-
08_原始套接字
知识点1【原始套接字概述】
ubuntu12.04中描述网络协议结构的文件如下


在TCP/IP协议栈中的每一层为了能够正确解析出上层的数据包,从而使用一些“协议类型”来标记,详细如下图

组装/拆解udp数据包流程

1、UDP封包格式
 IP封包格式:
IP封包格式:
Ethernet封包格式

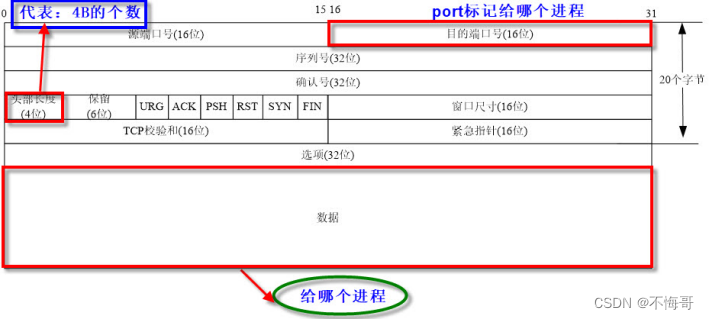
TCP封包格式:
ICMP封包格式:ping

知识点2【数据包的分析】
链路层数据格式

demo:recvfrom接受链路层帧数据


案例:网络分析器:
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<sys/socket.h>
- #include<netinet/ether.h>
- int main()
- {
- //1、 创建一个原始套接字 ETH_P_ALL收发任何数据类型
- int sockfd = socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL));
- if(sockfd < 0)
- {
- perror("socket");
- return 0;
- }
- printf("sockfd = %d\n", sockfd);
- //2、使用recvfrom接受网络数据 数据很多
- while(1)
- {
- //定义buf存放帧数据 大小1500 unsigned char
- unsigned char buf[1500]="";
- int len = recvfrom(sockfd, buf, sizeof(buf),0,NULL,NULL);
- printf("len = %d\n", len);
- //buf不要用%s遍历 帧数大多都是不识别的ASCII值 有太多的0x00
- //printf("buf=%s\n",buf);
- //sleep(1);//别sleep会丢失数据
- //解析buf-->mac头信息-->必须明白mac头的结构
- //1、mac头部:目的mac(6B) 源mac(6B) 类型(2B)
- //[mac][ip][tcp/udp][data] ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- char src_mac[18]="";
- char dst_mac[18]="";
- sprintf(dst_mac,"%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",\
- buf[0],buf[1],buf[2],buf[3],buf[4],buf[5]);
- sprintf(src_mac,"%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",\
- buf[0+6],buf[1+6],buf[2+6],buf[3+6],buf[4+6],buf[5+6]);
- printf("%s--->%s\n", src_mac, dst_mac);
- //判断mac头部中协议类型 0x0800 IP 0x0806 ARP 0x8035 RARP
- unsigned short mac_type = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)(buf+12));
- if( mac_type == 0x0800 )
- {
- printf("mac_type = %#x IP报文\n",mac_type);
- //2、分析IP头部
- unsigned char *ip_addr = buf+14;//+14跳过mac头
- //ip_addr跳到源IP的起始位置
- ip_addr += 12;
- char src_ip[16]="";
- char dst_ip[16]="";
- sprintf(src_ip,"%d.%d.%d.%d", \
- ip_addr[0],ip_addr[1],ip_addr[2],ip_addr[3]);
- ip_addr += 4;
- sprintf(dst_ip,"%d.%d.%d.%d", \
- ip_addr[0],ip_addr[1],ip_addr[2],ip_addr[3]);
- printf("%s--->%s\n",src_ip,dst_ip);
- //判断完成网路层的上一层协议类型
- ip_addr = buf+14;
- unsigned char *ip_type = ip_addr +9;
- if(*ip_type == 1)
- {
- printf("ICMP报文\n");
- }
- else if(*ip_type == 2)
- {
- printf("IGMP报文\n");
- }
- else if(*ip_type == 6)
- {
- printf("TCP报文\n");
- ip_addr = buf+14;//ip报文起始位置
- int ip_head_len = (*ip_addr&0x0f)*4;//提取ip报文的头部长度
- unsigned char *tcp_addr = buf+14+ip_head_len;
- unsigned src_port = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)tcp_addr);
- unsigned dst_port = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)(tcp_addr+2));
- printf("%hu--->%hu\n", src_port, dst_port);
- //调到tcp首部长度的位置
- unsigned char *tcp_headLen_addr = tcp_addr+12;
- int tcp_head_len = ((*tcp_headLen_addr>>4)&0x0f)*4;
- printf("TCP:%s\n", tcp_addr+tcp_head_len);
- }
- else if(*ip_type == 17)
- {
- printf("UDP报文\n");
- ip_addr = buf+14;//ip报文起始位置
- int ip_head_len = (*ip_addr&0x0f)*4;//提取ip报文的头部长度
- unsigned char *udp_addr = buf+14+ip_head_len;
- unsigned short src_port = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)udp_addr);
- unsigned short dst_port = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)(udp_addr+2));
- printf("%hu--->%hu\n", src_port, dst_port);
- printf("%s\n", udp_addr+8);//应用层数据
- }
- }
- else if(mac_type == 0x0806)
- {
- printf("mac_type = %#x ARP报文\n",mac_type);
- }
- else if(mac_type == 0x8035)
- {
- printf("mac_type = %#x RARP报文\n",mac_type);
- }
- }
- //关闭套接字
- close(sockfd);
- return 0;
- }
运行结果:


知识点2【混杂模式】接受数据(了解)
linux下设置
1、设置混杂模式:ifconfig eth0 promisc
2、取消混杂模式:ifconfig eth0 -promisc

linux下通过程序设置网卡混杂模式:

知识点3【原始套接字发送数据】sendto
- sendto(sock_raw_fd, msg, msg_len, 0,(struct sockaddr*)&sll, sizeof(sll));
- 注意:
- 1、sock_raw_fd:原始套接字
- 2、msg:发送的消息(封装好的协议数据)
- 3、sll:本机网络接口,指发送的数据应该从本机的哪个网卡出去,而不是以前的目的地址
- 想一想:
- 如何定义sll?

原始套接字:组帧数据报文----->从本机的哪块网卡sendto发出去
1、本机的接口地址结构
- #include
- struct sockaddr_ll sll;

只需要对sll.sll_ifindex赋值,就可使用
- sll.sll_ifindex=本地接口;//关键就是本地接口如何获得
- sendto(sock_raw_fd, msg, msg_len, 0,(struct sockaddr*)&sll, sizeof(sll));
2、获取我们的本地接口
通过ioctl来获取网络接口地址
- struct ifreq:#include
- IFNAMSIZ 16

ioctl参数对照表:

知识点4【案例:扫描mac地址 ARP】
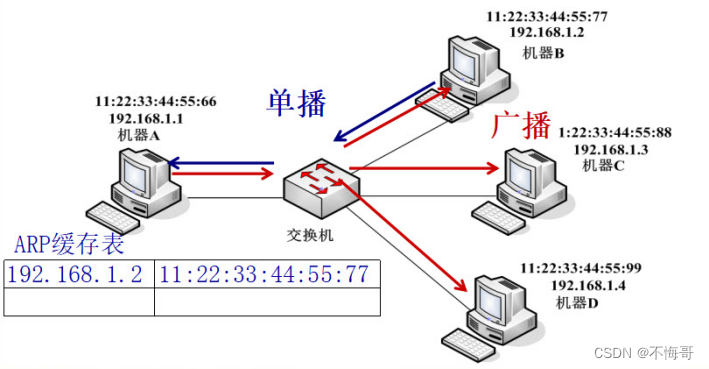
ARP概述
ARP(Address Resolution Protocol,地址解析协议)
1、是TCP/IP协议族中的一个
2、主要用于查询指定ip所对应的的MAC
3、请求方使用广播来发送请求
4、应答方使用单播来回送数据
5、为了在发送数据的时候提高效率在计算中会有一个ARP缓存表,用来暂时存放ip所对应的MAC,在linux中使用ARP即可查看,在xp中使用ARP -a
在linux与xp系统下查看ARP的方式:

以机器A获取机器B的MAC为例:
ARP协议格式:

-
相关阅读:
IDEA gradle新增依赖报Could not resolve symbol “XXX“错误
【TensorFlow深度学习】张量Broadcasting机制与数学运算实践
Redis-cluster集群详细部署配置--有手就行
跳动的爱心源码
嵌入式系统,典型嵌入式系统基本组成,微处理器,嵌入式微处理器,嵌入式软硬件裁减原则,嵌入式实时操作系统
rabbitMQ 面试题
Jetson Nano TensorRT C++加速 YOLOV5,集成进qt项目中
图像配准之图像重采样
如何使用chorme版本对应的ChromeDriver(不用更改Chrome版本)
用ChatGPT+Midjourney 5分钟生成30条爆款小红书图文(内有详细教程)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/buhuidage/article/details/127952882
