-
Ansible教程
一、Ansible基础
1.环境准备
主机列表按照以上要求准备6台机器,最小化安装RHEL8,可以先安装一台Control,配置主机名,IP,yum源等等,其他的5台机器直接使用Control克隆,更改主机名和IP。172.16.11.1 control 172.16.11.2 node1 172.16.11.3 node2 172.16.11.4 node3 172.16.11.5 node4 172.16.11.6 node5 2.修改hosts文件
[root@control ~]# vim /etc/hosts172.16.11.1 control 172.16.11.2 node1 172.16.11.3 node2 172.16.11.4 node3 172.16.11.5 node4 172.16.11.6 node5- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

3.配置ssh密钥
[root@control ~]# ssh-keygen -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa
[root@control ~]# for i in node{1…5}; do ssh-copy-id $i; done
[root@control ~]# ssh node1 #以node1为例,测试ssh免密登录4.部署软件(control节点)
yum install epel-release -y yum install ansible -y ansible --version #查看版本- 1
- 2
- 3

二、Ansible基本配置
1.主配置文件:/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
[root@control ~]# mkdir ~/ansible
[root@control ~]# cd ~/ansible
[root@control ansible]# vim ansible.cfg
[defaults]
inventory = ~/ansible/hosts #主机清单配置文件

2.iventory主机清单文件,参考/etc/ansible/hosts
[root@control ansible]# vim hosts
[test] #定义主机组(组名随意)
node1 #定义组中的具体主机[proxy]
node2[webserver]
node[3:4][database]
node5[cluster:children] #嵌套组(children为关键字,不能改变)
webserver
database3.测试Ansible环境与配置是否正常
[root@control ansible]# ansible all --list-hosts #all,查看所有主机列表

[root@control ansible]# ansible node1 -m ping #调用ping模块,ping一个主机
[root@control ansible]# ansible webserver -m ping #ping一个组
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1,webserver -m ping #ping 主机或者组
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m ping #多个主机
[root@control ansible]# ansible webserver,test -m ping #多个组三、Ansible ad-hoc命令行
1.命令行语法格式
Ansible ad-hoc是一种通过命令行批量管理的方式
格式: ansible 主机集合 -m模块名 -a "参数”
其他选项:k使用密码远程、-i指定主机列表文件[root@control ansible]# ansible node1 -m ping #调用ping模块
默认模块为command,把linux操作系统中所有可以执行的命令,传递给被管理主机,之执行命令
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1 -m command -a “uptime”
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1 -m command -a “uname -r”
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1 -a “ip a s”
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -a “date”2.如何获取帮助
[root@control ansible]# ansible-doc -l #列出所有模块
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-doc -l | wc -l # 统计模块
[root@control ansible]# ansible-doc -l | grep yum #过滤模块
[root@control ansible]# ansible-doc yum #查看模块帮助四、ansible常用模块应用案例(上)
1.Shell 模块
command不支持bash特性,如管道和重定向等功能所有需要调用shell的功能都无法使用。
[root@control ~]# cd ~/ansible
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1 -m command -a ‘ps &’ #报错
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1 -m command -a ‘ps > a.txt’ #报错
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1 -m command -a ‘ps aux | wc -l’ #报错
shell模块会启动shell执行命令,不可以使用shell模块执行交互命令,如vim,top等[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a ‘ps aux | wc -l’ #成功
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a ‘touch /tmp/123.txt’ #创建成功
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a ‘who’使用shell模块注意事项,ssh远程连接被管理主机,退出ssh后所有状态失效
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a ‘cd /tmp’
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a ‘touch my.txt’ #创建my.txt,node1主机查看,tmp目录下面没有my.txt,在当前用户的家目录下面
可以用以下方法解决
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a ‘chdir=/tmp touch my.txt’ #使用chdir切换目录
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a ‘chdir=/tmp touch a.txt b.txt c.txt’ #创建多个
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a ‘chdir=/tmp rm -rf a.txt b.txt c.txt’ #删除多个shell模块支持判断(creates、removes )
creates 文件名:文件存在,不执行shell命令,文件不存在,则执行
removes 文件名:文件不存在,不执行shell命令,文件存在,执行命令[root@contorl ansible]# ansible test -m shell -a "ssh-keygen -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -N '' creates=~/.ssh/id_rsa"- 1

#如果已经有密钥文件id_rsa, 则不创建密钥(skip跳过)node1安装unzip,node1和node2上传一个压缩包测试,可以利用Windows制作test.Zip压缩包,然后传到node1和node2的/root/目录
[root@node1 ~]# yum -y install unzip
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m shell -a “unzip /root/test.zip removes=/bin/unzip” #如果没有安装unzip软件包,则不执行解压命令(skip跳过)2.Script模块,结合脚本使用
[root@control ansible]# vim test.sh
#!/bin/bash
yum -y install httpd
systemctl restart httpd
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m script -a “./test.sh” #调用脚本执行node1验证
[root@node1 ~]# rpm -qa httpd
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl status httpd五、ansible常用模块应用案例(中)
file模块案例
file模块:可以创建文件、目录、链接;修改权限与属性等新建文件 [root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m file -a "path=/tmp/file.txt state=touch" 新建目录 [root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m file -a "path=/tmp/mydir state=directory" 修改文件权限 [root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m file -a "path=/tmp/file.txt owner=sshd group=adm mode=0777" 删除目录 [root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m file -a "path=/tmp/mydir state=absent" 创建连接文件 [root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m file -a "src=/etc/hosts path=/tmp/host.txt state=link"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
copy模块案例
将文件拷贝到远程主机
backup=yes如果目标主机有同名文件,则先备份
[root@control ansible]# echo AAA > ~/a3.txt #新建测试文件
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m copy -a “src=~/a3.txt dest=/root” #将~/a3.txt拷贝到test主机组/root/目录下
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m copy -a “src=~/a3.txt dest=/root/3a.txt” #将~/a3.txt拷贝到test主机组/root/目录下,并且重命名为3a.txt没有原文件执行拷贝
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m copy -a “content=‘hello the world\n’ dest=/root/test.txt” #通过content可以直接提供文件内容,\n代表回车fetch模块案例
与copy类似,但是作用相反,可以将其他主机的文件拷贝到本地
[root@control ansible]# ansible node1,node2 -m fetch -a “src=/etc/hostname dest=~/” #将远程主机的hostname文件下载到本地家目录(文件存放在对应主机名目录下)lineinfile|replace模块案例
lineinfile | replace模块
在修改单个文件的单行内容时可以使用lineinfile模块
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lineinfile -a “path=/etc/issue line=‘hello world’” #在/etc/issue文件中添加一行内容hello world,默认添加到最后,重复执行,基于幂等原则,不会创建多行内容[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lineinfile -a ‘path=/etc/issue line=“insert” insertafter=“Kernel”’ #将内容插入到Kernel行的后面
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lineinfile -a 'path=/etc/issue regexp=‘hello’ line=“ni hao” ’ #在/etc/issue文件中正则匹配包含hello的行,把整行内容替换为ni hao
#如果无法匹配到hello,则在文件最后添加一行nihao
#如果有多行内容包含hello,则仅替换最后一行lineinfile会替换一整行,replace可以替换关键词
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m replace -a “path=/etc/issue.net regexp=Kernel replace=Ocean” #将/etc/issue文件全文所有的KerneI替换为Ocean六、ansible常用模块应用案例(下)
user模块案例
user模块:可以实现Linux系统账户管理
远程test组中的所有主机并创建系统账户tuser[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m user -a “name=tuser1”
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible test -m user -a “name=tuser2 uid=1010 group=adm groups=daemon,root home=/home/tuser2” #创建账户并设置对应的账户属性
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m user -a “name=tuser1 password={{‘abc’| password_hash(‘sha512’)}}” #修改账户密码
[root@control ansible]# ssh tuser1@node1 #通过tuser1用户远程nond1主机
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m user -a “name=tuser1 groups=root,daemon” #修改tuser1账户的附加组
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m user -a “name=tuser1 state=absent” #删除账户tuser1
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m user -a “name=tuser2 state=absent remove=true” #删除tuser2账户, (remove=true实现删除家目录、邮箱)yum_repository模块案例
使用yum_repository可以创建或修改yum源配置文件
新建一个yum源配置文件/etc/yum.repos.d/myyum.repo[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m yum_repository -a “name=myyum description=hello baseurl=file:///media gpgcheck=0”
#yum源文件名为myyum,该文件的内容如下:
[myyum]
baseurl = file:///media
gpgcheck = 0
name = hello修改yum源内容
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m yum_repository -a “name=myyum description=test baseurl=file:///media gpgcheck=1”删除yum源文件
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m yum_repository -a "name=myyum state=absentyum模块案例
使用yum模块可以安装、卸载、升级软件包
state: present (安装) absent (卸载) latest (升级)
[root@control ansible]# ansible node2 -m yum -a “name=unzip state=present” #安装
[root@control ansible]# ansible node2 -m yum -a “name=unzip state=latest” #升级
[root@control ansible]# ansible node2 -m yum -a “name=unzip state=absent” #卸载service模块案例
service为服务管理模块(启动、关闭、重启服务等)
state:started stopped restarted
enabled:yes 设置开机启动
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m yum -a “name=httpd” #安装https
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m service -a “name=httpd state=started” #启服务
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m service -a “name=httpd state=stopped” #停服务
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m service -a “name=httpd enabled=yes” #设置开机自启逻辑卷相关模块案例
lvg模块:创建、删除卷组(VG), 修改卷组大小
state: present (创建) absent (删除)
node1主机关机添加一块20G的磁盘
[root@node1 ~]# lsblk
[root@node1 ~]# parted /dev/sdb mklabel gpt mkpart primary 1 50%
[root@node1 ~]# parted /dev/sdb mkpart primary 50% 100%
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m yum -a “name=lvm2” #安装Ivm2软件包
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lvg -a “vg=myvg pvs=/dev/sdb1” #创建名称为myvg的卷组,该卷组由/dev/sdb1组成[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lvg -a “vg=myvg pvs=/dev/sdb1,/dev/sdb2” #修改卷组大小
lvol模块:创建,删除逻辑卷(LV),修改逻辑卷大小
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lvol -a “lv=mylv vg=myvg size=2G” #使用myvg这个卷组创建一个名称为myIv的逻辑卷
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lvol -a “lv=mylv vg=myvg size=4G” #修改LV逻辑卷大小
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lvol -a “lv=mylv vg=myvg state=absent force=yes” #删除逻辑卷
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m lvg -a “vg=myvg state=absent” #删除卷组myvg七、sudu提权
概述
sudo
superuser or another do
以超级管理员或其它人的身份执行命令基本流程 管理员需要授权(修改/etc/sudoers文件) 普通用户以suod的形式执行命令 可以通过sudo -l查看授权情况- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
案例
sudoers语法
修改/etc/sudoers的方法
visudo(带语法检查,默认没有颜色提示)
vim /etc/sudoers(不带语法检查,默认有颜色提示)**授权格式** 用户或组 主机列表=(提权身份) [NOPASSWD]:命令列表 命令需要写绝对路径 **配置sudo提权** [root@node1 ~]# useradd dachui [root@node1 ~]# echo a | passwd --stdin dachui [root@node1 ~]# su - dachui [dachui@node1 ~]$ systemctl restart httpd Authenticating as: root Password: #需要输入root用户密码 [dachui@node1 ~]$ exit [root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/sudoers dachui ALL=(root) /usr/bin/systemctl 需要强制保存退出才可以 再次测试: [root@node1 ~]# su - dachui [dachui@node1 ~]$ sudo systemctl restart httpd [sudo] password for dachui: #输入的是自己的密码 [dachui@node1 ~]$ sudo -l #查看有哪些授权 在执行的时候如果不想要输入密码,需要在授权文件里面添加NOPASSWD [root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/sudoers dachui ALL=(root) NOPASSWD:/usr/bin/systemctl ansible支持以sudo的形式远程批量管理 给所有被管理主机创建授权用户,设置密码 [root@control ansible]# ansible all -m user -a "name=alice password={{'a'| password_hash('sha512')}}" [root@control ansible]# ssh alice@node1 #可以正常登陆 alice@node1's password: [alice@node1 ~]$ exit [root@control ansible]# ansible all -m lineinfile -a "path=/etc/sudoers line='alice ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL'" #更改授权文件- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
八、ansible配置进阶
使用普通用户远程被管理主机
[root@control ansible]# vim ansible.cfg
[defaults]
inventory = ~/ansible/hosts
remote_user = alice #以什么用户远程被管理主机
[privilege_escalation]
become=True #是否需要切换用户
become_method=sudo #如何切换用户
become_user=root #切换成什么用户
become_ask_pass=False #sudo是否需要输入密码配置免密登录,之前使用的是root用户,现在是普通用户alice
[root@control ansible]#for i in node{1..5} do ssh-copy-id alice@$i done- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
[root@control ansible]# ssh alice@node1
[root@control ansible]# ansible all -m shell -a “who” #测试,普通用户远程连接九、Ansible Playbook基础
测试第一个playbook,ping模块测试
[root@control ansible]# vim test.yml--- - hosts: all tasks: - name: this is my first playbook ping:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook test.yml
hosts由一个或多个组或主机组成,逗号分隔;tasks由一个或多个任务组成,多个任务按照顺序执行;可以使用-f选项自定义并发量
[root@control ansible]# vim test.yml--- - hosts: test,webserver tasks: - name: this is my first playbook ping: - name: run a shell command shell: touch ~/shell.txt- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook test.yml -f 5 #定义并发量,一次性连接5个
可选操作
修改VIM配置
~使用2个空格自动替换tab键
√ tabstop=2 、 expandtab~开启自动缩进对齐,缩进宽度为2个空格
√ shiftwidth=2

setlocal局部设置, ai自动缩进,et自动把tab见换成空格,换成ts=2两个空格,sw=2位自动缩进对齐十、Ansible Playbook应用案例(上)
Playbook应用案例之用户
编写Playbook创建系统账户、账户属性、设置密码
[root@contorl ansible]# vim test_john.yml--- - hosts: webserver tasks: - name: add the user johnd user: name: johnd uid: 1040 group: daemon password: "{{ '123' | password_hash('sha512')}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook test_john.yml
验证一下
[root@node3 ~]# tail -1 /etc/passwd

[root@node4 ~]# id johnd

[root@contorl ansible]# vim test_james.yml--- - hosts: webserver tasks: - name: Add 'james' with a bash shell, set 'bin' and 'adm' the users groups user: name: james shell: /bin/bash groups: bin,adm password: "{{ '123' | password_hash('sha512')}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
编写Playbook删除jhond用户
[root@contorl ansible]# vim test_johnd.yml--- - hosts: webserver tasks: - name: add the user johnd user: name: johnd uid: 1040 group: daemon password: "{{ '123' | password_hash('sha512')}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Playbook应用案例之软件管理
软件安装、软件升级、安装组包
[root@contorl ansible]# vim pacakge.yml--- - hosts: webserver tasks: - name: install a list of packages yum: name: - httpd - mariadb - mariadb-server - name: install the 'Development tools' package group yum: name: '@Development Tools' - name: update software yum: name: '*' state: latest- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook pacakge.yml
验证:
[root@node3 ~]# rpm -q httpd
httpd-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.5.x86_64
[root@node3 ~]# rpm -q mariadb
mariadb-5.5.68-1.el7.x86_64
[root@node3 ~]# rpm -q mariadb-server
mariadb-server-5.5.68-1.el7.x86_64

十一、Ansible Playbook应用案例(下)
setup模块
ansible_facts用于采集被管理设备的系统信息
所有收集的信息都被保存在变量中
每次执行playbook默认第一个任务就是Gathering Facts
使用setup模块可以查看收集到的facts信息[root@contorl ansible]# ansible test -m setup
node1 | SUCCESS => {
“ansible_facts”: {
“ansible_all_ipv4_addresses”: [
“172.16.11.2”
],
…(省略)
找出下列facts信息(有父子关系时使用.分隔)
ansible_all_ipv4_addresses
ansible_bios_version
ansible_memtotal_mb
ansible_hostname[root@contorl ansible]# ansible test -m setup -a “filter=ansible_mem*” #过滤关于内存的信息

[root@contorl ansible]# ansible test -m setup -a “filter=ansible_all_ip*” #过滤关于ip的信息

特殊模块-debug模块
debug模块可以显示变量的值,可以辅助排错
debug模块有两个参数,var(引用变量不需要{{}})和msg (引用变量需要{{}})
[root@contorl ansible]# vim debug.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - debug: var: ansible_all_ipv4_addresses - debug: msg: "the hostname is: {{ansible_hostname}}" - debug: var: ansible_devices.sdb.partitions.sdb1.size - debug: msg: "the memory size is : {{ansible_memtotal_mb}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook debug.yml
十二、Ansible定义变量
定义变量
Ansible支持十几种定义变量的方式
这里我们仅介绍其中一部分变量,根据优先级排序(从低到高)
Inventory变量
Host Facts变量
Register变量
Playbook变量
Playbook提示变量
变量文件
命令行变量
Inventory变量(在主机清单配置文件中定义变量)[root@contorl ansible]# vim hosts
[test]
node1 myvar1=“hello the world” myvar2=“content” #在node1主机中定义了两个变量[proxy]
node2[webserver]
node[3:4]
[database]
node5[cluster:children]
webserver
database[webserver:vars]
yourname=“jacob” #在webserver主机组所有主机定义变量[root@contorl ansible]# vim inventory_var.yaml
--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: create a file with var. shell: echo "{{myvar1}}" > /tmp/"{{myvar2}}" - hosts: webserver tasks: - name: create a user with var user: name: "{{yourname}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook inventory_var.yaml
[root@node1 ~]# ls /tmp
[root@node1 ~]# cat /tmp/content
[root@node3 ~]# id jocab
Host Facts变量(可以直接调用ansible收集的系统信息)[root@contorl ansible]# vim facts_var.yml
--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: use facts variable info. copy: content: "{{ansible_hostname}}:{{ansible_bios_version}}" dest: /tmp/facts.txt- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
[root@node1 ~]# cat /tmp/facts.txt
register语句可以将某个命令的执行结果保存到变量中
[root@contorl ansible]# vim register.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: save shell result to a variable shell: hostname register: myvar - name: print the variable's value through debug debug: msg: "{{myvar}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook register.yml
通过".”我们还可以仅提取部分数据
[root@contorl ansible]# vim register.yaml
--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: save shell result to a variable shell: hostname register: myvar - name: print the variable's value through debug debug: msg: "{{ myvar.stdout }}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook register.yaml
Playbook变量(使用vars关键词可以在playbook内定义变量)
[root@contorl ansible]# vim playbook_var.yml--- - hosts: test vars: iname: heal ipass: '123456' #密码必须是字符串,需要引号 tasks: - name: use variables create user user: name: "{{ iname }}" password: "{{ ipass | password_hash('sha512') }}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook playbook_var.yml
[root@node1 ~]# id heal

Playbook提示变量( 根据提示输入变量的值)
[root@contorl ansible]# vim prompt_var.yml--- - hosts: test vars_prompt: - name: iname prompt: "请输入用户名" private: no #回显用户名 - name: ipasswd prompt: "请输入密码" private: yes tasks: - name: create a user. user: name: "{{ iname }}" password: "{{ ipasswd | password_hash('sha512')}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook prompt_var.yml
请输入用户名: alin
请输入密码: #输入密码123456
[root@node1 ~]# id alin单独定义个变量文件,在playbook中 用vars_files调用该文件
[root@contorl ansible]# vim variables.yml--- iname: cloud ipass: '123456'- 1
- 2
- 3
[root@contorl ansible]# vim file_var.yml
--- - hosts: test vars_files: varsab.yml tasks: - name: create a user user: name: "{{iname}}" password: "{{ipass | password_hash('sha512')}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook file_var.yml
[root@node1 ~]# id cloud

执行ansible-playbook命令时使用-e参数定义变量
[root@contorl ansible]# vim command_var.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: create user user: name: "{{ iname }}" password: "{{ ipass | password_hash('sha512') }}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
[root@contorl ansible]# ansible-playbook command_var.yml -e iname=“beth” -e ipass=“123456”
[root@node1 ~]# id beth十三、Ansible模块应用
firewalld模块
使用firewalld模块可以配置防火墙策略
[root@node1 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports --permanent #查看规则
[root@control ansible]# vim firewall.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: install firewalld yum: name: firewalld state: present - name: run firewalld service: name: firewalld state: started enabled: yes - name: set firewalld rule firewalld: port: 80/tcp permanent: yes state: enabled- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook firewall.yml
测试:
[root@control ansible]# ssh node1
[root@node1 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports --permanent #有端口,但是如果把–permanent去掉查看,会显示没有规则
如果想要其立即生效,则需要另外设置
[root@control ansible]# vim firewall.yml..................... - name: set firewalld rule firewalld: port: 80/tcp permanent: yes immediate: yes #立即生效 state: enabled- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook firewall.yml
测试:
[root@control ansible]# ssh node1
[root@node1 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports #有策略,规则立即生效template模块
copy模块可以将一个文件拷贝给远程主机
Jinja2模块的表达式包含在分隔符"{{ }}"内给webserver主机拷贝首页,每个主机内容不同
定义一个模板文件
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m setup -a “filter=ansible_ens*” #查找自己的网卡变量信息
[root@control ansible]# mkdir ~/ansible/template
[root@control ansible]# cd ~/ansible/template
[root@control template]# vim index.html
Welcome to {{ansible_hostname}} on {{ansible_ens192.ipv4.address}}. #这里的网卡名字,根据实际查看到的改成你的网卡名,#模板文件中调用变量
{{}}不需要引号调用模板文件
[root@control template]# cd …
[root@control ansible]# vim template.yml--- - hosts: webserver tasks: - name: use template module,copy a file to webserver. template: src: ~/ansible/template/index.html dest: /var/www/html/index.html- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook template.yml
测试:结果不同
[root@control ansible]# ssh node3
[root@node3 ~]# cat /var/www/html/index.html

[root@control ansible]# ssh node4
[root@node4 ~]# cat /var/www/html/index.html

以上使用的是ansible里面自带的变量,直接调用使用,也可以自定义变量
调用自定义变量自定义变量
[root@control ansible]# vim template/source.j2
{{welcome}} {{iname}}…调用自定义变量
[root@control ansible]# vim template2.yml--- - hosts: webserver vars: welcome: 'hello' iname: 'jack' tasks: - name: use template copy a file to remote hosts template: src: ~/ansible/template/source.j2 dest: /tmp/- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook template2.yml
测试结果:
[root@control ansible]# ssh node3
[root@node3 ~]# cat /tmp/source.j2

[root@control ansible]# ssh node4
[root@node4 ~]# cat /tmp/source.j2

十四、 Ansible高级语法
error处理机制
默认ansible在遇到error会立刻停止playbook错误演示,启动一个不存在的服务
[root@control ansible]# vim error.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: start a server service: name: hehe state: started - name: touch a file file: path: /tmp/services.txt state: touch- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook error.yml #报错,不再继续执行
若想要解决这个文件,需要忽略此错误
[root@control ansible]# vim error.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: start a server service: name: hehe state: started ignore_errors: true .......................- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook error.yml #成功
以上忽略只是针对某一个任务忽略,若要忽略全部的错误,需要写到全局里面[root@control ansible]# vim error.yml
--- - hosts: test ignore_errors: true tasks: .....................- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook error.yml #成功
handlers
可以通过handlers定义一组任务
仅当某个任务触发(notify) handlers时才执行相应的任务
如果有多个notify触发执行handlers任务,也仅执行一次
仅当任务的执行状态为changed时handlers任务才执行
handlers任务在所有其他任务都执行后才执行[root@control ansible]# vim handlers.yml
--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: create dir. file: path: /tmp/parents/subdir/ state: directory notify: touch file handlers: - name: touch file file: path: /tmp/parents/subdir/new.txt state: touch- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook handlers.yml
when条件判断
when可以定义判断条件,条件为真时才执行某个任务
常见条件操作符: ==、!=、>、>=、<、<=
多个条件可以使用and或or分割
when表达式中调用变量不要使用{{}}远程主机剩余内存不足700M则关闭NetworkManager服务
[root@control ansible]# vim when_1.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: check memory sizi. service: name: NetworkManager state: stopped when: ansible_memfree_mb < 700- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook when_1.yml
node1主机查看,NetworkManager已经被关闭判断操作系统是RedHat7则创建测试文件
> 支持多行输入,不保留换行符
[root@control ansible]# vim when_2.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: touch a file file: path: /tmp/when.txt state: touch when: > ansible_distribution == "RedHat" and ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook when_2.yml
测试:
[root@control ansible]# ssh node1
[root@node1 ~]# ls /tmp/when.txt #成功block任务块
使用block可以将多个任务合并为一个组(block部分可以写多个任务)block可以将多个任务合并为一个组,结合when使用时,当条件成立,执行一组任务,而不是一个任务
[root@control ansible]# vim block_1.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: define a group of tasks block: - name: install httpd yum: name: httpd state: present - name: start service service: name: httpd state: started when: ansible_distribution == 'RedHat'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook block_1.yml #成功
可以修改条件,为windows,此时条件不满足,会跳过
[root@control ansible]# vim block_1.yml
…
when: ansible_distribution == ‘windows’[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook block_1.yml
block任务块
rescue定义block任务执行失败时要执行的其他任务
always定义无论block任务是否成功,都要执行的任务[root@control ansible]# vim block_2.yml
--- - hosts: test tasks: - block: - name: touch a file file: path: /tmp/test1.txt state: touch rescue: - name: touch a file test2.txt file: path: /tmp/test2.txt state: touch always: - name: touch a file test3.txt file: path: /tmp/test3.txt state: touch- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
[root@control ansible]#ansible-playbook block_2.yml #执行了test1.txt和test3.txt
测试:
[root@control ansible]# ssh node1
[root@node1 ~]# ls /tmp/test*

[root@node1 ~]# rm -rf /tmp/test* #删除继续测试
[root@control ansible]# vim block_2.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - block: - name: touch a file file: path: /tmp/test1.txt #条件不成立执行rescue和always state: touch- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook block_2.yml
loop循环
很多任务都在用相同的模块?使用loop循环避免重复使用关键字item 和loop循环创建目录
[root@control ansible]# vim simple_loop.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: mkdir multi directory file: path: /tmp/{{item}} #item是关键字 state: directory loop: - School - Legend - Life- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook simple_loop.yml
循环创建多个用户
[root@control ansible]# vim complex_loop.yml--- - hosts: test tasks: - name: create multi user user: name: "{{item.iname}}" password: "{{item.ipass | password_hash('sha512')}}" loop: - { iname: 'term',ipass: '123456' } - { iname: 'amy',ipass: '654321' }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook complex_loop.yml
测试:
[root@control ansible]# ssh node1
[root@node1 ~]# id term
[root@node1 ~]# id amy十五、Ansible Vault
加密敏感数据
Ansible有时需要访问一些敏感数据,如密码、Key等
使用ansible-vault可 以加密和解密数据
encrypt (加密)、decrypt (解密)、view (查看)[root@control ansible]# echo 123456 > data.txt
[root@control ansible]# cat data.txt
123456

[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault encrypt data.txt #加密
New Vault password: #密码
Confirm New Vault password: #确认密码
Encryption successful

[root@control ansible]# cat data.txt #查看,是加密数据

[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault view data.txt #viwe查看加密文件,需要输入密码
才可以

[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault decrypt data.txt #解密

[root@control ansible]# cat data.txt #重新查看
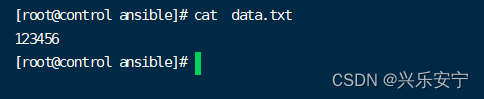
修改密码 rekey
[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault encrypt data.txt

[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault rekey data.txt

加密、解密每次都输入密码很麻烦,可以将密码写入文件
[root@control ansible]# echo data > data.txt #需要加密的文件
[root@control ansible]# echo 123456 > pass.txt #加密的密码文件
[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault --vault-id=pass.txt encrypt data.txt #使用
密码文件加密
[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault --vault-id=pass.txt view data.txt #查看
[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault --vault-id=pass.txt decrypt data.txt #解密Ansible Vault实践
传送敏感数据到远程数据
[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault --vault-id=pass.txt encrypt data.txt #使用
密码文件加密
[root@control ansible]# ansible test -m copy --vault-id=pass.txt -a “src=./data.txt
dest=/tmp/” #传递的同时解密Playbook调用 敏感数据(账户名、密码等)
[root@control ansible]# vim variables.yml--- iname: cloud ipass: '123456'- 1
- 2
- 3
[root@control ansible]# ansible-vault encrypt variables.yml

[root@control ansible]# vim vault.yml
--- - hosts: test vars_files: variables.yml tasks: - name: include vault data,create user user: name: "{{iname}}" password: "{{ipass | password_hash('sha512')}}"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook --ask-vault-pass vault.yml
Vault password: #输入密码

十六、Ansible Roles基础
Roles规范的目录结构
defualts/main.yml:定义变量的缺省值,优先级较低
files目录:存储静态文件的目录
handlers/main.yml:定义handlers
meta/main.yml:写作者、版本等描述信息
README.md:整个角色(role)的描述信息
tasks/main.yml:定义任务的地方
templates目录:存放动态数据文件的地方(模板文件)
vars/main.yml:定义变量,优先级高十七、Ansible Roles应用
创建Role
ansible-galaxy命令可以创建、管理自己的roles[root@control ~]# mkdir ~/ansible/roles
[root@control ~]# ansible-galaxy init ~/ansible/roles/issue #初始化创建一个role(角色)
[root@control ~]# cd ~/ansible/roles/
[root@control roles]# ls issue/把控制端本地的文件拷贝到被管理主机,如果拷贝的是常量文件,则把文件放到files目录下,如果拷贝的
是变量文件,则把文件放到templates目录下
定义issue模板文件
[root@control roles]# vim issue/templates/issue.j2
this is the system {{ansible_hostname}}
today’s date is: {{ansible_date_time.date}}
contact to {{admin}} #自己定义的变量定义变量文件
[root@control roles]# vim issue/vars/main.yml--- # vars file for /root/ansible/roles/issue admin: idc@idc.com- 1
- 2
- 3

编写任务文件,任务文件中不需要tasks关键词,Role的各个文件之间相互调用不需要写路径
[root@control roles]# vim issue/tasks/main.yml--- # tasks file for /root/ansible/roles/issue - name: delever issue file template: src: issue.j2 dest: /etc/issue- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
在playbook中调用role
方法一:在role相同目录下创建一个playbook调用
方法二:在ansible.cfg设置roles_ path=路径
[root@control roles]# cd ~/ansible
[root@control ansible]# vim ansible.cfg

编写playbook文件,通过roles关键词调用role
[root@control ansible]# vim issue.yml--- - hosts: test roles: - issue- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook issue.yml
测试:
[root@control ansible]# ssh node1
[root@node1 ~]# cat /etc/issue
Ansible Galaxy是官方提供的一个共享roles的平台,公共Roles仓库(https://galaxy.ansible.com)
虚拟机联网方可操作
[root@control ansible]# ansible-galaxy search "httpd’ #联网搜索roles
[root@control ansible]# ansible-galaxy info acandid.httpd #查看roles基本信息
[root@control ansible]# ansible-galaxy install acandid.httpd -p ~/ansible/roles/ #下载roles到特定的目录
[root@control ansible]# ansible-galaxy list -p roles/ #列出本地有哪些roles下载Roles的方法:
使用ansible- galaxy install或编写requirements. yml文件
[root@control ansible]# cat ~/ansible/roles/requirements.yml#格式一:直接从Ansible Galaxy官网下载
- src: acandid.httpd- 1
#格式二:从某个git服务器下载
- src: http://gitlab.com/xxx/xxx.git scm: git version: 56e00a54 name: nginx-acme- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
#格式三:下载tar包,支持http、https、 file
- src: http://example.com/myrole.tar name: myrole- 1
- 2
[root@control ansible]# ansible-galaxy install -r roles/requirements.yml -p roles
模拟格式三,进行下载(可选操作)
[root@control ansible]# cd roles/
[root@control roles]# tar -cf issue.tar issue/ #打包issue
[root@control roles]# yum -y install httpd
[root@control roles]# systemctl restart httpd
[root@control roles]# cp issue.tar /var/www/html/ #放在http默认共享路径,提供下载
[root@control roles]# pwd

[root@control roles]# vim requirements.yml- src: http://172.16.11.1/issue.tar name: myissue #下载下来的名字- 1
- 2

[root@control roles]# ansible-galaxy install -r requirements.yml -p ~/ansible/roles/

十八、综合案例
自动化部署web集群
项目要求:创建role,通过role完成项目(可能需要多个role)
部署nginx调度器(node2主机)
部署2台lnmp服务器(node3,node4主机)
部署mariadb数据库(node5主机)[root@control roles]# cd ~/ansible
创建role部署lnmp平台环境
[root@control ansible]# ansible-galaxy init ~/ansible/roles/lnmp
上传lnmp_soft.tar.gz里面的nginx-1.16-1.tar.gz软件包到 /root/ansible/roles/lnmp/files/
[root@control ansible]# tar -xf lnmp_soft.tar.gz
[root@control ansible]# cp lnmp_soft/nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz /root/ansible/roles/lnmp/files/编写部署lnmp的脚本,配置动静分离
[root@control ansible]# vim /root/ansible/roles/lnmp/files/install_nginx.sh
稍后会使用copy模块把nginx源码包放到tmp目录下,拷贝nginx源码,执行编译安装#!/bin/bash conf="/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf" yum -y install gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel make cd /tmp/ tar -xf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz cd nginx-1.16.1 ./configure --with-http_ssl_module make && make install sed -i '65,71s/#//' $conf sed -i '/SCRIPT_FILENAME/d' $conf sed -i 's/fastcgi_params/fastcgi.conf/' $conf- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
部署网页模板文件,通过template把包含变量的模板文件拷贝给目标主机node3 和 node4
[root@control ansible]# vim /root/ansible/roles/lnmp/templates/index.html
Welcome to {{ansible_hostname}} on {{ansible_all_ipv4_addresses}}编写tasks文件,定义任务
[root@control ansible]# vim /root/ansible/roles/lnmp/tasks/main.yml--- # tasks file for /root/ansible/roles/lnmp - name: copy nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz to webserver. copy: src: nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz dest: /tmp/ - name: install nginx through shell script. script: install_nginx.sh args: creates: /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx - name: copy index.html to webserver. template: src: index.html dest: /usr/local/nginx/html/index.html - name: install php yum: name: - php - php-fpm - php-mysqlnd - mariadb-devel - name: run all serveice block: - service: name: php-fpm state: started - shell: /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx args: creates: /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid #当nginx的进程号文件存在,说明nginx启动了。则不执行启动nginx- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
编写playbook剧本
[root@control ansible]# vim ~/ansible/lnmp.yml--- - hosts: webserver roles: - lnmp- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook lnmp.yml
验证webserver是否部署成功
[root@control ansible]# ssh node3
[root@node3 ~]# ls /usr/local/nginx/
[root@node3 ~]# ss -nultp | grep 80
[root@node3 ~]# rpm -q php-fpm
[root@node3 ~]# systemctl status php-fpm
[root@node3 ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/html/index.html

使用nginx部署代理服务器node2
[root@control ansible]# ansible-galaxy init ~/ansible/roles/proxy
[root@control ansible]# cp ~/ansible/roles/lnmp/files/* ~/ansible/roles/proxy/files/编写配置调度器的脚本,删掉之前的sed语句,添加定义集群,调用集群的语句
[root@control ansible]# vim ~/ansible/roles/proxy/files/install_nginx.sh#!/bin/bash conf="/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf" yum -y install gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel make cd /tmp/ tar -xf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz cd nginx-1.16.1 ./configure --with-http_ssl_module make && make install sed -i '/^http/a upstream webs {\n server 172.16.11.4;\n server 172.16.11.5;\n }\n' $conf sed -i '49i proxy_pass http://webs;' $conf /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
编写tasks文件,定义任务
[root@control ansible]# vim ~/ansible/roles/proxy/tasks/main.yml--- # tasks file for /root/ansible/roles/proxy - name: copy source file to node2 copy: src: nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz dest: /tmp/ - name: install nginx. script: install_nginx.sh args: creates: /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
编写playbook剧本,调用任务
[root@control ansible]# vim proxy.yml--- - hosts: node2 roles: - proxy - hosts: node5 tasks: - name: install mariadb server. #部署数据库服务器 yum: name: - mariadb - mariadb-server - mariadb-devel - name: run mariadb-server service: name: mariadb state: started- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
[root@control ansible]# ansible-playbook proxy.yml
node1测试访问:
node2,node3,node4关闭防火墙,
[root@node2 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service 或者
firewall-cmd --add-service=http 允许http访问都可以
[root@node3 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@node4 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@node1 ~]# curl http://172.16.11.3 #成功
-
相关阅读:
大数据如何进行测试
【面试】JVM垃圾回收
Data security.隐私保护-多方安全计算技术基础
“TaekwondoBasicMovement“ app Tech Support(URL)
基于SqlSugar的开发框架循序渐进介绍(12)-- 拆分页面模块内容为组件,实现分而治之的处理
09【保姆级】-GO语言的数组和切片
中国棉纺织行业市场深度分析及发展规划咨询综合研究报告
Node.Js基础知识
牛客训练3
字符串和内存函数
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42324463/article/details/127675053
