-
List——顺序表与链表(二)
前言
上一篇文章中,介绍了List接口以及ArrayList的使用,并且进行了简单的模拟实现,通过源码知道,ArrayList底层使用数组元素来存储元素。但是由于其底层是一段连续空间,当在ArrayList任意位置插入或者删除元素时,就需要将后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,时间复杂度为O(n),效率比较低,且频繁的扩容会导致不必要的内存空间浪费,因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入和删除比较多的场景。因此:java集合中又引入了LinkedList,即链表结构。
一、链表概念及结构
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
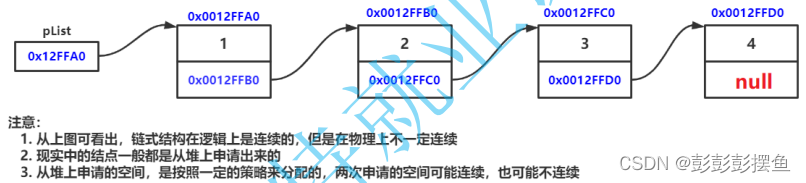
链表的结构非常多样,单向双向、带头或不带头、循环或非循环。这几种情况组合起来就有八种链表结构:
1.单向或者双向

2.带头或不带头
3.循环或非循环
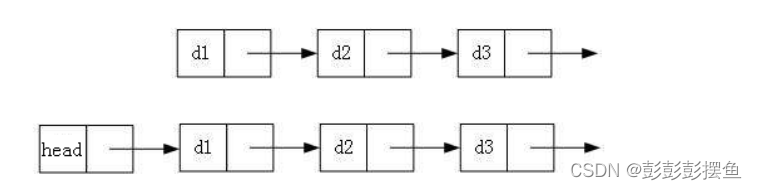
无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
二、LinkedList与链表
1.什么是LinkedList
LinkedList的底层是双向链表结构,由于链表没有将元素存储在连续的空间中,元素存储在单独的节点中,然后通过引用将节点连接起来了,因此在在任意位置插入或者删除元素时,不需要搬移元素,效率比较高。但是当需要查询时,就需要按图索骥按部就班的一个一个查,查询效率不高,这个后面总结对比时再详细说明。

说明:- LinkedList实现了List接口
- LinkedList的底层使用了双向链表
- LinkedList没有实现RandomAccess接口,因此LinkedList不支持随机访问
- LinkedList的任意位置插入和删除元素时效率比较高,时间复杂度为O(1)
- LinkedList比较适合任意位置插入的场景
2.LinkedList的常用方法
方法 解释 boolean add(E e 尾插 e void add(int index, E element 将e插入到index位置 boolean addAll(Collection c) 尾插c中的元素 E remove(int index) 删除index位置的元素 boolean remove(Object o) 删除遇到的第一个o E get(int index) 获取下标index位置的元素 E set(int index, E element) 将下标index位置的元素修改为element并返回修改之前的元素 void clear() 清空 boolean contains(Object o) 判断o是否在链表中 int indexOf(Object o) 返回第一个遇到的o的下标 int lastIndexOf(Object o) 返回最后一个o的下标 List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) 截取部分list void display() 打印链表 3.链表的遍历
遍历链表的几种方式:
public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插 list.add(2); list.add(3); list.add(4); list.add(5); list.add(6); list.add(7); System.out.println(list.size()); // foreach遍历 for (int e:list) { System.out.print(e + " "); } System.out.println(); // 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历 ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ System.out.print(it.next()+ " "); } System.out.println(); // 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历 ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size()); while (rit.hasPrevious()){ System.out.print(rit.previous() +" "); } System.out.println(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
三.实现自己的LinkedList
首先需要定义自己的MyList接口,接口中声明一系列方法后在MyLinkedList中实现,我们还需要定义一个结点类,这里我们实现的是带有前驱和后继的双向结点,以实现双向链表。具体实现如下:
MyList接口:
public interface MyList { /** * 返回链表中元素个数 * @return */ int size(); /** * 尾插 * @param e 将元素e尾插到线性表 * @return 返回true */ boolean add(Long e); /** * 将元素e插入到指定节点处 * @param index * @param e */ void add (int index,Long e); Long remove(int index); /** * 删除值为e的元素 * @param e 需要删除的元素 * @return 成功返回true 失败返回false */ boolean remove(Long e); /** * 获取index处元素的值 * @param index 数组下标 * @return 该下标处的元素值 */ Long get(int index); /** * 修改元素 * @param index [0,size) * @param e 修改后的元素 * @return 原来index处的元素 */ Long set(int index,Long e); /** * 从前往后,返回第一次遇到e的下标 * @param e 目标元素 * @return 返回在第几个 */ int indexOf(Long e); /** * 从后向前 * @param e * @return */ int lastIndexOf(Long e); /** * 线性表中是否包含e * @param e * @return */ boolean contains(Long e); /** * 打印顺序表 */ void display(); /** * 判空 * @return */ boolean isEmpty(); /** * 清空 */ void clear(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
定义结点类
public class MyNode { Long val; MyNode next; //指向后继节点,尾节点的后继是null MyNode prev; //指向前驱节点,头节点的前驱是null public MyNode() { //无参构造方法 } public MyNode(Long val) { //需传入值的有参构造 this.val = val; this.next = null; this.prev = null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
MyLinkedList实现类:
public class MyLinkedList implements MyList { //需要维护三个属性:链表的头节点、链表的尾节点、链表中元素个数 private MyNode head; private MyNode last; private int size; //构造方法,构造一个空的链表 public MyLinkedList() { this.head = this.last = null; this.size = 0; } @Override public int size() { return size; } @Override //链表的尾插 public boolean add(Long e) { MyNode node = new MyNode(e); //将元素e放入节点中 node.next = null; //分情况讨论 if (size > 0) { this.last.next = node; //这一步将尾节点的后继指向新节点 (链接) node.prev = this.last; //这一步让新节点的前驱指向之前的尾节点尾 (链接完成) this.last = node; //这一步让新节点成为新的尾节点 (善后) } else { node.prev = null; this.last = this.head = node; } this.size++; //涉及的增删的操作必须修改size! return true; } //链表的头插 private boolean addFirst(Long e) { MyNode node = new MyNode(e); //将元素e放入节点中 node.next = null; if (size > 0) { this.head.prev = node; node.next = this.head; this.head = node; } else { this.head = this.last = node; } return true; } @Override public void add(int index, Long e) { if (index < 0 || index > size) { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("下标越界"); } if (size == 0) { add(e); return; } if (size == 1) { if (index == 0) { addFirst(e); } else { add(e); } return; } if (index == 0) { addFirst(e); return; } else if (index == size) { add(e); return; } MyNode prevNode = this.head; for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { prevNode = prevNode.next; } MyNode curnode = prevNode.next; MyNode node = new MyNode(e); prevNode.next = node; curnode.prev = node; node.prev = prevNode; node.next = curnode; size++; } @Override public Long remove(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("下标异常"); } if (size == 1) { Long e = this.head.val; this.head = this.last = null; this.size = 0; return e; } if (index == 0) { Long e = this.head.val; this.head = this.head.next; this.head.prev = null; size--; return e; } if (index == size - 1) { Long e = this.head.val; this.last = this.last.prev; this.last.next = null; size--; return e; } //走到这儿 说明链表中至少有两个元素 MyNode curNode = this.head; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { curNode = curNode.next; } Long e = curNode.val; // MyNode prevNode = curNode.prev; // MyNode nextNode = curNode.next; // // // 修改引用关系,删除 curNode // prevNode.next = nextNode; // nextNode.prev = prevNode; curNode.prev.next = curNode.next; curNode.next.prev = curNode.prev; size--; return e; } @Override public boolean remove(Long e) { MyNode curNode = this.head; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (curNode.val.equals(e)) { //找到元素e后判断其所在位置 if (i == 0) { this.head = this.head.next; if (this.head != null) { this.head.prev = null; } else { this.last = null; } size--; return true; } if (i == size - 1) { this.last = this.last.prev; this.last.next = null; size--; return true; } //走到这儿说明在中间位置,既不是头删,也不是尾删 MyNode prevNode = curNode.prev; MyNode nextNode = curNode.next; prevNode.next = nextNode; nextNode.prev = prevNode; size--; return true; } curNode = curNode.next; } return false; } @Override public Long get(int index) { if(index<0||index>size-1){ throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("下标有误"); } MyNode cur=this.head; for (int i = 0; i <index ; i++) { cur=cur.next; } return cur.val; } @Override public Long set(int index, Long e) { if(index<0||index>size-1){ throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("下标有误"); } MyNode cur=this.head; for (int i = 0; i <index ; i++) { cur=cur.next; } Long olde=cur.val; cur.val=e; return olde; } @Override public int indexOf(Long e) { int i = 0; MyNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val.equals(e)) { return i; } i++; cur = cur.next; } return -1; } @Override public int lastIndexOf(Long e) { int i = size-1; MyNode cur = this.last; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val.equals(e)) { return i; } i--; cur = cur.prev; } return -1; } @Override public boolean contains(Long e) { // MyNode cur=this.head; // for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { // if(cur.val.equals(e)){ // return true; // } // cur=cur.next; // } // return false; return indexOf(e)!=-1; } @Override //打印链表 public void display() { MyNode cur=this.head; while (cur!=null){ System.out.print(cur.val+" "); cur=cur.next; } } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return size==0; } @Override public void clear() { this.head=this.last=null; this.size=0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
四.ArrayList和LinkedList的区别与优缺点
不同点 ArrayList LinkedList 存储空间上 物理上一定连续 逻辑上连续,物理上不一定连续 随机访问(查询) 支持O(1) 不支持O(N) 插入 需要搬移元素,效率低O(N) 只需要修改引用指向的方向,时间复杂度O(1) 多次插入 空间不够时需要扩容 没有容量的概念 应用场景 元素高效存储+频繁访问(改查) 任意位置的频繁插入删除(增删)
总结
以上两篇内容将ArrayList以及LinkedList通过自己的代码实现了简单的实现,也将其中常用的方法进行了罗列以及讲解,并对两者进行了归纳总结,总的来说就是增删频繁用链表,改查频繁用顺序表两者各有优缺点。后续将会更新与其相关的力扣题。
-
相关阅读:
BP神经网络算法基本原理,bp神经网络算法详解
Linux中的shell编程
Java内存马相关文章
Day83:服务攻防-开发组件安全&Jackson&FastJson各版本&XStream&CVE环境复现
Unity2021发布微信小游戏步骤(附带工具和源码)
Swift 周报 第十三期
基于图像识别的跌倒检测
How To Install and Configure VNC Server on Ubuntu 20.04
零售业的技术演变:远程支持软件的作用
配置Nginx和其他应用的HTTPS访问
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Xx_bjpyy/article/details/128166364
