C = E ( x , y ) ∈ D S L c e ( h ( x ) , y ) ( 1 )
样本 x " role="presentation">x x i " role="presentation">i i x " role="presentation">x x w i w i w i x " role="presentation">x x W " role="presentation">W W w i w i w i p " role="presentation">p p p ( x ∣ y = i ) " role="presentation">p ( x ∣ y = i ) p ( x ∣ y = i )
4.2.2 通过 Minimax Entropy 实现条件对齐 目标域缺少数据标签,所以使用 Eq.1 " role="presentation">Eq.1 Eq.1
解决办法:
将每个源原型移动到更接近其附近的目标样本; 围绕这个移动的原型聚类目标样本;
因此,提出 熵极小极大 实现上述两个目标。
具体来说,对于输入网络的每个样本 x t ∈ D T x t ∈ D T x t ∈ D T
L H = E x ∈ D T H ( x ) = − E x ∈ D T ∑ i = 1 c h i ( x ) log h i ( x ) ( 2 ) " role="presentation">L H = E x ∈ D T H ( x ) = − E x ∈ D T ∑ c i = 1 h i ( x ) log h i ( x ) ( 2 ) L H = E x ∈ D T H ( x ) = − E x ∈ D T ∑ i = 1 c h i ( x ) log h i ( x ) ( 2 )
通过在对抗过程中对齐源原型和目标原型来实现条件特征分布对齐:
训练 C " role="presentation">C C L H L H L H 训练 F " role="presentation">F F L H L H L H
4.3 标签转移的类平衡自训练 由于源标签分布 p ( y ) " role="presentation">p ( y ) p ( y ) q ( y ) " role="presentation">q ( y ) q ( y ) D S D S D S C " role="presentation">C C D T D T D T
为解决这个问题,本文使用[19]中的方法进行自我训练来估计目标标签分布并细化决策边界。自训练为了细化决策边界,本文建议通过自训练来估计目标标签分布。 我们根据分类器 C " role="presentation">C C y " role="presentation">y y p ( x ∣ y " role="presentation">p ( x ∣ y p ( x ∣ y q ( x ∣ y ) " role="presentation">q ( x ∣ y ) q ( x ∣ y ) q ( y ) " role="presentation">q ( y ) q ( y ) q ( y ) " role="presentation">q ( y ) q ( y ) C " role="presentation">C C
为了获得高置信度的伪标签,对于每个类别,本文选择属于该类别的具有最高置信度分数的目标样本的前 k " role="presentation">k k h ( x ) " role="presentation">h ( x ) h ( x ) x " role="presentation">x x ( x , y ) " role="presentation">( x , y ) ( x , y ) h ( x ) " role="presentation">h ( x ) h ( x ) k " role="presentation">k k m = 1 " role="presentation">m = 1 m = 1 m = 0 " role="presentation">m = 0 m = 0 D ^ T = { ( x i t , y ^ i t , m i ) i = 1 N t } D ^ T = { ( x t i , y ^ t i , m i ) N t i = 1 } D ^ T = { ( x i t , y ^ i t , m i ) i = 1 N t } D ^ T D ^ T D ^ T C " role="presentation">C C
L S T = L S C + E ( x , y ^ , m ) ∈ D ^ T L c e ( h ( x ) , y ^ ) ⋅ m " role="presentation">L S T = L S C + E ( x , y ^ , m ) ∈ D ^ T L c e ( h ( x ) , y ^ ) ⋅ m L S T = L S C + E ( x , y ^ , m ) ∈ D ^ T L c e ( h ( x ) , y ^ ) ⋅ m
通常,用 k 0 = 5 " role="presentation">k 0 = 5 k 0 = 5 k " role="presentation">k k k step = 5 " role="presentation">k step = 5 k step = 5 k max = 30 " role="presentation">k max = 30 k max = 30
Note:本文还对源域数据使用了平衡采样的方法,使得分类器不会偏向于某一类。
4.4 训练目标 总体目标:
C ^ = arg min C L S T − α L H F ^ = arg min F L S T + α L H C ^ = arg min C L S T − α L H F ^ = arg min F L S T + α L H C ^ = arg min C L S T − α L H F ^ = arg min F L S T + α L H
5 总结 略
__EOF__
-
本文作者: Blair 本文链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/BlairGrowing/p/17332967.html 关于博主: I am a good person 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处! 声援博主: 如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐 】