-
Flink的六种物理分区策略
😃😃😃😃😃
更多资源链接,欢迎访问作者gitee仓库:https://gitee.com/fanggaolei/learning-notes-warehouse/tree/master
物理分区(Physical Partitioning)
为了同keyBy相区别,我们把这些操作统称为“物理分区”操作。物理分区与keyBy另一大区别在于,keyBy之后得到的是一个KeyedStream,而物理分区之后结果仍是DataStream,且流中元素数据类型保持不变。从这一点也可以看出,分区算子并不对数据进行转换处理,只是定义了数据的传输方式。
🍕1.随机分区(shuffle)
最简单的重分区方式就是直接“洗牌”。通过调用DataStream的.shuffle()方法,将数据随机地分配到下游算子的并行任务中去。
随机分区服从均匀分布(uniform distribution),所以可以把流中的数据随机打乱,均匀地传递到下游任务分区。因为是完全随机的,所以对于同样的输入数据, 每次执行得到的结果也不会相同。=

package com.fang.chapter05; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; public class ShuffleTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建执行环境 StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements( new Event("Marry", "./home", 1000L), new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=1", 1000L), new Event("Li", "./home", 3500L), new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=2", 3200L), new Event("Marry", "./home", 1200L), new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=3", 110L), new Event("Anna", "./home", 3550L), new Event("Li", "./prod?id=4", 3210L) ); //经洗牌后打印输出,并行度为 4 stream.shuffle().print("shuffle").setParallelism(4); env.execute(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27

🍔2.轮询分区(Round-Robin)
轮询也是一种常见的重分区方式。简单来说就是“发牌”,按照先后顺序将数据做依次分发。通过调用DataStream的.rebalance()方法,就可以实现轮询重分区。rebalance 使用的是Round-Robin负载均衡算法,可以将输入流数据平均分配到下游的并行任务中去。

package com.fang.chapter05; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; public class ShuffleTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建执行环境 StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements( new Event("Marry", "./home", 1000L), new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=1", 1000L), new Event("Li", "./home", 3500L), new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=2", 3200L), new Event("Marry", "./home", 1200L), new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=3", 110L), new Event("Anna", "./home", 3550L), new Event("Li", "./prod?id=4", 3210L) ); // 经轮询重分区后打印输出,并行度为 4 stream.rebalance().print("rebalance").setParallelism(4); //stream.print("rebalance").setParallelism(4);//默认使用 env.execute(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30

🍟3. 重缩放分区(rescale)
重缩放分区和轮询分区非常相似。当调用rescale()方法时,其实底层也是使用Round-Robin 算法进行轮询,但是只会将数据轮询发送到下游并行任务的一部分中。也就是说,“发牌人”如果有多个,那么rebalance的方式是每个发牌人都面向所有人发牌;而rescale 的做法是分成小团体,发牌人只给自己团体内的所有人轮流发牌。

package com.fang.chapter05; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.RichParallelSourceFunction; public class ShuffleTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建执行环境 StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.addSource(new RichParallelSourceFunction<Integer>() { @Override public void run(SourceContext<Integer> sourceContext) throws Exception { for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { // 将奇数发送到索引为 1 的并行子任务 // 将偶数发送到索引为 0 的并行子任务 if ((i + 1) % 2 == getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask()) { sourceContext.collect(i + 1); } } } @Override public void cancel() { } }).setParallelism(2).rescale().print().setParallelism(4); env.execute(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32

🌭4.广播(broadcast)
这种方式其实不应该叫做“重分区”,因为经过广播之后,数据会在不同的分区都保留一份,可能进行重复处理。可以通过调用DataStream的broadcast()方法,将输入数据复制并发送到下游算子的所有并行任务中去。
package com.fang.chapter05; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; public class ShuffleTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建执行环境 StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.setParallelism(1); // 读取数据源,并行度为 1 DataStreamSource<Event> stream = env.fromElements( new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L), new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L), new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=1", 5 * 1000L), new Event("Cary", "./home", 60 * 1000L) ); // 经广播后打印输出,并行度为 4 stream.broadcast().print("broadcast").setParallelism(4); env.execute(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24

🥙5.全局分区
全局分区也是一种特殊的分区方式。这种做法非常极端,通过调用.global()方法,会将所有的输入流数据都发送到下游算子的第一个并行子任务中去。这就相当于强行让下游任务并行度变成了 1,所以使用这个操作需要非常谨慎,可能对程序造成很大的压力。
package com.fang.chapter05; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; public class ShuffleTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建执行环境 StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.setParallelism(1); // 读取数据源,并行度为 1 DataStreamSourcestream = env.fromElements( new Event("Mary", "./home", 1000L), new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L), new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=1", 5 * 1000L), new Event("Cary", "./home", 60 * 1000L) ); // 经广播后打印输出,并行度为 4 stream.global().print().setParallelism(4); env.execute(); } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24

🫔6.自定义分区
当 Flink 提 供 的 所 有 分 区 策 略 都 不 能 满 足 用 户 的 需 求 时 , 我 们 可 以 通 过 使 用partitionCustom()方法来自定义分区策略。
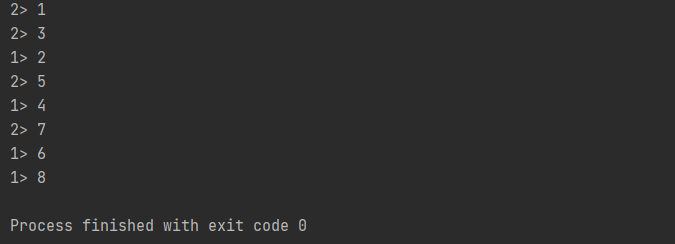
在调用时,方法需要传入两个参数,第一个是自定义分区器(Partitioner)对象,第二个是应用分区器的字段,它的指定方式与 keyBy 指定 key 基本一样:可以通过字段名称指定,也可以通过字段位置索引来指定,还可以实现一个 KeySelectorpackage com.fang.chapter05; import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.Partitioner; import org.apache.flink.api.java.functions.KeySelector; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; public class ShuffleTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建执行环境 StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.fromElements(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8) .partitionCustom(new Partitioner<Integer>() { @Override public int partition(Integer key, int numPartitions) { return key % 2; } }, new KeySelector<Integer, Integer>() { @Override public Integer getKey(Integer value) throws Exception { return value; } }) .print().setParallelism(2); env.execute(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
-
相关阅读:
Django日志配置
个人电影网站web网页设计制作—— 影视公司5页 DIV+CSS制作 浮动布局
《网络安全笔记》第十一章:物理层
第十七章《MySQL数据库及SQL语言简介》第6节:数据查询
软件工程与计算总结(十七)软件构造
Unity微信小游戏登录授权获取用户信息
深入理解JVM - 内存区域介绍(抄录整理)
python练习题集锦之一
C语言生成随机数、C++11按分布生成随机数学习
【lesson13】进程地址空间收尾
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_58022371/article/details/127901046