-
2022.11.25Extended Traffic LightOJ - 1074
Dhaka city is getting crowded and noisy everyday. Certain roads always remain blocked for congestion. In order to convince people avoid shortest routes as it's the number one reason for roads crowded; the city authority has come up with a new plan.
Each junction of the city is marked with a positive integer (≤ 20) denoting the busy-ness of the junction. Whenever someone goes from one junction (the source junction) to another (the destination junction), the city authority gets an amount of money (busy-ness of destination - busy-ness of source)3 (that means the cube of the difference) from the traveler.
Now, the authority has appointed you to find the minimum total amount that can be earned when someone goes from a certain junction (the zero point) to several others.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 50), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case contains a blank line and an integer n (1 < n ≤ 200) denoting the number of junctions. The next line contains n integers denoting the busyness of the junctions from 1 to n respectively.
The next line contains an integer m, the number of roads in the city. Each of the next m lines (one for each road) contains two junction-numbers (source, destination) that the corresponding road connects (all roads are unidirectional). The next line contains the integer q, the number of queries. The next q lines each contain a destination junction-number. There can be at most one direct road from a junction to another junction.
Output
For each case, print the case number in a single line. Then print q lines, one for each query, each containing the minimum total earning when one travels from junction 1 (the zero point) to the given junction. However, for the queries that gives total earning less than 3, or if the destination is not reachable from the zero point, then print a
?.Sample
Inputcopy Outputcopy 2 5 6 7 8 9 10 6 1 2 2 3 3 4 1 5 5 4 4 5 2 4 5 2 10 10 1 1 2 1 2
Case 1: 3 4 Case 2: ?
原题链接:传送门
题意:给出n个点的权值(不超过20),点i到点j之间的距离(如果可达)为(a[j]-a[i])^3,求到点的最短路径
思路:有负环,所以选择spfa
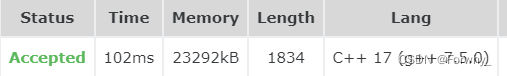
ps:反而stl要比数组模拟的循环队列快一点
- #include
- typedef long long ll;
- const int M = 1006;
- const int N = 1e6 + 9;
- bool st[N];
- int n, m;
- int dist[N], c[N], q[N], ft[N];
- int h[M], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
- void add(int a, int b, int c){
- e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
- }
- void spfa(){
- int hh = 0, tt = 0;
- memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
- memset(ft, 0, sizeof ft);
- dist[1] = 0;
- q[tt++] = 1;
- // std::queue
q; - // q.push(1);
- st[1] = true;
- ft[1] = 1;
- while (hh != tt /*q.size()*/){
- int t = q[hh++];
- if (hh == N) hh = 0;
- // int t = q.front();
- // q.pop();
- st[t] = false;
- for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
- int j = e[i];
- if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]){
- dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
- if (!st[j] && ft[j] <= n){
- ft[j]++;
- q[tt++] = j;
- // q.push(j);
- if (tt == N) tt = 0;
- st[j] = true;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- int t;
- scanf("%d", &t);
- int cnt = 1;
- while (t--){
- scanf("%d", &n);
- memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
- memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &c[i]);
- scanf("%d", &m);
- while (m--){
- int a, b;
- scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
- int vule = int(pow(c[b] - c[a], 3));
- add(a, b, vule);
- }
- spfa();
- // for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("%d ",dist[i]);
- // puts("");
- int h;
- scanf("%d", &h);
- printf("Case %d:\n", cnt++);
- while (h--){
- int x;
- scanf("%d", &x);
- if (dist[x] == 0x3f3f3f3f || dist[x] < 3 || ft[x] > n) printf("?\n");
- else printf("%d\n", dist[x]);
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }
- #include
- typedef long long ll;
- const int M = 1006;
- const int N = 1e6 + 9;
- bool st[N];
- int n, m;
- int dist[N], c[N] /*, q[N]*/, ft[N];
- int h[M], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
- void add(int a, int b, int c){
- e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
- }
- void spfa()
- {
- int hh = 0, tt = 0;
- memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
- memset(ft, 0, sizeof ft);
- dist[1] = 0;
- // q[tt ++ ] = 1;
- std::queue<int> q;
- q.push(1);
- st[1] = true;
- ft[1] = 1;
- while (q.size()){
- // int t = q[hh ++ ];
- // if (hh == N) hh = 0;
- int t = q.front();
- q.pop();
- st[t] = false;
- for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
- int j = e[i];
- if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]){
- dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
- if (!st[j] && ft[j] <= n){
- ft[j]++;
- // q[tt ++ ] = j;
- q.push(j);
- // if (tt == N) tt = 0;
- st[j] = true;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- int main(){
- int t;
- scanf("%d", &t);
- int cnt = 1;
- while (t--){
- scanf("%d", &n);
- memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
- memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &c[i]);
- scanf("%d", &m);
- while (m--){
- int a, b;
- scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
- int vule = int(pow(c[b] - c[a], 3));
- add(a, b, vule);
- }
- spfa();
- // for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("%d ",dist[i]);
- // puts("");
- int h;
- scanf("%d", &h);
- printf("Case %d:\n", cnt++);
- while (h--){
- int x;
- scanf("%d", &x);
- if (dist[x] == 0x3f3f3f3f || dist[x] < 3 || ft[x] > n) printf("?\n");
- else printf("%d\n", dist[x]);
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }
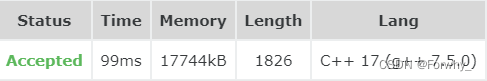
-
相关阅读:
flutter实现底部弹出框
HIVE数据导入ES并避免字段空值占用空间
浅谈以驱动为中心的运维架构
[二进制漏洞]PWN学习之格式化字符串漏洞 Linux篇
【软件测试】使用边界值分析法和等价类划分法计算佣金
【算法训练营】 - ⑨ 贪心算法
【无标题】
HDU - 2859 Phalanx(DP)
RTP GB28181 文件测试工具
2.6 PE结构:导出表详细解析
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_62802134/article/details/128059459
