-
知识蒸馏算法汇总
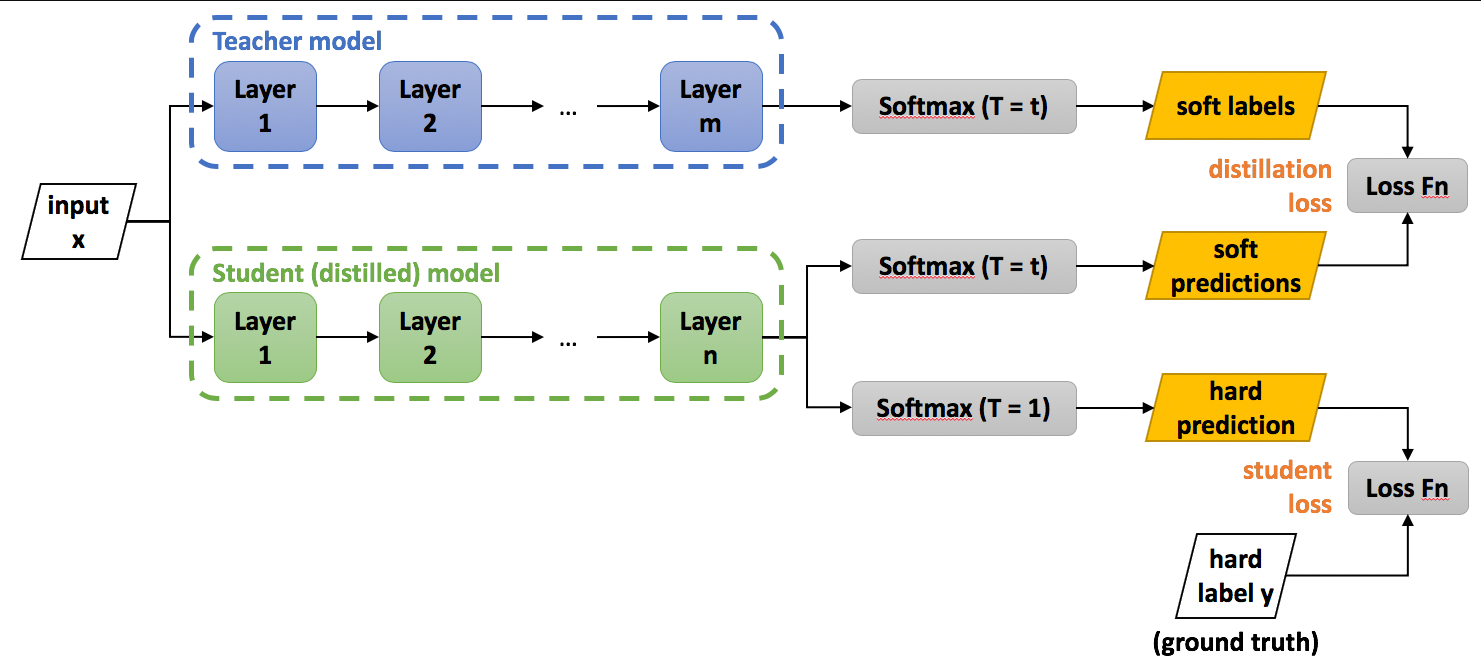
知识蒸馏有两大类:一类是logits蒸馏,另一类是特征蒸馏。logits蒸馏指的是在softmax时使用较高的温度系数,提升负标签的信息,然后使用Student和Teacher在高温softmax下logits的KL散度作为loss。中间特征蒸馏就是强迫Student去学习Teacher某些中间层的特征,直接匹配中间的特征或学习特征之间的转换关系。例如,在特征No.1和No.2中间,知识可以表示为如何模做两者中间的转化,可以用一个矩阵让学习者产生这个矩阵,学习者和转化之间的学习关系。
这篇文章汇总了常用的知识蒸馏的论文和代码,方便后续的学习和研究。1、Logits
论文链接:https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2014/file/ea8fcd92d59581717e06eb187f10666d-Paper.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class Logits(nn.Module): ''' Do Deep Nets Really Need to be Deep? http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5484-do-deep-nets-really-need-to-be-deep.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(Logits, self).__init__() def forward(self, out_s, out_t): loss = F.mse_loss(out_s, out_t) return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
2、ST
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.02531.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class SoftTarget(nn.Module): ''' Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.02531.pdf ''' def __init__(self, T): super(SoftTarget, self).__init__() self.T = T def forward(self, out_s, out_t): loss = F.kl_div(F.log_softmax(out_s/self.T, dim=1), F.softmax(out_t/self.T, dim=1), reduction='batchmean') * self.T * self.T return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
3、AT
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.03928.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F ''' AT with sum of absolute values with power p ''' class AT(nn.Module): ''' Paying More Attention to Attention: Improving the Performance of Convolutional Neural Netkworks wia Attention Transfer https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.03928.pdf ''' def __init__(self, p): super(AT, self).__init__() self.p = p def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t): loss = F.mse_loss(self.attention_map(fm_s), self.attention_map(fm_t)) return loss def attention_map(self, fm, eps=1e-6): am = torch.pow(torch.abs(fm), self.p) am = torch.sum(am, dim=1, keepdim=True) norm = torch.norm(am, dim=(2,3), keepdim=True) am = torch.div(am, norm+eps) return am- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
4、Fitnet
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6550.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class Hint(nn.Module): ''' FitNets: Hints for Thin Deep Nets https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6550.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(Hint, self).__init__() def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t): loss = F.mse_loss(fm_s, fm_t) return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
5、NST
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01219.pdf
from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F ''' NST with Polynomial Kernel, where d=2 and c=0 ''' class NST(nn.Module): ''' Like What You Like: Knowledge Distill via Neuron Selectivity Transfer https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01219.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(NST, self).__init__() def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t): fm_s = fm_s.view(fm_s.size(0), fm_s.size(1), -1) fm_s = F.normalize(fm_s, dim=2) fm_t = fm_t.view(fm_t.size(0), fm_t.size(1), -1) fm_t = F.normalize(fm_t, dim=2) loss = self.poly_kernel(fm_t, fm_t).mean() \ + self.poly_kernel(fm_s, fm_s).mean() \ - 2 * self.poly_kernel(fm_s, fm_t).mean() return loss def poly_kernel(self, fm1, fm2): fm1 = fm1.unsqueeze(1) fm2 = fm2.unsqueeze(2) out = (fm1 * fm2).sum(-1).pow(2) return out- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
6、PKT
论文链接:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ECCV_2018/papers/Nikolaos_Passalis_Learning_Deep_Representations_ECCV_2018_paper.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F ''' Adopted from https://github.com/passalis/probabilistic_kt/blob/master/nn/pkt.py ''' class PKTCosSim(nn.Module): ''' Learning Deep Representations with Probabilistic Knowledge Transfer http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ECCV_2018/papers/Nikolaos_Passalis_Learning_Deep_Representations_ECCV_2018_paper.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(PKTCosSim, self).__init__() def forward(self, feat_s, feat_t, eps=1e-6): # Normalize each vector by its norm feat_s_norm = torch.sqrt(torch.sum(feat_s ** 2, dim=1, keepdim=True)) feat_s = feat_s / (feat_s_norm + eps) feat_s[feat_s != feat_s] = 0 feat_t_norm = torch.sqrt(torch.sum(feat_t ** 2, dim=1, keepdim=True)) feat_t = feat_t / (feat_t_norm + eps) feat_t[feat_t != feat_t] = 0 # Calculate the cosine similarity feat_s_cos_sim = torch.mm(feat_s, feat_s.transpose(0, 1)) feat_t_cos_sim = torch.mm(feat_t, feat_t.transpose(0, 1)) # Scale cosine similarity to [0,1] feat_s_cos_sim = (feat_s_cos_sim + 1.0) / 2.0 feat_t_cos_sim = (feat_t_cos_sim + 1.0) / 2.0 # Transform them into probabilities feat_s_cond_prob = feat_s_cos_sim / torch.sum(feat_s_cos_sim, dim=1, keepdim=True) feat_t_cond_prob = feat_t_cos_sim / torch.sum(feat_t_cos_sim, dim=1, keepdim=True) # Calculate the KL-divergence loss = torch.mean(feat_t_cond_prob * torch.log((feat_t_cond_prob + eps) / (feat_s_cond_prob + eps))) return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
7、FSP
论文链接:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/papers/Yim_A_Gift_From_CVPR_2017_paper.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class FSP(nn.Module): ''' A Gift from Knowledge Distillation: Fast Optimization, Network Minimization and Transfer Learning http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/papers/Yim_A_Gift_From_CVPR_2017_paper.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(FSP, self).__init__() def forward(self, fm_s1, fm_s2, fm_t1, fm_t2): loss = F.mse_loss(self.fsp_matrix(fm_s1,fm_s2), self.fsp_matrix(fm_t1,fm_t2)) return loss def fsp_matrix(self, fm1, fm2): if fm1.size(2) > fm2.size(2): fm1 = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(fm1, (fm2.size(2), fm2.size(3))) fm1 = fm1.view(fm1.size(0), fm1.size(1), -1) fm2 = fm2.view(fm2.size(0), fm2.size(1), -1).transpose(1,2) fsp = torch.bmm(fm1, fm2) / fm1.size(2) return fsp- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
8、FT
论文链接:http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7541-paraphrasing-complex-network-network-compression-via-factor-transfer.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class FT(nn.Module): ''' araphrasing Complex Network: Network Compression via Factor Transfer http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7541-paraphrasing-complex-network-network-compression-via-factor-transfer.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(FT, self).__init__() def forward(self, factor_s, factor_t): loss = F.l1_loss(self.normalize(factor_s), self.normalize(factor_t)) return loss def normalize(self, factor): norm_factor = F.normalize(factor.view(factor.size(0),-1)) return norm_factor- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
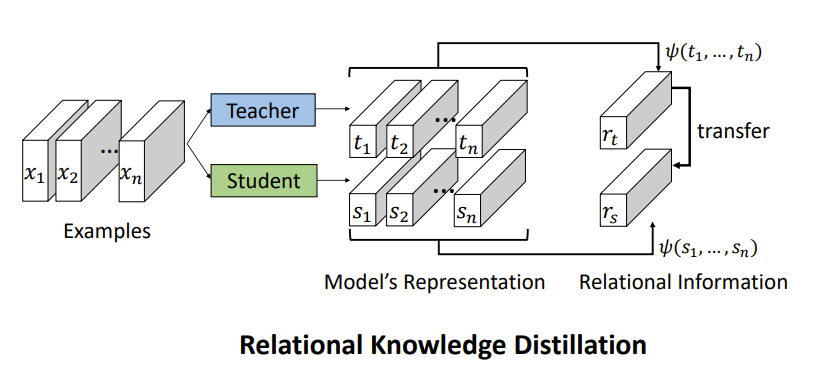
9、RKD
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05068.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F ''' From https://github.com/lenscloth/RKD/blob/master/metric/loss.py ''' class RKD(nn.Module): ''' Relational Knowledge Distillation https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05068.pdf ''' def __init__(self, w_dist, w_angle): super(RKD, self).__init__() self.w_dist = w_dist self.w_angle = w_angle def forward(self, feat_s, feat_t): loss = self.w_dist * self.rkd_dist(feat_s, feat_t) + \ self.w_angle * self.rkd_angle(feat_s, feat_t) return loss def rkd_dist(self, feat_s, feat_t): feat_t_dist = self.pdist(feat_t, squared=False) mean_feat_t_dist = feat_t_dist[feat_t_dist>0].mean() feat_t_dist = feat_t_dist / mean_feat_t_dist feat_s_dist = self.pdist(feat_s, squared=False) mean_feat_s_dist = feat_s_dist[feat_s_dist>0].mean() feat_s_dist = feat_s_dist / mean_feat_s_dist loss = F.smooth_l1_loss(feat_s_dist, feat_t_dist) return loss def rkd_angle(self, feat_s, feat_t): # N x C --> N x N x C feat_t_vd = (feat_t.unsqueeze(0) - feat_t.unsqueeze(1)) norm_feat_t_vd = F.normalize(feat_t_vd, p=2, dim=2) feat_t_angle = torch.bmm(norm_feat_t_vd, norm_feat_t_vd.transpose(1, 2)).view(-1) feat_s_vd = (feat_s.unsqueeze(0) - feat_s.unsqueeze(1)) norm_feat_s_vd = F.normalize(feat_s_vd, p=2, dim=2) feat_s_angle = torch.bmm(norm_feat_s_vd, norm_feat_s_vd.transpose(1, 2)).view(-1) loss = F.smooth_l1_loss(feat_s_angle, feat_t_angle) return loss def pdist(self, feat, squared=False, eps=1e-12): feat_square = feat.pow(2).sum(dim=1) feat_prod = torch.mm(feat, feat.t()) feat_dist = (feat_square.unsqueeze(0) + feat_square.unsqueeze(1) - 2 * feat_prod).clamp(min=eps) if not squared: feat_dist = feat_dist.sqrt() feat_dist = feat_dist.clone() feat_dist[range(len(feat)), range(len(feat))] = 0 return feat_dist- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
10、AB
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.03233.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class AB(nn.Module): ''' Knowledge Transfer via Distillation of Activation Boundaries Formed by Hidden Neurons https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.03233.pdf ''' def __init__(self, margin): super(AB, self).__init__() self.margin = margin def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t): # fm befor activation loss = ((fm_s + self.margin).pow(2) * ((fm_s > -self.margin) & (fm_t <= 0)).float() + (fm_s - self.margin).pow(2) * ((fm_s <= self.margin) & (fm_t > 0)).float()) loss = loss.mean() return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
11、SP
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.09682.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class SP(nn.Module): ''' Similarity-Preserving Knowledge Distillation https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.09682.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(SP, self).__init__() def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t): fm_s = fm_s.view(fm_s.size(0), -1) G_s = torch.mm(fm_s, fm_s.t()) norm_G_s = F.normalize(G_s, p=2, dim=1) fm_t = fm_t.view(fm_t.size(0), -1) G_t = torch.mm(fm_t, fm_t.t()) norm_G_t = F.normalize(G_t, p=2, dim=1) loss = F.mse_loss(norm_G_s, norm_G_t) return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
12、Sobolev
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.04859.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.autograd import grad class Sobolev(nn.Module): ''' Sobolev Training for Neural Networks https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.04859.pdf Knowledge Transfer with Jacobian Matching http://de.arxiv.org/pdf/1803.00443 ''' def __init__(self): super(Sobolev, self).__init__() def forward(self, out_s, out_t, img, target): target_out_s = torch.gather(out_s, 1, target.view(-1, 1)) grad_s = grad(outputs=target_out_s, inputs=img, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(target_out_s), create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)[0] norm_grad_s = F.normalize(grad_s.view(grad_s.size(0), -1), p=2, dim=1) target_out_t = torch.gather(out_t, 1, target.view(-1, 1)) grad_t = grad(outputs=target_out_t, inputs=img, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(target_out_t), create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)[0] norm_grad_t = F.normalize(grad_t.view(grad_t.size(0), -1), p=2, dim=1) loss = F.mse_loss(norm_grad_s, norm_grad_t.detach()) return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
13、BSS
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.05532.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.autograd.gradcheck import zero_gradients ''' Modified by https://github.com/bhheo/BSS_distillation ''' def reduce_sum(x, keepdim=True): for d in reversed(range(1, x.dim())): x = x.sum(d, keepdim=keepdim) return x def l2_norm(x, keepdim=True): norm = reduce_sum(x*x, keepdim=keepdim) return norm.sqrt() class BSS(nn.Module): ''' Knowledge Distillation with Adversarial Samples Supporting Decision Boundary https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.05532.pdf ''' def __init__(self, T): super(BSS, self).__init__() self.T = T def forward(self, attacked_out_s, attacked_out_t): loss = F.kl_div(F.log_softmax(attacked_out_s/self.T, dim=1), F.softmax(attacked_out_t/self.T, dim=1), reduction='batchmean') #* self.T * self.T return loss class BSSAttacker(): def __init__(self, step_alpha, num_steps, eps=1e-4): self.step_alpha = step_alpha self.num_steps = num_steps self.eps = eps def attack(self, model, img, target, attack_class): img = img.detach().requires_grad_(True) step = 0 while step < self.num_steps: zero_gradients(img) _, _, _, _, _, output = model(img) score = F.softmax(output, dim=1) score_target = score.gather(1, target.unsqueeze(1)) score_attack_class = score.gather(1, attack_class.unsqueeze(1)) loss = (score_attack_class - score_target).sum() loss.backward() step_alpha = self.step_alpha * (target == output.max(1)[1]).float() step_alpha = step_alpha.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(1) if step_alpha.sum() == 0: break pert = (score_target - score_attack_class).unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(1) norm_pert = step_alpha * (pert + self.eps) * img.grad / l2_norm(img.grad) step_adv = img + norm_pert step_adv = torch.clamp(step_adv, -2.5, 2.5) img.data = step_adv.data step += 1 return img- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
14、CC
论文链接:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/Peng_Correlation_Congruence_for_Knowledge_Distillation_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import math ''' CC with P-order Taylor Expansion of Gaussian RBF kernel ''' class CC(nn.Module): ''' Correlation Congruence for Knowledge Distillation http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/ Peng_Correlation_Congruence_for_Knowledge_Distillation_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf ''' def __init__(self, gamma, P_order): super(CC, self).__init__() self.gamma = gamma self.P_order = P_order def forward(self, feat_s, feat_t): corr_mat_s = self.get_correlation_matrix(feat_s) corr_mat_t = self.get_correlation_matrix(feat_t) loss = F.mse_loss(corr_mat_s, corr_mat_t) return loss def get_correlation_matrix(self, feat): feat = F.normalize(feat, p=2, dim=-1) sim_mat = torch.matmul(feat, feat.t()) corr_mat = torch.zeros_like(sim_mat) for p in range(self.P_order+1): corr_mat += math.exp(-2*self.gamma) * (2*self.gamma)**p / \ math.factorial(p) * torch.pow(sim_mat, p) return corr_mat- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
15、LwM
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.08051.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.autograd import grad ''' LwM is originally an incremental learning method with classification/distillation/attention distillation losses. Here, LwM is only defined as the Grad-CAM based attention distillation. ''' class LwM(nn.Module): ''' Learning without Memorizing https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.08051.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(LwM, self).__init__() def forward(self, out_s, fm_s, out_t, fm_t, target): target_out_t = torch.gather(out_t, 1, target.view(-1, 1)) grad_fm_t = grad(outputs=target_out_t, inputs=fm_t, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(target_out_t), create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)[0] weights_t = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(grad_fm_t, 1) cam_t = torch.sum(torch.mul(weights_t, grad_fm_t), dim=1, keepdim=True) cam_t = F.relu(cam_t) cam_t = cam_t.view(cam_t.size(0), -1) norm_cam_t = F.normalize(cam_t, p=2, dim=1) target_out_s = torch.gather(out_s, 1, target.view(-1, 1)) grad_fm_s = grad(outputs=target_out_s, inputs=fm_s, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(target_out_s), create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)[0] weights_s = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(grad_fm_s, 1) cam_s = torch.sum(torch.mul(weights_s, grad_fm_s), dim=1, keepdim=True) cam_s = F.relu(cam_s) cam_s = cam_s.view(cam_s.size(0), -1) norm_cam_s = F.normalize(cam_s, p=2, dim=1) loss = F.l1_loss(norm_cam_s, norm_cam_t.detach()) return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
16、IRG
论文链接:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Liu_Knowledge_Distillation_via_Instance_Relationship_Graph_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class IRG(nn.Module): ''' Knowledge Distillation via Instance Relationship Graph http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/ Liu_Knowledge_Distillation_via_Instance_Relationship_Graph_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf The official code is written by Caffe https://github.com/yufanLIU/IRG ''' def __init__(self, w_irg_vert, w_irg_edge, w_irg_tran): super(IRG, self).__init__() self.w_irg_vert = w_irg_vert self.w_irg_edge = w_irg_edge self.w_irg_tran = w_irg_tran def forward(self, irg_s, irg_t): fm_s1, fm_s2, feat_s, out_s = irg_s fm_t1, fm_t2, feat_t, out_t = irg_t loss_irg_vert = F.mse_loss(out_s, out_t) irg_edge_feat_s = self.euclidean_dist_feat(feat_s, squared=True) irg_edge_feat_t = self.euclidean_dist_feat(feat_t, squared=True) irg_edge_fm_s1 = self.euclidean_dist_fm(fm_s1, squared=True) irg_edge_fm_t1 = self.euclidean_dist_fm(fm_t1, squared=True) irg_edge_fm_s2 = self.euclidean_dist_fm(fm_s2, squared=True) irg_edge_fm_t2 = self.euclidean_dist_fm(fm_t2, squared=True) loss_irg_edge = (F.mse_loss(irg_edge_feat_s, irg_edge_feat_t) + F.mse_loss(irg_edge_fm_s1, irg_edge_fm_t1 ) + F.mse_loss(irg_edge_fm_s2, irg_edge_fm_t2 )) / 3.0 irg_tran_s = self.euclidean_dist_fms(fm_s1, fm_s2, squared=True) irg_tran_t = self.euclidean_dist_fms(fm_t1, fm_t2, squared=True) loss_irg_tran = F.mse_loss(irg_tran_s, irg_tran_t) # print(self.w_irg_vert * loss_irg_vert) # print(self.w_irg_edge * loss_irg_edge) # print(self.w_irg_tran * loss_irg_tran) # print() loss = (self.w_irg_vert * loss_irg_vert + self.w_irg_edge * loss_irg_edge + self.w_irg_tran * loss_irg_tran) return loss def euclidean_dist_fms(self, fm1, fm2, squared=False, eps=1e-12): ''' Calculating the IRG Transformation, where fm1 precedes fm2 in the network. ''' if fm1.size(2) > fm2.size(2): fm1 = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(fm1, (fm2.size(2), fm2.size(3))) if fm1.size(1) < fm2.size(1): fm2 = (fm2[:,0::2,:,:] + fm2[:,1::2,:,:]) / 2.0 fm1 = fm1.view(fm1.size(0), -1) fm2 = fm2.view(fm2.size(0), -1) fms_dist = torch.sum(torch.pow(fm1-fm2, 2), dim=-1).clamp(min=eps) if not squared: fms_dist = fms_dist.sqrt() fms_dist = fms_dist / fms_dist.max() return fms_dist def euclidean_dist_fm(self, fm, squared=False, eps=1e-12): ''' Calculating the IRG edge of feature map. ''' fm = fm.view(fm.size(0), -1) fm_square = fm.pow(2).sum(dim=1) fm_prod = torch.mm(fm, fm.t()) fm_dist = (fm_square.unsqueeze(0) + fm_square.unsqueeze(1) - 2 * fm_prod).clamp(min=eps) if not squared: fm_dist = fm_dist.sqrt() fm_dist = fm_dist.clone() fm_dist[range(len(fm)), range(len(fm))] = 0 fm_dist = fm_dist / fm_dist.max() return fm_dist def euclidean_dist_feat(self, feat, squared=False, eps=1e-12): ''' Calculating the IRG edge of feat. ''' feat_square = feat.pow(2).sum(dim=1) feat_prod = torch.mm(feat, feat.t()) feat_dist = (feat_square.unsqueeze(0) + feat_square.unsqueeze(1) - 2 * feat_prod).clamp(min=eps) if not squared: feat_dist = feat_dist.sqrt() feat_dist = feat_dist.clone() feat_dist[range(len(feat)), range(len(feat))] = 0 feat_dist = feat_dist / feat_dist.max() return feat_dist- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
17、VID
论文链接:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Ahn_Variational_Information_Distillation_for_Knowledge_Transfer_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import numpy as np def conv1x1(in_channels, out_channels): return nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False) ''' Modified from https://github.com/HobbitLong/RepDistiller/blob/master/distiller_zoo/VID.py ''' class VID(nn.Module): ''' Variational Information Distillation for Knowledge Transfer https://zpascal.net/cvpr2019/Ahn_Variational_Information_Distillation_for_Knowledge_Transfer_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf ''' def __init__(self, in_channels, mid_channels, out_channels, init_var, eps=1e-6): super(VID, self).__init__() self.eps = eps self.regressor = nn.Sequential(*[ conv1x1(in_channels, mid_channels), # nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels), nn.ReLU(), conv1x1(mid_channels, mid_channels), # nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels), nn.ReLU(), conv1x1(mid_channels, out_channels), ]) self.alpha = nn.Parameter( np.log(np.exp(init_var-eps)-1.0) * torch.ones(out_channels) ) for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu') if m.bias is not None: nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) # elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): # nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1) # nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t): pred_mean = self.regressor(fm_s) pred_var = torch.log(1.0+torch.exp(self.alpha)) + self.eps pred_var = pred_var.view(1, -1, 1, 1) neg_log_prob = 0.5 * (torch.log(pred_var) + (pred_mean-fm_t)**2 / pred_var) loss = torch.mean(neg_log_prob) return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
18、OFD
论文链接:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/Heo_A_Comprehensive_Overhaul_of_Feature_Distillation_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import numpy as np ''' Modified from https://github.com/clovaai/overhaul-distillation/blob/master/CIFAR-100/distiller.py ''' class OFD(nn.Module): ''' A Comprehensive Overhaul of Feature Distillation http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/ Heo_A_Comprehensive_Overhaul_of_Feature_Distillation_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf ''' def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels): super(OFD, self).__init__() self.connector = nn.Sequential(*[ nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels) ]) for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu') if m.bias is not None: nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1) nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t): margin = self.get_margin(fm_t) fm_t = torch.max(fm_t, margin) fm_s = self.connector(fm_s) mask = 1.0 - ((fm_s <= fm_t) & (fm_t <= 0.0)).float() loss = torch.mean((fm_s - fm_t)**2 * mask) return loss def get_margin(self, fm, eps=1e-6): mask = (fm < 0.0).float() masked_fm = fm * mask margin = masked_fm.sum(dim=(0,2,3), keepdim=True) / (mask.sum(dim=(0,2,3), keepdim=True)+eps) return margin- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
19、AFD
论文链接:https://openreview.net/pdf?id=ryxyCeHtPB
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import math ''' In the original paper, AFD is one of components of AFDS. AFDS: Attention Feature Distillation and Selection AFD: Attention Feature Distillation AFS: Attention Feature Selection We find the original implementation of attention is unstable, thus we replace it with a SE block. ''' class AFD(nn.Module): ''' Pay Attention to Features, Transfer Learn Faster CNNs https://openreview.net/pdf?id=ryxyCeHtPB ''' def __init__(self, in_channels, att_f): super(AFD, self).__init__() mid_channels = int(in_channels * att_f) self.attention = nn.Sequential(*[ nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, in_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True) ]) for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu') if m.bias is not None: nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) def forward(self, fm_s, fm_t, eps=1e-6): fm_t_pooled = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(fm_t, 1) rho = self.attention(fm_t_pooled) # rho = F.softmax(rho.squeeze(), dim=-1) rho = torch.sigmoid(rho.squeeze()) rho = rho / torch.sum(rho, dim=1, keepdim=True) fm_s_norm = torch.norm(fm_s, dim=(2,3), keepdim=True) fm_s = torch.div(fm_s, fm_s_norm+eps) fm_t_norm = torch.norm(fm_t, dim=(2,3), keepdim=True) fm_t = torch.div(fm_t, fm_t_norm+eps) loss = rho * torch.pow(fm_s-fm_t, 2).mean(dim=(2,3)) loss = loss.sum(1).mean(0) return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
20、CRD
论文链接:https://openreview.net/pdf?id=SkgpBJrtvS
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import math ''' Modified from https://github.com/HobbitLong/RepDistiller/tree/master/crd ''' class CRD(nn.Module): ''' Contrastive Representation Distillation https://openreview.net/pdf?id=SkgpBJrtvS includes two symmetric parts: (a) using teacher as anchor, choose positive and negatives over the student side (b) using student as anchor, choose positive and negatives over the teacher side Args: s_dim: the dimension of student's feature t_dim: the dimension of teacher's feature feat_dim: the dimension of the projection space nce_n: number of negatives paired with each positive nce_t: the temperature nce_mom: the momentum for updating the memory buffer n_data: the number of samples in the training set, which is the M in Eq.(19) ''' def __init__(self, s_dim, t_dim, feat_dim, nce_n, nce_t, nce_mom, n_data): super(CRD, self).__init__() self.embed_s = Embed(s_dim, feat_dim) self.embed_t = Embed(t_dim, feat_dim) self.contrast = ContrastMemory(feat_dim, n_data, nce_n, nce_t, nce_mom) self.criterion_s = ContrastLoss(n_data) self.criterion_t = ContrastLoss(n_data) def forward(self, feat_s, feat_t, idx, sample_idx): feat_s = self.embed_s(feat_s) feat_t = self.embed_t(feat_t) out_s, out_t = self.contrast(feat_s, feat_t, idx, sample_idx) loss_s = self.criterion_s(out_s) loss_t = self.criterion_t(out_t) loss = loss_s + loss_t return loss class Embed(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim): super(Embed, self).__init__() self.linear = nn.Linear(in_dim, out_dim) def forward(self, x): x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) x = self.linear(x) x = F.normalize(x, p=2, dim=1) return x class ContrastLoss(nn.Module): ''' contrastive loss, corresponding to Eq.(18) ''' def __init__(self, n_data, eps=1e-7): super(ContrastLoss, self).__init__() self.n_data = n_data self.eps = eps def forward(self, x): bs = x.size(0) N = x.size(1) - 1 M = float(self.n_data) # loss for positive pair pos_pair = x.select(1, 0) log_pos = torch.div(pos_pair, pos_pair.add(N / M + self.eps)).log_() # loss for negative pair neg_pair = x.narrow(1, 1, N) log_neg = torch.div(neg_pair.clone().fill_(N / M), neg_pair.add(N / M + self.eps)).log_() loss = -(log_pos.sum() + log_neg.sum()) / bs return loss class ContrastMemory(nn.Module): def __init__(self, feat_dim, n_data, nce_n, nce_t, nce_mom): super(ContrastMemory, self).__init__() self.N = nce_n self.T = nce_t self.momentum = nce_mom self.Z_t = None self.Z_s = None stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(feat_dim / 3.) self.register_buffer('memory_t', torch.rand(n_data, feat_dim).mul_(2 * stdv).add_(-stdv)) self.register_buffer('memory_s', torch.rand(n_data, feat_dim).mul_(2 * stdv).add_(-stdv)) def forward(self, feat_s, feat_t, idx, sample_idx): bs = feat_s.size(0) feat_dim = self.memory_s.size(1) n_data = self.memory_s.size(0) # using teacher as anchor weight_s = torch.index_select(self.memory_s, 0, sample_idx.view(-1)).detach() weight_s = weight_s.view(bs, self.N + 1, feat_dim) out_t = torch.bmm(weight_s, feat_t.view(bs, feat_dim, 1)) out_t = torch.exp(torch.div(out_t, self.T)).squeeze().contiguous() # using student as anchor weight_t = torch.index_select(self.memory_t, 0, sample_idx.view(-1)).detach() weight_t = weight_t.view(bs, self.N + 1, feat_dim) out_s = torch.bmm(weight_t, feat_s.view(bs, feat_dim, 1)) out_s = torch.exp(torch.div(out_s, self.T)).squeeze().contiguous() # set Z if haven't been set yet if self.Z_t is None: self.Z_t = (out_t.mean() * n_data).detach().item() if self.Z_s is None: self.Z_s = (out_s.mean() * n_data).detach().item() out_t = torch.div(out_t, self.Z_t) out_s = torch.div(out_s, self.Z_s) # update memory with torch.no_grad(): pos_mem_t = torch.index_select(self.memory_t, 0, idx.view(-1)) pos_mem_t.mul_(self.momentum) pos_mem_t.add_(torch.mul(feat_t, 1 - self.momentum)) pos_mem_t = F.normalize(pos_mem_t, p=2, dim=1) self.memory_t.index_copy_(0, idx, pos_mem_t) pos_mem_s = torch.index_select(self.memory_s, 0, idx.view(-1)) pos_mem_s.mul_(self.momentum) pos_mem_s.add_(torch.mul(feat_s, 1 - self.momentum)) pos_mem_s = F.normalize(pos_mem_s, p=2, dim=1) self.memory_s.index_copy_(0, idx, pos_mem_s) return out_s, out_t- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
21、DML
论文链接:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers/Zhang_Deep_Mutual_Learning_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf
代码:from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F ''' DML with only two networks ''' class DML(nn.Module): ''' Deep Mutual Learning https://zpascal.net/cvpr2018/Zhang_Deep_Mutual_Learning_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf ''' def __init__(self): super(DML, self).__init__() def forward(self, out1, out2): loss = F.kl_div(F.log_softmax(out1, dim=1), F.softmax(out2, dim=1), reduction='batchmean') return loss- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
-
相关阅读:
关于数字化转型的know how
【算法】折半查找解析
【详细图文】Windows下安装RustRover和配置Rust环境
cesium glb/gltf模型节点高亮
easyswoole ORM 对于having 连贯操作
MongoDB聚合运算符:$sampleRate
得物 Redis 设计与实践yu
云服务器CVM_云主机_云计算服务器_弹性云服务器-腾讯云
ABS新设海事软件公司ABS Wavesight™,引领船队运营驶入21世纪
【Excel密码】四个方法,设置excel表格只读模式
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/hhhhhhhhhhwwwwwwwwww/article/details/127802486
