-
活动的四种启动模式详解
android:launchMode
前言
本文部分内容参考了郭神的《第一行代码》
活动的启动模式一般在AndroidManifest.xml中定义标签android:launchMode=" "
接下来开始具体介绍这四个启动模式的区别以及用途
standard singleInstance singleTop singleTask
说到这,我们先来看看返回栈是个什么呢?原文是这样的:Android是使用任务(Task)来管理活动的,一个任务就是一组存放在栈里的活动的集合,这个栈被称为返回栈(Back Stack)。
理解:现在我们有一堆活动,activity(简称a),a1,a2,a3,a4,…,an,然后把这些活动都存在返回栈中.最先入栈的a1就在栈底,最后入栈的an就在栈顶,那么这些活动每次工作时,就会出栈入栈,整个流程如下图:
说实在的,我还是觉得上图有点点抽象,再来张新图理解一下子。

概念说明
standard
标准模式:这是Android默认模式,当AndroidManifest中不声明时的模式。首先,Android通过返回栈来管理活动的(栈的特点就是先进后出,就像一个罗汉塔,最先取出栈顶的数据)。每当我们启动一个新的活动时,这个新活动就会进入返回栈,处于栈顶。每新建一次,它就会往栈顶堆一个活动,它不会去看这个栈是否已经存在这个活动。
这里我们不妨把活动看成下面的小星星,串呢就是一个返回栈。我们每启动一个新活动,就串一个小星星,我们不会去管下面那个是不是相同的,只会一直串。串了之后要返回呢,我们就只能一个一个地去返回,就是把上面 的小星星一个一个取出来。

standard的模式示意图如下(摘自郭神的《第一行代码》):

所以像上诉的情况,当你点击button2次时,你要按3次返回键才能退出最开始的活动。而且这个模式下每启动一次活动就会新建一次,但是它也有它的运用。上面只是为了演示,通常app不会从现在活动跳转到现在的活动应用场景:大部分app应用,因为一般都不会在当前活动反复横跳。
singleTop
在这种模式下,比如启动活动A时,发现返回栈的栈顶就是活动A,那么就可以直接使用它,而不用创建新的活动实例。
还是将活动看成串串上的串,那么如下图示例

所以像上诉的情况,当你点击button2次时,你点击一次返回键就退出了app。但是如果栈顶元素不是该活动,它还是会创建新的活动。
应用场景:大部分app应用,或者浏览器或者今日头条等新闻推送。
比如你进入手机浏览器,我点了个新冠查看,然后一不小心点了个返回主页,然后我点击返回,它又返回新冠页面了。
如下图,我先从主页面点击搜索框进入搜索页面,查看新冠疫情状况,然后点击底部直接回到主页面,不用点击它出现的那个返回的那个标志,直接手机返回,我的是屏幕手指左滑或者右滑就行,然后就又返回到了新冠页面,再次点击返回,又回到了搜索页面,再返回,进入原先的主页面,整个过程如下图。(主页面貌似有广告会违规,然后去掉那些广告图,直接看底部导航栏)

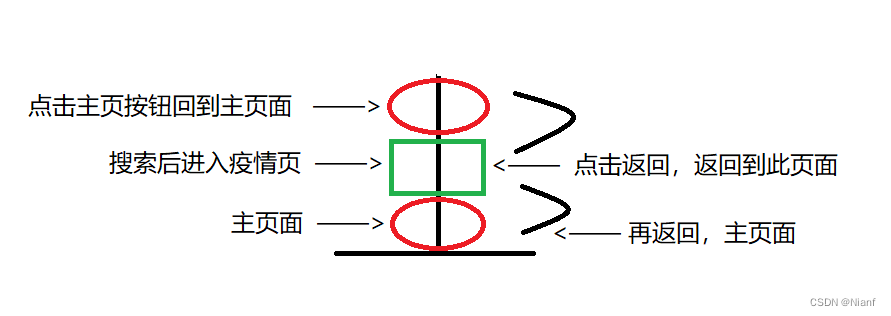
singleTask
singleTop虽然解决了大量重复创建栈顶活动的问题,但是目标活动不位于栈顶时,依然会创建大量重复的活动占用内存。singleTask模式很好滴解决了这个问题,每次启动目标活动时,系统会在返回栈中去搜寻是否已经存在该活动,如果存在,就把栈中位于该活动上方的活动全部出栈,如果没有再创建新的。

然后你发现,当再来一个新活动(是蓝色菱形)时,因为前面的活动已经出栈了,所以会创建新的活动应用场景:购物页面,比如淘宝、拼多多、京东等购物app。
当从首页搜索后,进入商品浏览页,进入商品详情页面之后,点击购买,然后跳转至付款页面,付完款后购买成功,点击button又可以直接返回到首页,也即是说,商品浏览页,商品详情页,付款页出栈,button直接导向首页。singleInstance
singleInstance会启用新的返回栈(stack)来管理活动。为什么这么干呢?
首先从字面来看,它是单一实例模式。也即是说Activity单独占用一个任务栈,而且由于栈内复用的特性,后续的请求不会再创建新的Activity实例,除非这个任务栈被销毁(destroy())
目标活动(给它取个名叫special)有了单独的栈来存放自己,这样当程序A想来调用special,程序B想调用它,程序C还想调用它时,程序之间共享此活动的实例在这个模式下就能很容易地实现了。而每个应用程序都有自己的返回栈,所以前三种模式并不能解决共享活动实例的问题,singleInstance模式就能起到很大的作用了。参考引用 :按照惯例,先放一张引用自《第一行代码》的模式示意图。
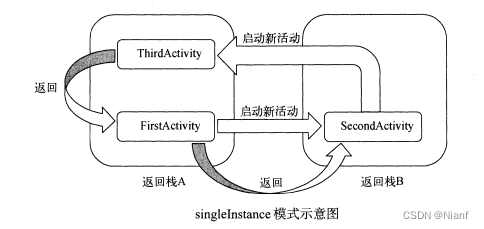
图解
有3个不同的进程(返回栈),可以看到,当活动启动方式为singleInstance的时候,就可以实现不同的程序共享同一个实例。
对于返回栈1:粉色箭头代表启动活动,蓝色代表返回,那么返回的顺序会如下图所示。因为活动1.1,1。2,1.3和活动优秀不在同一个栈中,所以优先返回自己所在栈中的活动,最后切回优秀

应用场景: 一些系统应用,比如日程、电话、系统通讯录、闹钟、相册等等。
在QQ或者微信或者支付宝都要打开相册,打开的都是相册那个页面。Codes演示
说明
来说说代码咋个写。File --> New -->New Project,选择Empty Activity
然后,我们就拥有了一个mainActivity,现在再在com.example.xx包下再建立2个Activity,分别取名为SecondActivity和ThirdActivity,对应的Layout里面放上一个Button.
可以通过打印日志来进行理解活动不同启动模式下的差异standard代码
MainActivity
这里其它的Activity暂时不用改变,或者你先只创建这么一个activity,standard模式演示。android默认模式import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, this.toString()); Log.d(TAG, "Task id is" + getTaskId());//打印当前返回栈 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button but1 = findViewById(R.id.button_1); but1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,MainActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } }); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
你点击n次but1,会发现退出app需要点击n+1次返回键。
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/button_1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button1" android:textAllCaps="false"/> LinearLayout>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
singleTop代码
看过来,把AndroidManifest.xml,就是本文的第一张图的那个launchmode后面改成singleTop
其他部分代码不变,如上standard,然后你会发现, 不管你开始点击多少次button1按钮,最终你点击一次返回就能够退出程序了。但是呢,当栈顶元素不是该活动时,仍然会有新的活动入栈。就是栈顶元素不是它时,当再次启动它的时候还是会创建一个新的它,所以当跳转多个不同的页面时,效果和standard就很相似。
现在你继续修改代码,从界面1跳转至界面2,再点击button2,跳转到界面1,然后你点击返回,它会先返回到界面2,再点击返回再返回到界面1,再点击返回最后退出,会发现这个返回和standard就很相似了。因为都是不同的活动,所以每启动新的活动时,依旧会创建新活动入栈。
AndroidManifest
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.test4"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/Theme.Test4"> <activity android:name=".ThirdActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Third"/> <activity android:name=".SecondActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Sec" android:launchMode="singleTop"/> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Main" android:launchMode="singleTop"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> intent-filter> activity> application> manifest>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
MainActivity
package com.example.test4; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, this.toString()); Log.d(TAG, "Task id is" + getTaskId());//打印当前返回栈 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button but1 = findViewById(R.id.button_1); but1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override protected void onRestart(){ super.onRestart(); Log.d(TAG, "onRestart"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
activity_main
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/button_1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button1" android:textAllCaps="false"/> LinearLayout>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
SecondActivity
package com.example.test4; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "SecondActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, this.toString()); Log.d(TAG, "Task id is" + getTaskId()); setContentView(R.layout.activity_second); Button button2 = findViewById(R.id.button_2); button2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(SecondActivity.this,FirstActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override protected void onDestroy(){ super.onDestroy(); Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
activity_second.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".SecondActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/button_2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button2" android:textAllCaps="false"/> LinearLayout>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
singleTask代码
这里你会发现,当你点击button从页面1跳转到页面2,再点击页面2的按钮跳转到页面1,按一下返回键就可以退出程序了。
MainActivity
package com.example.test4; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, this.toString()); Log.d(TAG, "Task id is" + getTaskId());//打印当前返回栈 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button but1 = findViewById(R.id.button_1); but1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override protected void onRestart(){ super.onRestart(); Log.d(TAG, "onRestart"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
xml不发生改变
SecondActivitypackage com.example.test4; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "SecondActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, this.toString()); Log.d(TAG, "Task id is" + getTaskId()); setContentView(R.layout.activity_second); Button button2 = findViewById(R.id.button_2); button2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(SecondActivity.this,MainActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override protected void onDestroy(){ super.onDestroy(); Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
second.xml不发生改变
AndroidManifest<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.test4"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/Theme.Test4"> <activity android:name=".ThirdActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Third"/> <activity android:name=".SecondActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Sec" android:launchMode="singleTask"/> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Main" android:launchMode="singleTask"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> intent-filter> activity> application> manifest>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
singleInstance代码
这里因为secondActivity模式设置为了singleInstance,所以MainActivity和ThirdActivity在一个返回栈中,2号单独在一个栈中。所以你会发现,当你点击按钮1到达页面2,再点击button2到达页面3,点击返回键时,你会回到页面1去,再点击返回键回到页面2,再点击返回退出app。
MainActivity.java
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, this.toString()); Log.d(TAG, "Task id is" + getTaskId());//打印当前返回栈 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button but1 = findViewById(R.id.button_1); but1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override protected void onRestart(){ super.onRestart(); Log.d(TAG, "onRestart"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
SecondActivity.java
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "SecondActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, this.toString()); Log.d(TAG, "Task id is" + getTaskId()); setContentView(R.layout.activity_second); Button button2 = findViewById(R.id.button_2); button2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(SecondActivity.this,ThirdActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override protected void onDestroy(){ super.onDestroy(); Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
ThirdActivity.java
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; public class ThirdActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "ThirdActivity"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d(TAG, "Task id is" + getTaskId()); setContentView(R.layout.activity_third); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
androidmanifest
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.test4"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/Theme.Test4"> <activity android:name=".ThirdActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Third"/> <activity android:name=".SecondActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Sec" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:exported="true" android:label="Main"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> intent-filter> activity> application> manifest>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/button_1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button1" android:textAllCaps="false"/> LinearLayout>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
activity_second.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".SecondActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/button_2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button2" android:textAllCaps="false"/> LinearLayout>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
activity_third.xml
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".ThirdActivity"> <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="52dp" android:layout_marginLeft="52dp" android:layout_marginTop="340dp" android:text="Hello,smart person !!!" android:textSize="36sp" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
-
相关阅读:
JavaScript基础语法(流程控制语句)
【hadoop运维】running beyond physical memory limits:正确配置yarn中的mapreduce内存
关于低代码开发,你是真的了解了吗?
【JavaSE】多线程篇(五)线程专项练习题
介绍 TensorFlow 的基本概念和使用场景。
C#将一个文件复制到成千上百个文件夹中
transformer_01
Go:关于‘fresh‘ 不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序问题的解决方案
CUDA用户对象
“Python+”集成技术高光谱遥感数据处理与机器学习深度应用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43738932/article/details/126022497
