-
AQS之CountDownLatch分析 (八)
1.CountDownLatch 介绍
CountDownLatch即减少计数,是AQS共享锁的另一个经典应用。其应用主要是一个(或多个)线程等待一系列线程完成某些操作后才继续向下执行的场景。
换种程序上的描述:A线程申请资源await,进行阻塞等待,一系列线程进行某些操作(共state个),每完成一个释放一次资源coutDown。所有操作完成后,A线程资源获取成功,继续向下执行。

2.实例代码
6个线程全部离开后, 进行main线程
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 减少计数 CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6); for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { new Thread(()->{ countDownLatch.countDown(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "号离开"); }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); } countDownLatch.await(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "班长离开"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16

3.源码分析
3.1 构造器
CountDown只有一个构造方法
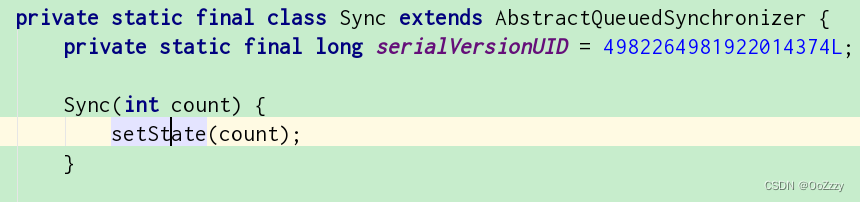
public CountDownLatch(int count),用于设置AQS的state,这儿一般称呼为count,即任务数。public CountDownLatch(int count) { if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0"); this.sync = new Sync(count); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

3.2 获取资源 await
public void await() throws InterruptedException { sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1); } public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException(); if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
尝试去获取资源, 如果可以的话, 那么执行获取资源的操作
tryAcquireShared

判断count是否为0, 为0的话任务全部完成, 不为0返回-1, 任务没有全部完成。这里返回的是1和-1,没有0, 因为成功的时候其他线程申请资源也是成功的。
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); boolean failed = true; try { for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head) { int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); if (r >= 0) { setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return; } } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) throw new InterruptedException(); } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
和之前的ReentrantLock 逻辑大致。
3.3 释放资源 countDown
public void countDown() { sync.releaseShared(1); }- 1
- 2
- 3

尝试释放资源, 如果可以, 执行释放资源的操作
tryReleaseShared
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) { // Decrement count; signal when transition to zero for (;;) { int c = getState(); if (c == 0) return false; int nextc = c-1; if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) return nextc == 0; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
对count进行减1。
doReleaseShared
private void doReleaseShared() { for (;;) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h != tail) { int ws = h.waitStatus; if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0)) continue; // loop to recheck cases unparkSuccessor(h); } else if (ws == 0 && !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE)) continue; // loop on failed CAS } if (h == head) // loop if head changed break; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
通过判断waitStatus进行不同的操作, 如果为-1, 通过cas换为0, 然后
unparkSuccessor, 如果为0的话, 重复操作。线程调用该方法后,计数器的值将递减,如果计数器值为 0, 则唤醒所有因调用 await 方法而被阻塞的线程,否则什么都不做。
3.4 源码总结
当多个线程调动 countDown() 时实际是原子性递减 AQS 的状态值。当调用 await() 后当前线程会被放入 AQS 的阻塞队列等待计数器为0 再返回。
其它线程调用 countDown() 让计数器递减1,当计数器值变为0时,当前线程还要调用 AQS 的 doReleaseShared 来激活由于调用 await() 而被阻塞的线程。
-
相关阅读:
今天是个好日子,TaxCore(POS软件)备案指北
持续集成如何进行Jenkins管理?
在云服务器上安装VNC远程桌面服务
Excelpoi导入导出--上完整代码!
【Java 进阶篇】MySQL启动与关闭、目录结构以及 SQL 相关概念
如何使用Tushare+ Backtrader进行股票量化策略回测
【无标题】
概率论与数理统计
【2024最新华为OD-C/D卷试题汇总】[支持在线评测] 游乐园门票 (200分) - 三语言AC题解(Python/Java/Cpp)
弘辽科技:淘宝9月什么时候有活动?99大促有哪些活动?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43141726/article/details/127798367
