-
Python标准库之os
文章目录
- 1. OS标准库简介
- 2. OS标准库常用函数和属性
- 2.1 文件和目录
- 2.2 os.path常见路径操作
- 2.2.1 `os.path.abspath(path)`
- 2.2.2 `os.path.basename(path)`
- 2.2.3 `os.path.dirname(path)`
- 2.2.4 `os.path.exists(path)`
- 2.2.5 `os.path.isabs(path)`
- 2.2.6 `os.path.isfile(path)`
- 2.2.7 `os.path.isdir(path)`
- 2.2.8 `os.path.islink(path)`
- 2.2.9 `os.path.join(path, *paths)`
- 2.2.10 `os.path.normcase(path)`
- 2.2.11 `os.path.split(path)`
- 2.2.12 `os.path.splitext(path)`
- 2.3 其他常用命令
- 3. 参考文献
1. OS标准库简介
顾名思义,OS表示Operating System,即操作系统。OS标准库是一个操作系统接口模块,提供一些方便使用操作系统相关功能的函数,具体安装位置可通过导入os模块查看
os.__file__属性得到。当需要在Python代码中调用OS相关功能实现业务逻辑或者无法直接使用命令行工具时,我们就需要考虑导入此模块,因此有必要进行深入学习。2. OS标准库常用函数和属性
2.1 文件和目录
2.1.1
os.getcwd()返回表示当前工作目录的字符串
print("当前工作目录为:{}".format(os.getcwd())) # 返回当前工作目录- 1

2.1.2
os.mkdir(path, mode=0o777, *, dir_fd=None)以指定数字表示的权限模式mode创建一个名为path的目录。某些系统会忽略 mode,如果没有忽略,那么Linux系统来说,新建文件夹的权限=指定数字表示的权限模式mode-当前系统用户的umask默认权限,如下所示
""" Linux操作系统可通过umask命令获得4个八进制数表示的默认权限,root用户默认是0022,普通用户默认是 0002 第1位数代表文件所具有的特殊权限(SetUID、SetGID、Sticky BIT),后3位数表示表示umask权限值 分别对应所有者、用户组、其他人的权限值,权限与数字对应关系为:r->4,w->2,x->1 """ exit_code=os.system("umask")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

""" 文件夹模式mode赋值为十进制511,等价于八进制0o777 """ set_mode=511 os.mkdir(path="./cyr",mode=set_mode) # 在当前目录创建名为cyr的文件夹- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
# 长格式查看新创建的文件夹cyr可知其权限字符串为rwxr-xr-x,等价于转换后的数字权限111101101 !ls -l | grep cyr- 1
- 2
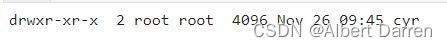
umask_value=0o0022 # 当前系统用户八进制表示umask默认权限 new_dir_mode=set_mode-umask_value print("新建文件夹的权限为:{:b}".format(new_dir_mode))- 1
- 2
- 3

-
os.rmdir(path, *, dir_fd=None)移除(删除)目录 path。如果目录不存在或不为空,则会分别抛出
FileNotFoundError或OSError异常。os.rmdir("./cyr") # 删除空文件夹成功,无法查到cyr目录 !ls | grep cyr- 1
- 2
os.rmdir("./why") # 删除不存在的文件夹FileNotFoundError报错- 1

os.rmdir("./nnunet/") # 删除不为空文件夹OSError报错- 1

-
os.chdir(path)将当前工作目录更改为 path
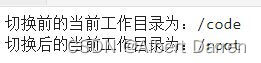
print("切换前的当前工作目录为:{}".format(os.getcwd())) # 返回当前工作目录 dst_path="/root" # 目标文件夹 os.chdir(dst_path) # 将当前工作目录切换为/root print("切换后的当前工作目录为:{}".format(os.getcwd())) # 返回当前工作目录- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
os.listdir(path='.')返回一个包含指定path下所有文件和目录名称的按任意顺序排列的列表,特殊条目’.‘和’…'除外
dst_path="/code/" # 目标目录 dirs_ls=os.listdir(path=dst_path) # 获得指定目录下全部文件和文件夹名称列表 print(dirs_ls)- 1
- 2
- 3

2.2 os.path常见路径操作
2.2.1
os.path.abspath(path)返回路径path 的绝对路径(标准化的),相当于字符串拼接,路径path不存在也不会报错
relative_path="tests/test_steps_for_sliding_window_prediction.py" # 路径path存在 print("{}对应的绝对路径为{}".format(relative_path,os.path.abspath(relative_path)))- 1
- 2

no_path="tests/none.py" # 路径path不存在 print("{}对应的绝对路径为{}".format(relative_path,os.path.abspath(no_path)))- 1
- 2

2.2.2
os.path.basename(path)返回路径 path 的基本名称
full_pathname="/proc/bus/pci/3a/08.0" # 路径path存在 print("全路径名称对应的文件名为{}".format(os.path.basename(full_pathname)))- 1
- 2

no_full_pathname="/demo/none.cpp" # 路径path不存在 print("全路径名称对应的文件名为{}".format(os.path.basename(no_full_pathname)))- 1
- 2

2.2.3
os.path.dirname(path)返回路径 path 的目录名称
full_pathname="/proc/bus/pci/3a/08.0" # 路径path存在 print("全路径名称对应的目录名称为{}".format(os.path.dirname(full_pathname)))- 1
- 2

no_full_pathname="/demo/none.cpp" # 路径path不存在 print("全路径名称对应的目录名称为{}".format(os.path.dirname(no_full_pathname)))- 1
- 2

2.2.4
os.path.exists(path)判断path是否指向一个已存在路径或已打开的文件描述符,存在返回True,不存在返回False
full_pathname="/proc/bus/pci/3a/08.0" # 路径path存在 print("全路径名称对应的目录是否存在?{}".format(os.path.exists(full_pathname)))- 1
- 2

no_full_pathname="/demo/none.cpp" # 路径path不存在 print("全路径名称对应的目录是否存在?{}".format(os.path.exists(no_full_pathname)))- 1
- 2

2.2.5
os.path.isabs(path)判断path是否为一个绝对路径,是则返回True,不是或不存在则返回False。在 Unix 上,它就是以斜杠开头,而在 Windows 上,它可以是去掉驱动器号后以斜杠(或反斜杠)开头。
abs_pathname="/proc/bus/pci/3a/08.0" # 路径path存在 print("全路径名称对应的目录是否为绝对路径?{}".format(os.path.isabs(abs_pathname)))- 1
- 2

rel_pathname="./nnunet/__init__.py" # 路径path是相对路径 print("全路径名称对应的目录是否绝对路径?{}".format(os.path.isabs(rel_pathname)))- 1
- 2

no_pathname="./nnunet/none.py" # 路径path是不存在 print("全路径名称对应的目录是否绝对路径?{}".format(os.path.isabs(no_pathname)))- 1
- 2

2.2.6
os.path.isfile(path)若path为指向一个已存在文件的符号链接或一个已存在文件路径,返回True。若path为一个文件夹路径或不存在路径,返回False。
ls -li /opt/conda/bin/python* # 带inode节点信息并长格式查看python开头的文件和文件夹- 1

由上图可发现/opt/conda/bin/python为一个符号链接(软链接)指向一个已存在文件路径/opt/conda/bin/python3.7
abs_pathname="/opt/conda/bin/python3.7" # path为一个已存在文件路径 print("全路径名称对应的文件是否存在?{}".format(os.path.isfile(abs_pathname)))- 1
- 2

symbolic_link="/opt/conda/bin/python" # path为指向一个已存在文件/opt/conda/bin/python3.7的符号链接 print("全路径名称对应的文件是否存在?{}".format(os.path.isfile(symbolic_link)))- 1
- 2

abs_path="/opt/conda/bin/" # 文件夹路径 print("全路径名称对应的文件是否存在?{}".format(os.path.isfile(abs_path)))- 1
- 2

no_full_pathname="/demo/none.cpp" # 路径path不存在 print("全路径名称对应的文件是否存在?{}".format(os.path.isfile(no_full_pathname)))- 1
- 2

2.2.7
os.path.isdir(path)若path为指向一个已存在文件夹的符号链接或一个已存在文件夹路径,返回True。若path为一个文件路径或不存在路径,返回False。
ls /code/nnunet/ # 查看已存在文件夹路径/code/nnunet/- 1

ln -s /code/nnunet/ ./symlink2codennunet # 当前目录即root下创建一个软链接指向一个已存在文件夹路径/code/nnunet/- 1
ls -l /root/- 1

由上图可知root用户主目录下存在一个软链接symlink2codennunet指向一个已存在文件夹路径
exist_dir_path="/code/nnunet/"# path为一个已存在文件夹路径 print("全路径名称对应的文件夹是否存在?{}".format(os.path.isdir(exist_dir_path)))- 1
- 2

exist_dir_symlink="/root/symlink2codennunet/"# path为指向一个已存在文件夹的符号链接 print("全路径名称对应的文件夹是否存在?{}".format(os.path.isdir(exist_dir_symlink)))- 1
- 2

exist_file_path="/opt/conda/bin/python3.7"# path为一个已存在文件路径 print("全路径名称对应的文件夹是否存在?{}".format(os.path.isdir(exist_file_path)))- 1
- 2

no_path="/demo/none.cpp" # 路径path不存在 print("全路径名称对应的文件夹是否存在?{}".format(os.path.isdir(no_path)))- 1
- 2

2.2.8
os.path.islink(path)若path代表一个已存在的符号链接,则返回True,反之则返回False。如果 Python 运行时不支持符号链接,则总是返回 False
exist_symbolic_link="/opt/conda/bin/python" # path为指向一个已存在的符号链接 print("全路径名称对应的符号链接是否存在?{}".format(os.path.islink(exist_symbolic_link)))- 1
- 2

no_symbolic_link="/demo/no_link" # path为指向一个不存在的符号链接 print("全路径名称对应的符号链接是否存在?{}".format(os.path.islink(no_symbolic_link)))- 1
- 2

exist_file_path="/opt/conda/bin/python3.7"# path为一个已存在文件路径 print("全路径名称对应的符号链接是否存在?{}".format(os.path.islink(exist_file_path)))- 1
- 2

exist_dir_path="/root/"# path为一个已存在文件夹路径 print("全路径名称对应的符号链接是否存在?{}".format(os.path.islink(exist_dir_path)))- 1
- 2

2.2.9
os.path.join(path, *paths)拼接两个或多个路径部分,按需要插入
/。如果参数中某个部分是绝对路径,则绝对路径前的路径都将被丢弃,并从绝对路径部分开始连接。如果最后一部分为空,则结果将以分隔符结尾。previous_path,abs_dirname,basename,empty_part="model","/code","demo.py",""- 1
print("参数中某个部分是绝对路径拼接后为{}".format(os.path.join(previous_path,abs_dirname,basename)))- 1

print("拼接两个或多个路径部分,按需要插入'/'拼接后为{}".format(os.path.join(previous_path,basename)))- 1

print("最后一部分为空以分隔符结尾{}".format(os.path.join(previous_path,basename,empty_part)))- 1

2.2.10
os.path.normcase(path)规范路径名称的大小写。 在 Windows 上,将路径名称中的所有字符转为小写,并将正斜杠转为反斜杠。 在其他操作系统上,将路径不加修改地返回。
Linux操作系统
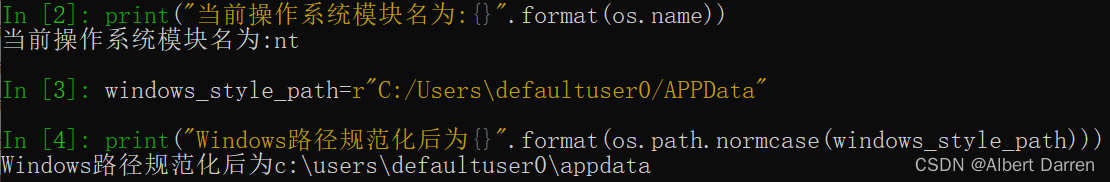
print("当前操作系统模块名为:{}".format(os.name)) windows_style_path=r"C:/Users\defaultuser0/APPData" print("Windows路径规范化后为{}".format(os.path.normcase(windows_style_path)))- 1
- 2
- 3

Windows操作系统
2.2.11
os.path.split(path)将路径 path 拆分为一对,即 (head, tail),其中,tail 是路径的最后一部分,而 head 里是除最后部分外的所有内容。tail 部分不会包含斜杠,如果 path 以斜杠结尾,则 tail 将为空。如果 path 中没有斜杠,head 将为空。如果 path 为空,则 head 和 tail 均为空。head 末尾的斜杠会被去掉,除非它是根目录(即它仅包含一个或多个斜杠)。
norm_path="/nnunet/configuration.py" # 一般路径 ends_with_slash_path="/code/nnunet/" # 以斜杠结尾的路径 no_slash_path="HIP_Logo.png" # 没有斜杠的路径 empty_path="" # 空路径 root_path="/" # 根目录 print("一般路径head={},tail={}".format(*os.path.split(norm_path))) print("以斜杠结尾的路径head={},tail={}".format(*os.path.split(ends_with_slash_path))) print("没有斜杠的路径head={},tail={}".format(*os.path.split(no_slash_path))) print("空路径head={},tail={}".format(*os.path.split(empty_path))) print("根目录head={},tail={}".format(*os.path.split(root_path)))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

2.2.12
os.path.splitext(path)将路径 path 拆分为一对,即 (root, ext),使 root + ext == path,其中 ext 为空或以英文句点开头,且最多包含一个句点。路径前的句点将被忽略,例如 splitext(‘.cshrc’) 返回 (‘.cshrc’, ‘’)。
dir_path="/code/nnunet/" # 文件夹路径 multi_dot_file_path="/code/i.thy.py" # 包含多个句点的文件路径 single_dot_file_path="/code/we.py" # 包含单个句点的文件路径 starts_with_dot_file_path=".bashrc" # 以句点开头的路径 print("文件夹路径root={},ext={}".format(*os.path.splitext(dir_path))) print("包含多个句点的文件路径root={},ext={}".format(*os.path.splitext(multi_dot_file_path))) print("包含单个句点的文件路径root={},ext={}".format(*os.path.splitext(single_dot_file_path))) print("以句点开头的路径root={},ext={}".format(*os.path.splitext(starts_with_dot_file_path)))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

2.3 其他常用命令
2.3.1
os.name导入的依赖特定操作系统的模块的名称,返回’posix’表示Linux,'nt’表示Windows,'java’表示Java虚拟机
print("当前操作系统平台名称为{}".format(os.name))- 1

2.3.2
os.__file__以字符串形式返回os模块安装的绝对路径
import os print("os模块安装绝对路径是{}".format(os.__file__))- 1
- 2

3. 参考文献
-
相关阅读:
html+css仿制小米商城首页
静态成员变量和成员函数
前端对普通数字数组排序示例
linux下安装 Chrome 和 chromedriver 以及 selenium webdriver 使用
Spring-IOC控制反转
E. Mishap in Club
.NET借助虚拟网卡实现一个简单异地组网工具
【OpenCV】—输入输出XML和YAML文件
MongoDB聚合运算符:$sinh
npm,registry,镜像源,npm切换源,yarn,cnpm,taobao,nrs
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46223009/article/details/128065092