-
【OpenCV-Python】教程:3-9 轮廓(2)轮廓特征
OpenCV Python 轮廓特征
【目标】
- 轮廓矩
- 轮廓周长、轮廓面积
- 轮廓拟合、轮廓凸包、轮廓凹凸性检查
- 外接矩形、最小包围圈
- 椭圆拟合、直线拟合
【代码】
- 周长、面积、矩

第一幅图像为原始轮廓图像,第二幅图像为轮廓点拟合图像(精度为周长的1/10),第三幅图像为轮廓点拟合图像(精度为周长的 5/1000)
import numpy as np import cv2 # 读入图像并二值化 img = cv2.imread('star1.png', 0) img_color = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 寻找轮廓,图像中第一个轮廓就是需要的轮廓, # 如果在其他程序中,需要根据一定条件进行筛选 # 图像矩可以计算一些特征,例如:物体的质心,物体的面积 # Cx = M10 / M00, Cy = M01 / M00 contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) cnt = contours[0] M = cv2.moments(cnt) print("星号的矩为:", M ) img_color0 = img_color.copy() cv2.drawContours(img_color0, [cnt], 0, (0, 128, 255), 3, maxLevel=0) cv2.imshow("contours-src", img_color0) # contour的面积可以直接使用 contourArea # 也可以用 M['m00'] 来获得 area = cv2.contourArea(cnt) print("星号的面积为:", area) # 输出周长 # 第二个参数如果为True,则为闭合的轮廓,否则为弧 perimeter = cv2.arcLength(cnt, True) print("星号的周长为:", perimeter) # 轮廓近似 # 用另一个更少点的形状去拟合原来的轮廓(使用算法为 道格拉斯-普克算法 , # 将曲线近似表示为一系列点,并减少点的数量的一种 算法) img_color1 = img_color.copy() epsilon = 0.1 * perimeter approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt, epsilon, True) cv2.drawContours(img_color1, [approx], 0, (0, 255, 0), 3, maxLevel=0) cv2.imshow("0.1-approxPolyDP", img_color1) # 拟合精度更高,需要的点回更多一些 img_color2 = img_color.copy() epsilon2 = 0.005 * perimeter approx2 = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt, epsilon2, True) cv2.drawContours(img_color2, [approx2], 0, (0, 255, 255), 3, maxLevel=0) cv2.imshow("0.005-approxPolyDP", img_color2) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
以上代码打印如下:
星号的矩为: {'m00': 130522.0, 'm10': 33632144.0, 'm01': 24005228.166666664, 'm20': 10974770282.666666, 'm11': 6224358011.416666, 'm02': 5406270574.5, 'm30': 4011914771313.0, 'm21': 2046283287276.75, 'm12': 1408108180508.5833, 'm03': 1363179635382.75, 'mu20': 2308636527.15621, 'mu11': 38831506.65739727, 'mu02': 991298544.2389975, 'mu30': -5751574310.887695, 'mu21': 7823576580.904053, 'mu12': 768507355.5574036, 'mu03': 4240497589.183838, 'nu20': 0.13551523513082395, 'nu11': 0.0022793803586064827, 'nu02': 0.058188482130994895, 'nu30': -0.0009344959758346628, 'nu21': 0.001271147765169143, 'nu12': 0.00012486442708533664, 'nu03': 0.000688981436808956} 星号的面积为: 130522.0 星号的周长为: 2386.9503506422043- 1
- 2
- 3
- 凸包

# 什么是凸包? # 凸: 凸对象内部任意两点连接所有点都在图像内部,则为凸对象,否则为非凸或凹对象。 # 包: 能够完全包住对象的最小形状 import numpy as np import cv2 # 读入灰度图像,并阈值化 image = cv2.imread("worldmap.png", 0) ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(image, 200, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV) # 寻找阈值图像的轮廓 contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # # 画出所有轮廓 map_color = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) cv2.drawContours(map_color, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 1) # 计算各个轮廓的凸包 hull = [] for i in range(len(contours)): hull.append(cv2.convexHull(contours[i], False)) # 创建一个黑色的画布 drawing = np.zeros((thresh.shape[0], thresh.shape[1], 3), np.uint8) # 画轮廓和凸包点 for i in range(len(contours)): color_contours = (0, 255, 0) # green - color for contours hullcolor = (0, 0, 255) # blue - color for convex hull # 画轮廓 cv2.drawContours(drawing, contours, i, color_contours, 1, 8, hierarchy) # 画凸包 cv2.drawContours(drawing, hull, i, hullcolor, 1, 8) cv2.imshow("drawing", drawing) cv2.imshow("map_color", map_color) cv2.imshow("thresh", thresh) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 拟合
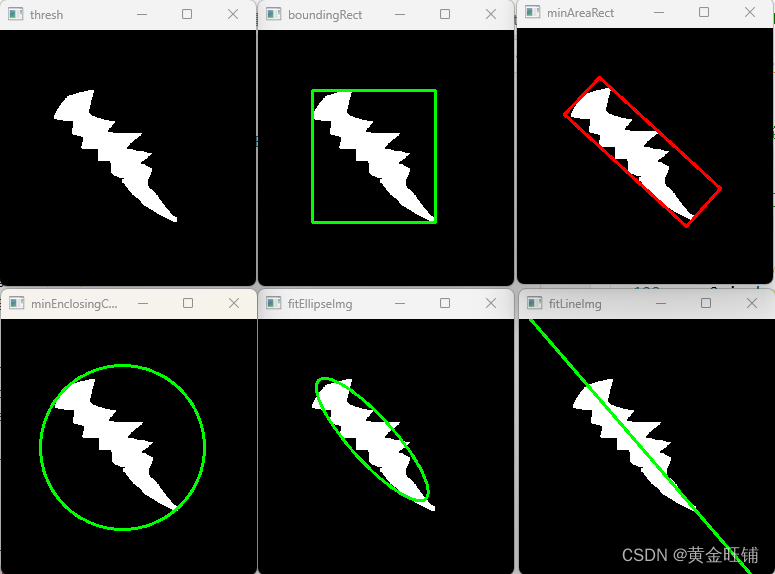
import numpy as np import cv2 # 读入灰度图像,并阈值化 image = cv2.imread("testfit.png", 0) ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(image, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) colorim = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) # 寻找阈值图像的轮廓 contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours( thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) cnt = contours[0] # 找到最小的外接矩形 boundingRectImg = colorim.copy() x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) cv2.rectangle(boundingRectImg, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2) # 找到最小倾斜矩形 minAreaRectImg = colorim.copy() rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt) box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) box = np.int0(box) cv2.drawContours(minAreaRectImg, [box], 0, (0, 0, 255), 2) # 最小圆拟合 minEnclosingCircleImg = colorim.copy() (x,y),radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(cnt) center = (int(x),int(y)) radius = int(radius) cv2.circle(minEnclosingCircleImg, center, radius, (0,255,0), 2) # 最小椭圆拟合 fitEllipseImg = colorim.copy() ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(cnt) cv2.ellipse(fitEllipseImg, ellipse, (0,255,0), 2) # 直线拟合 fitLineImg = colorim.copy() rows, cols = image.shape[:2] [vx, vy, x, y] = cv2.fitLine(cnt, cv2.DIST_L2, 0, 0.01, 0.01) lefty = int((-x*vy/vx) + y) righty = int(((cols-x)*vy/vx)+y) cv2.line(fitLineImg, (cols-1, righty), (0, lefty), (0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.imshow("thresh", thresh) cv2.imshow("boundingRect", boundingRectImg) cv2.imshow("minAreaRect", minAreaRectImg) cv2.imshow("minEnclosingCircleImg", minEnclosingCircleImg) cv2.imshow("fitEllipseImg", fitEllipseImg) cv2.imshow("fitLineImg", fitLineImg) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
【接口】
- moments
Moments cv::moments ( InputArray array, bool binaryImage = false );- 1
- 2
- 3
cv2.moments( array[, binaryImage] ) -> retval- 1
计算图像最高到三阶的所有矩;
- array: 数字化图像, 单通道, 8位或2D浮点矩阵或者 1xN 或者 Nx1 的二维点集
- binaryImage: 如果为真,则所有非零为1,该参数只适合图像。
- contourArea
double cv::contourArea ( InputArray contour, bool oriented = false );- 1
- 2
- 3
cv2.contourArea( contour[, oriented] ) -> retval- 1
计算一个轮廓的面积
- contour: 输入的2维点集的vector, 存储为 std::vector或者Mat
- oriented: 定向区域标志,如果为真,则返回有符号的面积值,可以通过值的正负来确定方向,一般情况下默认为false.
- arcLength
double cv::arcLength ( InputArray curve, bool closed );- 1
- 2
- 3
cv2.arcLength( curve, closed ) -> retval- 1
计算一个轮廓的周长或者一个曲线的弧长
- curve: 输入的2维点集的vector, 存储为 std::vector或者Mat
- closed: 表明曲线是否为闭合
- approxPolyDP
void cv::approxPolyDP ( InputArray curve, OutputArray approxCurve, double epsilon, bool closed );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
cv2.approxPolyDP( curve, epsilon, closed[, approxCurve] ) -> approxCurve- 1
近似拟合以一定精度拟合很多个点的曲线,道格拉斯-普克算法
- curve: 输入的2维点集的vector, 存储为 std::vector或者Mat
- approxCurve: 近似拟合的曲线结果
- epsilon: 精度
- closed: 如果为真,则为闭合的曲线,首尾相连
- convexHull
void cv::convexHull ( InputArray points, OutputArray hull, bool clockwise = false, bool returnPoints = true );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
cv2.convexHull( points[, hull[, clockwise[, returnPoints]]] ) -> hull- 1
找到点集的一个凸包
- points: 输入的2维点集的vector, 存储为 std::vector或者Mat
- hull: 输出的凸包点集
- clockwise: 方向标志,如果为真,则为顺时针
- returnPoints: 操作标记,在矩阵(二维图像)下,如果flag为真,则返回的是凸包点集,否则返回的是索引。当输出是 std::vector 时,该标记被忽略。std::vector implies returnPoints=false, std::vector implies returnPoints=true.
- boundingRect
Rect cv::boundingRect ( InputArray array )- 1
cv2.boundingRect( array ) -> retval- 1
计算一个灰阶图像中点集或非零像素的外接矩形
- array: 点集
- minAreaRect
RotatedRect cv::minAreaRect ( InputArray points );- 1
cv2.minAreaRect( points ) -> retval- 1
找二维点集的最小面积外接矩形(可能旋转的)
- points: 输入的2维点集的vector, 存储为 std::vector或者Mat
- boxPoints
void cv::boxPoints ( RotatedRect box, OutputArray points );- 1
- 2
- 3
cv2.boxPoints( box[, points] ) -> points- 1
找一个旋转矩形的四个顶点,用于画旋转矩形
- box: 旋转矩形
- points: 输出的4个顶点
- fitEllipse
RotatedRect cv::fitEllipse ( InputArray points )- 1
cv2.fitEllipse( points ) -> retval- 1
拟合二维点集的椭圆
- points: 输入的二维点集.
- minEnclosingCircle
void cv::minEnclosingCircle ( InputArray points, Point2f & center, float & radius );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
cv2.minEnclosingCircle( points ) -> center, radius- 1
计算一个二维点集最小的包围圆
- points: 输入的二维点集
- center: 输入的圆心
- radius: 输出的半径
- fitLine
void cv::fitLine ( InputArray points, OutputArray line, int distType, double param, double reps, double aeps );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
cv2.fitLine( points, distType, param, reps, aeps[, line] ) -> line- 1
直线拟合二维或者三维点集
- points: 输入的二维或者三维点集,存储为 std::vector<> or Mat.
- line: 输出的直线参数,如果是二维点集,则 (like Vec4f) - (vx, vy, x0, y0), where (vx, vy) is a normalized vector collinear to the line and (x0, y0) is a point on the line. In case of 3D fitting, it should be a vector of 6 elements (like Vec6f) - (vx, vy, vz, x0, y0, z0), where (vx, vy, vz) is a normalized vector collinear to the line and (x0, y0, z0) is a point on the line.
- distType: 距离计算的类型;
- param: Numerical parameter ( C ) for some types of distances. If it is 0, an optimal value is chosen.
- reps: 半径的精度(坐标轴中心到直线的距离)
- aeps: 角度的精度,0.01是一个比较好的默认值。

【参考】
-
相关阅读:
项目时间管理-架构真题(二十四)
感恩节跟进技巧(附邮件模板)
63:第五章:开发admin管理服务:16:开发【删除友情链接,接口】;(核心是:理解MongoDB,删除数据的逻辑)
如何给运行中的容器添加--restart=always
TypeError: RedLock is not a constructor.
sql语句创建数据库
1108 - 正整数N转换成一个二进制数
react路由传参3种方式
【数据结构】3000字剖析链表及双向链表
【学习笔记二十六】EWM 盘点后台配置和前台演示
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zhoujinwang/article/details/128009836