-
八数码问题
八数码问题
我想大家小时候一定玩过八数码的游戏,如下图:在一个九宫格里面放入8个数字,数字只能上下左右移动,并且只能移动到空白处。通过若干此移动后,能把数字移动成图1.1右方所示图案。

图1.1(左边为开始格局,右边为移动后最终格局
下图是图1.1下一个格局的三种情况:

如果按正常的思维,采用盲目搜索的话,不仅搜索的次数多,而且往往容易陷入死循环中,所以面对此问题需要一种策略——启发式搜索
启发式搜索:启发式搜索就是在状态空间中的搜索对每一个搜索的位置进行评估,得到最好的位置,再从这个位置进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无谓的搜索路径,提高了效率
解决此问题的启发策略:
每次移动的时候,正确位置数码的个数要大于交换前正确位置数码个数。
正确位置数码个数:每个数码的位置与最终格局的对比,如果位置相同,则说明此数码在正确位置。
如下图:
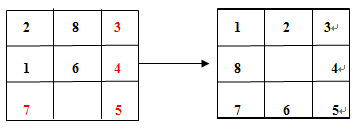
图1.3
图1.3中右边为最终格局,左边为当前格局,红色字体标识的数码为 正确位置数码,由此可以发现其正确位置的数码个数为4个。那么图1.2中正确数码如下图所示:
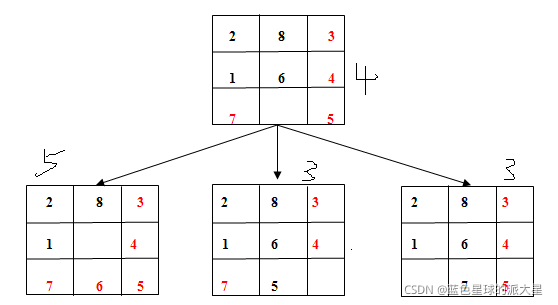
由上图所示可得,正确位置数码个数大于等于4的只有左下方的格局,那么下一步选择的就是左下方的格局,再次调用次算法如下图:

这样一步步的最终即可得到最终格局
BFS+Cantor 解决方法- #include
- const int LEN = 362880; //状态共9!=362880种
- using namespace std;
- struct node
- {
- int state[9]; //记录一个八数码的排列,即一个状态
- int dis; //记录到起点的距离
- };
- int dir[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}};
- //左,上,右,下顺时针方向,左上角的坐标是(0,0)
- int visited[LEN] = {0}; //与每个状态对应的记录,Cantor()函数对它置数,并判重
- int start[9]; //开始状态
- int goal[9]; //目标状态
- long int factory[] = {1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880}; // Cantor()用到的常数 即阶乘
- //用康托展开判重
- bool Cantor(int str[], int n)
- {
- long result = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- int counted = 0;
- for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
- {
- //当前未出现的元素排在第几个
- if (str[i] > str[j])
- ++counted;
- }
- result += counted * factory[n - i - 1];
- }
- if (!visited[result]) //没有被访问过
- {
- visited[result] = 1;
- return 1;
- }
- else
- return 0;
- }
- int bfs()
- {
- node head;
- memcpy(head.state, start, sizeof(head.state)); //复制起点的状态
- head.dis = 0;
- queue
q; //队列中的内容是记录状态 - Cantor(head.state, 9); //用康托展开判重,目的是对起点的visited[]赋值
- q.push(head); //第一个进队列的是起点状态
- while (!q.empty()) //处理队列
- {
- head = q.front();
- q.pop(); //可在此处打印head.state,看弹出队列的情况
- int z;
- for (z = 0; z < 9; z++) //找到这个状态中元素0的位置
- {
- if (head.state[z] == 0) //找到了
- break;
- }
- int x = z % 3; //横坐标
- int y = z / 3; //纵坐标
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) //上,下,左,右最多可能有4个新状态
- {
- int newx = x + dir[i][0]; //元素0转移后的新坐标
- int newy = y + dir[i][1];
- int nz = newx + 3 * newy; //转化为一维
- if (newx >= 0 && newx < 3 && newy >= 0 && newy < 3) //未越界
- {
- node newnode;
- memcpy(&newnode, &head, sizeof(struct node)); //复制这个新状态
- swap(newnode.state[z], newnode.state[nz]); //把0移动到新的位置
- newnode.dis++;
- if (memcmp(newnode.state, goal, sizeof(goal)) == 0) //与目标状态对比
- return newnode.dis; //到达目标状态,返回距离,结束
- if (Cantor(newnode.state, 9)) //用康托展开判重
- q.push(newnode); //把新的状态放入队列
- }
- }
- }
- return -1; //没找到
- }
- int main()
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) //初始状态
- cin >> start[i];
- for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) //目标状态
- cin >> goal[i];
- int num = bfs();
- if (num != -1)
- cout << num << endl;
- else
- cout << "Impossible" << endl;
- return 0;
- }
A* + Set 解决方法- #include
- using namespace std;
- const int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
- int fx, fy;
- char ch;
- struct Matrix
- {
- int e[5][5];
- bool operator<(Matrix x) const
- {
- for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
- for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++)
- if (e[i][j] != x.e[i][j])
- return e[i][j] < x.e[i][j];
- return false;
- }
- } first, standard;
- // 函数h可以定义为,不在应该在的位置的数字个数。
- // 容易发现h满足以上两个性质,此题可以使用 A*算法求解。
- int h(Matrix m)
- {
- int ret = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
- for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++)
- if (m.e[i][j] != standard.e[i][j])
- ret++;
- return ret;
- }
- struct node
- {
- Matrix matrix;
- int t;
- bool operator<(node x) const { return t + h(matrix) > x.t + h(x.matrix); }
- } x;
- priority_queue
qu; //搜索队列 - set
st; //防止搜索队列重复 - int main()
- {
- standard.e[1][1] = 1; //定义标准表
- standard.e[1][2] = 2;
- standard.e[1][3] = 3;
- standard.e[2][1] = 8;
- standard.e[2][2] = 0;
- standard.e[2][3] = 4;
- standard.e[3][1] = 7;
- standard.e[3][2] = 6;
- standard.e[3][3] = 5;
- for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) //输入
- for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++)
- {
- scanf(" %c", &ch);
- first.e[i][j] = ch - '0';
- }
- qu.push({first, 0});
- while (!qu.empty())
- {
- x = qu.top();
- qu.pop();
- if (!h(x.matrix))
- { //判断是否与标准矩阵一致
- printf("%d\n", x.t);
- return 0;
- }
- for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
- for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++)
- if (!x.matrix.e[i][j])
- fx = i, fy = j; //如果该点上的数不为0
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
- { //对四种移动方式分别进行搜索
- int xx = fx + dx[i], yy = fy + dy[i];
- if (1 <= xx && xx <= 3 && 1 <= yy && yy <= 3)
- {
- swap(x.matrix.e[fx][fy], x.matrix.e[xx][yy]);
- if (!st.count(x.matrix))
- st.insert(x.matrix),
- qu.push({x.matrix, x.t + 1}); //这样移动后,将新的情况放入搜索队列中
- swap(x.matrix.e[fx][fy], x.matrix.e[xx][yy]); //如果不这样移动的情况
- }
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }
-
相关阅读:
(11)点云数据处理学习——Colored point cloud registration(彩色点注册)
密码学技术总结
[杂记]C++中关于虚函数的一些理解
Vue笔记之入门
采用策略分布曲线评估信用风险模型的效果
2023计算机毕业设计题目 毕设选题大全
【jQuery Demo】图片瀑布流实现
分布式 PostgreSQL 集群(Citus)官方示例 - 多租户应用程序实战
springboot集成Redis
javacc之路5---词法分析器技巧
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_61983575/article/details/127823502
