-
Linux systemctl 详解&自定义 systemd unit
Linux systemctl 详解&自定义 systemd unit
systemctl
序
大家都知道,我们安装了很多服务之后,使用
systemctl来管理这些服务,比如开启、重启、关闭等等,所以systemctl是一个systemd系统。centos 使用systemctl来代替daemon和chkconfig,原来的所有系统启动和管理系统服务全部由systemctl来代替。systemctl 命令
我们可以查看官方给出的命令:
systemctl --help- 1

可以看到
systemctl包含两类命令,OPTIONS和COMMAND。OPTIONS是-开头,而COMMAND则不会。行头
如果我们直接执行
systemctl,则会打印systemctl- 1
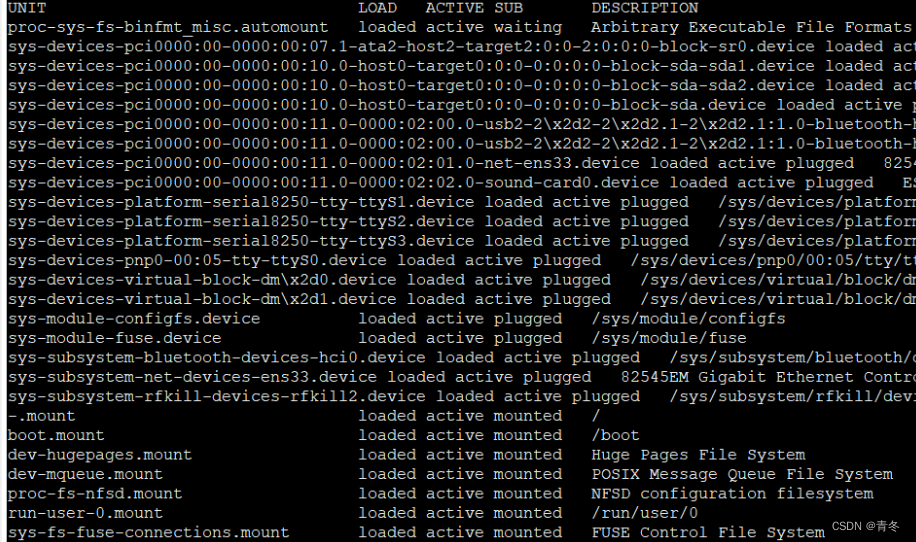
可以看到行头为:
UNIT
UNIT 是统一了各种不同系统资源的配置格式,列如服务器的启停、定时任务、设备挂载、网络配置、虚拟内存等等。通过不同的后缀来区分这些配置文件。
包含 12 类:
LOAD
systemd 是否正确解析了单元的配置并将该单元加载到内存中。
loaded 表示成功加载到内存中,没有问题。
ACTIVE
高级单元激活状态。
The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type.
active 表示成功激活。
failed 表示激活失败。
SUB
低级单元激活状态。
The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type.
active 表示成功激活。
failed 表示激活失败。
DESCRIPTION
对该 unit 的一些描述。
OPTIONS
由于命令太多,只演示一些重要、常用的:
-t --type=TYPE List units of a particular type –state=STATE List units with particular LOAD or SUB or ACTIVE state -p --property=NAME Show only properties by this name -a --all Show all loaded units/properties, including dead/empty ones. To list all units installed on the system, use the ‘list-unit-files’ command instead. -l --full Don’t ellipsize unit names on output -r --recursive Show unit list of host and local containers –reverse Show reverse dependencies with ‘list-dependencies’ –job -mode=MODE Specify how to deal with already queued jobs, when queueing a new job –show-types When showing sockets, explicitly show their type -i --ignore-inhibitors When shutting down or sleeping, ignore inhibitors –kill-who=WHO Who to send signal to -s --signal=SIGNAL Which signal to send –now Start or stop unit in addition to enabling or disabling it -q --quiet Suppress output –no-block Do not wait until operation finished –no-wall Don’t send wall message before halt/power-off/reboot –no-reload Don’t reload daemon after en-/dis-abling unit files –no-legend Do not print a legend (column headers and hints) –no-pager Do not pipe output into a pager –no-ask-password Do not ask for system passwords –global Enable/disable unit files globally –runtime Enable unit files only temporarily until next reboot -f --force When enabling unit files, override existing symlinks When shutting down, execute action immediately –preset-mode= Apply only enable, only disable, or all presets –root=PATH Enable unit files in the specified root directory -n --lines=INTEGER Number of journal entries to show -o --output=STRING Change journal output mode (short, short-iso, short-precise, short-monotonic, verbose, export, json, json-pretty, json-sse, cat) –plain Print unit dependencies as a list instead of a tree -t --type=TYPE
根据 UNIT 的 12 种类型来筛选,比如找出为 UNIT 为 service 类型:
systemctl --type=service # 所有服务的运行状态,但不包含系统服务- 1
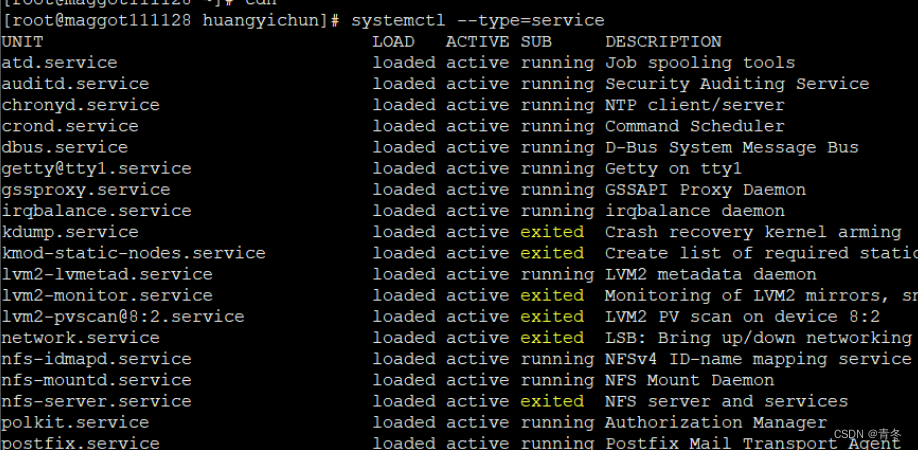
–state=ACTIVE
根据 state 进行筛选,如筛选运行中的:
systemctl --state=active --type=service- 1
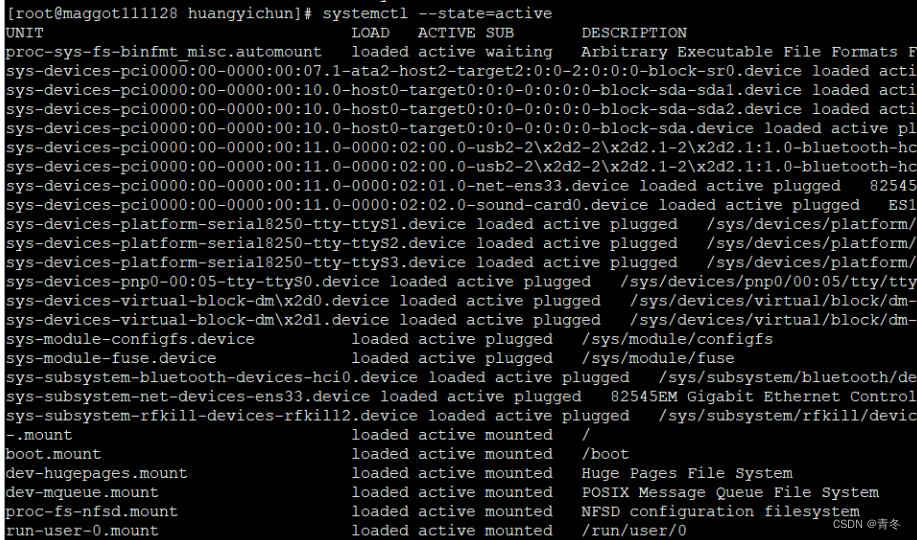
当然可以复合筛选,比如运行中的服务:
systemctl --state=active --type=service- 1
COMMAND
mask 屏蔽服务
将服务进行屏蔽后,就无法通过
systemctl来进行各种管理,如:systemctl mask firewalld- 1

可以看到,在
mask之前是 loaded 状态,但是在之后就变成了masked状态,而且现在无法操控:
必须手动取消屏蔽,才可以继续操控(这里操控其实是启动,停止不收影响):
systemctl unmask firewalld systemctl start firewalld- 1
- 2

enable 开机启动
如果我们想将一个服务开机启动,那么我们可以:
systemctl enable chronyd systemctl is-enabled chronyd # 查看是否设置了开机启动- 1
- 2

关闭开机启动也很简单:
systemctl disable chronyd- 1
start stop 启停
对某服务进行启停操作:
systemctl start chronyd systemctl stop chronyd- 1
- 2
status 查看当前状态
systemctl status chronyd- 1

状态打印出来分为两大部分,上面为该 UNIT 的状态,下面为最近的日志。
状态栏里面有:
● chronyd.service - NTP client/server # 基本描述
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/chronyd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) # 当前是否加载进内存(服务文件地址;;是否开机启动;)
Active: active (running) since 日 2022-11-27 17:25:18 CST; 1 day 4h ago # 当前运行情况;开始时间;持续时间
Docs: man:chronyd(8) # 在线文档地址 或者 man
man:chrony.conf(5)
Main PID: 6075 (chronyd) # 当前运行该 Unit 的进程
CGroup: /system.slice/chronyd.service # cgrpup 相关,包含调用栈
└─6075 /usr/sbin/chronyd
这里主要说下 Active:active(running),其实可能还有其他运行状态:
状态 含义 active(running) 表示程序正在执行 atcive(exited) 执行一次就正常退出的服务,不在系统中执行任何程序 active(waiting) 正在执行中,处于阻塞状态,需要等待其他程序执行完才能执行 inactive (dead) 未启动状态 和开机启动项的状态(前面是当前状态,后面是默认状态):
启动状态 含义 inactive 服务关闭 disable 服务开机不启动 enabled 服务开机启动 static 服务开机启动项被管理 failed 服务配置错误 kill 杀死某服务
一般建议使用
stop进行关闭,在无法stop情况下再使用该命令systemctl kill chronyd- 1
systemd 创建
我们刚刚看了很多关于
systemctl的命令了,基本上学会了怎么进行使用,接下来我们需要自己创建一个 unit.server 进行一些简单的服务编排。配置文件
在前面进行
status命令讲解时,看到 Loaded 行有对应 server 的配置文件,我们以chronyd为例,查看这个程序是怎么加载的。ll /usr/lib/systemd/system/chronyd.service vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/chronyd.service- 1
- 2

[Unit]
定义该 Unit 的加载问题和 status 上各种显示。
可选项 描述 Description 对当前服务的简单描述 After 在XX启动后才启动。 Before 在XX启动之前需要启动。 Conflicts 异斥的服务,不能与这些服务共存。 Documentation 使用手册说明,提供一个URIS的位置,一般用于man或者web访问,会被 status 公开,以便于发现。 ConditionPathExists 这些路径存在才执行(如配置文件)。 Requires 可以指定服务依赖于哪些服务(这种依赖是"强依赖",一旦所依赖的服务异常,当前的服务也随之停止) Wants 可以指定服务依赖于哪些服务(这种依赖是"弱依赖",即使所依赖的服务的启动情况不影响当前的服务是否启动) [Install]
一般
[Install]是在配置文件的最后一部分,是可选项。用于定义该UNIT的行为,一般是 enable 或者 disable 时发生调用。[Install] 描述 Alias 别名,可使用systemctl command Alias.service RequiredBy 被哪些units所依赖,强依赖 WantedBy 被哪些units所依赖,弱依赖 Also 安装本服务的时候还要安装别的相关服务 [Service]
用于提供适用于 .service 的配置(只有 service,才需要这块)。
[Service] 描述 EnvironmentFile 环境配置文件,用来指定当前服务启动的环境变量 ExecStart 指定服务启动时执行的命令或脚本 ExecStartPre 指定服务启动前执行的命令或脚本 ExecStartPost 指定服务启动后执行的命令或脚本 ExecStop 指明停止服务要运行的命令或脚本 ExecStopPost 指定服务停止之后执行的命令或脚本 RestartSec 指定服务在重启时等待的时间,单位为秒 ExecReload 指明重启服务要运行的命令或脚本 Restart 当设定Restart=1 时,则当次daemon服务意外终止后,会再次自动启动此服务,具体看下列类型 PrivateTmp 设定为yes时,会在生成/tmp/systemd-private-UUID-NAME.service-XXXXX/tmp/目录 KillMode control-goup 杀掉所有进程以及子进程;process 杀死主进程; mixed 给主进程发送 sigterm,字进程sigkill;none五操作 Restart no 退出后不重启;no-success 退出编码0重启;on-failure 退出不为0重启; on-abnormal 被kill或者超时时重启;on-abort 没有捕捉到信号时重启;on-watchdog 看门狗超时时重启;always 总是重启。 Type simple ExecStart为主进程;forking 以fork()子进程执行; oneshot执行一次;notify 启动完毕后通知systemd; idle 其他任务结束才运行 其他种类 Unit [xxx] 部分
所以本篇文章不再意义列举了,可以参考:https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/understanding-systemd-units-and-unit-files
打印当前时间的服务
到这里我们已经可以开发很多种服务,挂载 systemd 上面了,那么我们就来个简单的每过 5s 打印一次当前时间的服务。
打印当前时间程序开发
在 /usr/bin/ 中新建文件 printNow.sh 进行打印:
vim /usr/bin/printNow.sh #! /bin/bash # Copyright◎2022, Maggot. All rights reserved. # # This program is print the now to screen. # Date: 2022-11-28 # Auth: huangyichun # Version: 0.1 date # exit # 更改权限 chmod 755 /usr/bin/printNow.sh- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
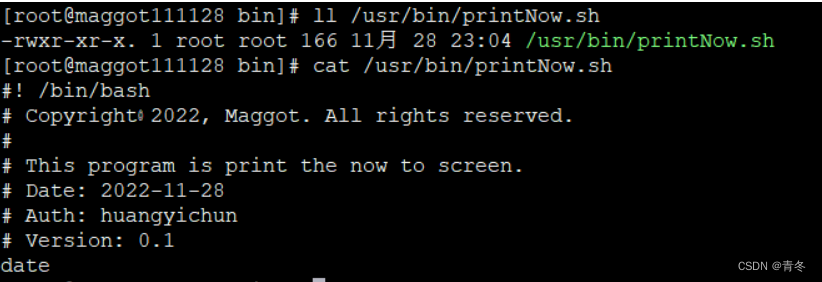
执行一次进行测试:
/usr/bin/printNow.sh- 1

服务配置
进入到配置目录 /lib/systemd/system 中,编辑 myprint.service 文件:
cd /lib/systemd/system vim myprint.service [Unit] Description=my print now ConditionPathExists=/usr/bin/printNow.sh [Service] RestartSec=5s #每五秒进行一次 Type=simple Restart=always ExecStart=/usr/bin/printNow.sh ExecReload=/usr/bin/printNow.sh LimitNOFILE=102400 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
刷新
systemctl服务systemctl daemon-reload- 1
查看
myprint服务状态:systemctl status myprint- 1

启动
myprint服务:systemctl start myprint systemctl status myprint- 1
- 2

可以看到确实每 5s 运行了一次,但日志呢?
我们在 [Service] 中再添加(警告,centos8 可以使用):
vim /lib/systemd/system/myprint.service # [Service] 中添加 StandardOutput=append:/tmp/myprintNow.log StandardError=append:/tmp/myprintNow.log systemctl daemon-reload watch systemctl status myprint- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

这里看不到的原因是因为 restart 会清空日志。
-
相关阅读:
DDD - 事件风暴从理论到落地
开发者生态:共享知识,携手共进,共创技术辉煌
【Java笔试强训】Day9(CM72 另类加法、HJ91 走方格的方案数)
网络协议常见问题
【vue】如何打开别人编译后的vue项目
Shader Graph学习各种特效案例
Java基础知识讲解-ArrayList类
Linux综合使用练习
安装dock打包前端项目遇到的一些错误
【NeurIPS&&知识图谱】联邦环境下,基于元学习的图谱知识外推(阿里&浙大&含源码)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36610426/article/details/128089685
