-
C++ 继承
面向对象的四大特点:抽象、封装、继承、多态。其中抽象、封装分别对应类、对象。
1、概念
继承指的是在既有类的基础上产生新的类。
1.1、派生类的生成
派生类的生成过程
- 吸收基类的成员
- 改造基类的成员
- 添加自己新的成员
1.2、继承的局限性
不能继承的基类特征
- 构造函数
- 析构函数
- 用户重载的
operator new|delete运算符 - 用户重载的
operator=赋值运算符 - 友元关系
1.3、继承方式
三种继承方式
- public:公有成员,在本类、派生类和外部都可访问。
- protected:保护成员,只能在本类和派生类中访问,是一种区分血缘关系内外有别的成员。
- private:私有成员,默认方式,只能被本类的成员函数访问,派生类和类外都不能访问。
总结:派生类的访问权限,不管以什么继承方式
- 基类中的私有成员都不能在派生类中访问
- 基类中的非私有成员都可以在派生类中访问。
- 派生类对象只能访问基类中的共有成员,其他都不能访问。
2、派生类单继承
2.1、对象创建
派生类构造函数的特点
- 形式:派生类构造函数的初始化列表中显示调用基类的构造函数
- 特点:先初始化基类部分,再初始化派生类部分。
- 原因:构造函数和析构函数不能继承,为了初始化数据成员,派生类必须定义构造函数和析构函数。由于派生类包含基类数据成员,因此,创建派生类对象必须先通过派生类的构造函数来调用基类的构造函数,完成基类成员初始化,然后对派生类成员进行初始化。
例如:
class Derived: public Base { public: Derived(long base, long derived) : Base(base) // 显示调用基类的构造函数 , _derived(derived) {} long _derived; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
派生类构造函数的调用顺序
- 首先初始化基类成员
- 其次初始化派生类特殊成员:对象成员、引用成员、const 成员、static 成员
- 最后执行派生类的构造函数体
2.2、对象销毁
与对象创建顺序相反,在执行派生类析构函数时,基类析构函数会被自动调用。执行顺序是先执行派生类的析构函数,再执行基类的析构函数
- 先调用派生类的析构函数
- 再调用派生类中成员对象的析构函数
- 最后调用普通基类的析构函数
3、派生类多继承
3.1、对象创建
单即继承和多基继承的派生类构造函数功能没有本质不同,首先要执行所有基类的构造函数,再执行派生类构造函数初始化列表中的其他内容,最后是构造函数体。
注意:各基类构造函数的执行顺序与其在初始化表中的顺序无关,而是由定义派生类时指定的基类顺序决定的。
3.2、对象销毁
析构函数的执行顺序同样是与构造函数的执行顺序相反。但在使用多基继承过程中,会产生两种二义性。
3.3、多继承的问题
3.3.1、成员名冲突二义性
- 概念:多个基类存在同名成员,编译器无法判断要访问哪个基类的成员。
- 解决:通过类名来访问一个类的成员,例:
A::print()
3.3.2、存储二义性(菱形继承)
菱形继承
- 概念:多基派生,多条继承路径上有一个共同的基类,D 对象有共同基类 A 的双重拷贝。
- 解决:虚拟继承
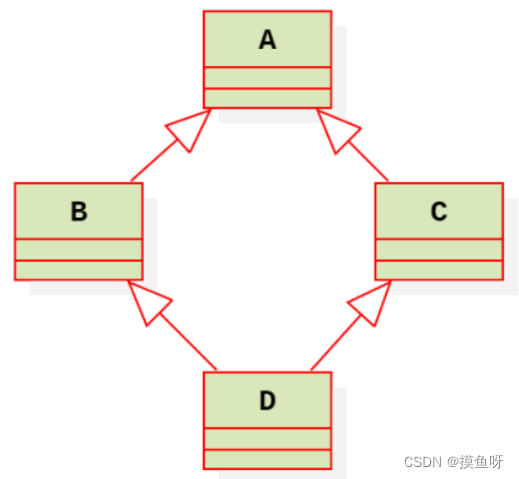
class B: virtual public A // 1个虚基指针 + 数据 class C: virtual public A // 1个虚基指针 + 数据 class D: public B, public C // 2个虚基指针 + 数据- 1
- 2
- 3
4、基类与派生类的转化
4.1、派生类转化为基类
派生类适应于基类,派生类对象能直接用于基类对象的场景,具体形式为:
- 派生类的对象赋值给基类的对象
- 基类的引用绑定到派生类的对象
- 基类的指针指向派生类的对象(向上转型)
// 1、派生类的对象赋值给基类的对象 base = derived; base.operator=(derived); // 2、基类的引用绑定到派生类的对象 const Base &ref = derived; // 3、基类的指针指向派生类的对象 Base *pbase = &derived;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4.2、基类转换为派生类
向上转型与向下转型
- 向上转型:安全,派生类指针转化为基类指针,
Base *pbase = &derived; - 向下转型:不安全,基类指针转化为派生类指针。此时,新的指针多控制了内存,可能存在内存越界问题。
例:
// 不安全的向下转型:直接将 base 指针转换为 derived 指针 // base 8B, derived 16B,新的指针多控制了 8B,可能存在内存越界的问题 Derived *pderived = static_cast<Derived *>(&base); // 安全的向下转型 Base *pbase = &derived; // base 指针指向派生类对象,先向上转型 Derived *pderived = static_cast<Derived *>(pbase); // 再向下转型- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
5、派生类对象间的复制控制
原则:先构造基类部分,后构造派生类部分
派生类对象的复制控制
- 派生类没有显示定义复制控制函数,则会自动调用基类相应的复制控制函数,不管基类是否有显示定义。
- 派生类有显示定义复制控制函数,那么基类部分不会再自动调用相应的复制控制函数,若要调用基类的复制控制函数需要手动调用。
测试代码:
#include#include using std::cout; using std::endl; class Base { public: Base() : _pbase(nullptr) { cout << "Base()" << endl; } Base(const char *pbase) : _pbase(new char[strlen(pbase) + 1]()) { cout << "Base(const char *)" << endl; strcpy(_pbase, pbase); } Base(const Base &rhs) : _pbase(new char[strlen(rhs._pbase) + 1]()) { cout << "Base(const Base &)" << endl; strcpy(_pbase, rhs._pbase);; } Base &operator=(const Base &rhs) { cout << "Base &operator=(const Base &)" << endl; if(this != &rhs) { delete [] _pbase; _pbase = nullptr; _pbase = new char[strlen(rhs._pbase) + 1](); strcpy(_pbase, rhs._pbase); } return *this; } ~Base() { cout << "~Base()" << endl; if(_pbase) { delete [] _pbase; _pbase = nullptr; } } friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Base &rhs); private: char *_pbase; }; std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Base &rhs) { if(rhs._pbase) { os << rhs._pbase; } return os; } class Derived : public Base { public: Derived() : Base() , _pderived(nullptr) { cout << "Derived()" << endl; } Derived(const char *pbase, const char *pderived) : Base(pbase) , _pderived(new char[strlen(pderived) + 1]()) { cout << "Derived(const char *)" << endl; strcpy(_pderived, pderived); } Derived(const Derived &rhs) : Base(rhs) // 显示调用基类的构造函数 , _pderived(new char[strlen(rhs._pderived) + 1]()) { cout << "Derived(const Derived &)" << endl; strcpy(_pderived, rhs._pderived); } Derived &operator=(const Derived &rhs) { cout << "Derived &operator=(const Derived &)" << endl; if(this != &rhs) { Base::operator=(rhs); // 显示调用基类的赋值运算符函数 delete [] _pderived; _pderived = nullptr; _pderived = new char[strlen(rhs._pderived) + 1](); strcpy(_pderived, rhs._pderived); } return *this; } ~Derived() { cout << "~Derived()" << endl; if(_pderived) { delete [] _pderived; _pderived = nullptr; } } friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Derived &rhs); private: char *_pderived; }; std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Derived &rhs) { // const引用指向const对象,基类的引用绑定到派生类的对象 const Base &ref = rhs; // <<重载(基类、派生类) os << ref << ", " << rhs._pderived; return os; } int main() { Derived d1("hello", "world"); cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl; cout << endl; Derived d2 = d1; cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl; cout << "d2 = " << d2 << endl; cout << endl; Derived d3("hubei", "wuhan"); cout << "d3 = " << d3 << endl; d3 = d1; cout << "d1 = " << d1 << endl; cout << "d3 = " << d3 << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
-
相关阅读:
JVM调优-JProfiler
JavaScript将页面里的图标或者按钮改成可拖动的
时序预测 | MATLAB实现POA-CNN-LSTM鹈鹕算法优化卷积长短期记忆神经网络时间序列预测
express学习30-多人管理22验证joi
Kafka消费者重平衡
计算机基础--Git
Rasa Core实践 报时机器人
python面向对象编程:类和对象
df -h 显示/根目录占100%
vue.js毕业设计,基于vue.js前后端分离外卖点餐小程序系统设计与实现
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/you_fathe/article/details/127898189
