-
机器学习 —— 支持向量机SVM(Support Vector Machine)
【关键词】支持向量,最大几何间隔,拉格朗日乘子法
一、支持向量机的原理
Support Vector Machine。支持向量机,其含义是通过支持向量运算的分类器。其中“机”的意思是机器,可以理解为分类器。 那么什么是支持向量呢?在求解的过程中,会发现只根据部分数据就可以确定分类器,这些数据称为支持向量。 见下图,在一个二维环境中,其中点R,S,G点和其它靠近中间黑线的点可以看作为支持向量,它们可以决定分类器,也就是黑线的具体参数。
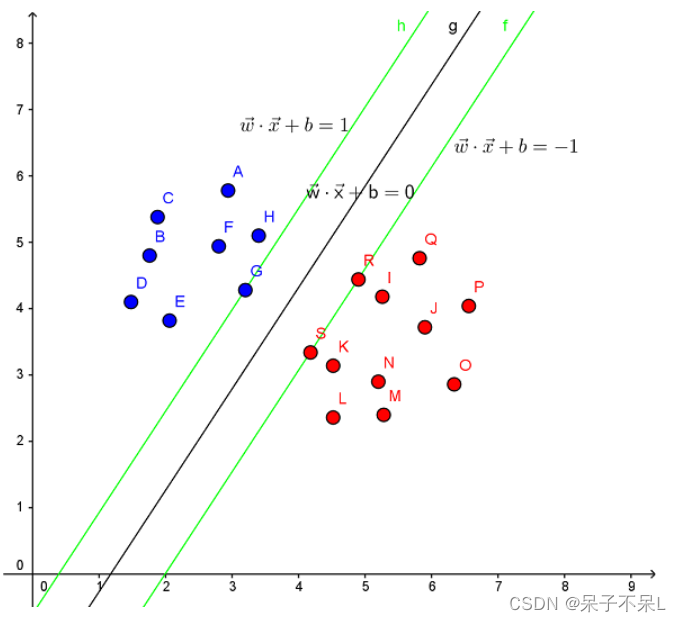
解决的问题:
- 线性分类
在训练数据中,每个数据都有n个的属性和一个二类类别标志,我们可以认为这些数据在一个n维空间里。我们的目标是找到一个n-1维的超平面(hyperplane),这个超平面可以将数据分成两部分,每部分数据都属于同一个类别。 其实这样的超平面有很多,我们要找到一个最佳的。因此,增加一个约束条件:这个超平面到每边最近数据点的距离是最大的。也成为最大间隔超平面(maximum-margin hyperplane)。这个分类器也成为最大间隔分类器(maximum-margin classifier)。 支持向量机是一个二类分类器。
- 非线性分类
SVM的一个优势是支持非线性分类。它结合使用拉格朗日乘子法和KKT条件,以及核函数可以产生非线性分类器。
二、实战
1、画出决策边界
导包sklearn.svm
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- %matplotlib inline
- # SVC: 分类
- # SVR:回归
- from sklearn.svm import SVC,SVR
随机生成数据,并且进行训练
- from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
- from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
- data,target = make_blobs(centers=2)
- target
- plt.scatter(data[:,0],data[:,1],c=target)

创建SVC模型(使用线性核函数),并训练
- # C=1.0, 惩罚系数,C越大越严格(有可能过拟合),C越小越不严格
- # kernel='rbf', 核函数
- # linear:线性核函数,不常用
- # rbf:默认值,高斯核函数,基于半径的和函数,可以解决非线性问题
- # poly:多项式核函数
- svc = SVC(C=1.0,kernel='linear')
- svc.fit(data,target)
提取系数获取斜率
- w1,w2 = svc.coef_[0]
- w1,w2
- # (1.0522835977410239, -0.8013229035839045)
线性方程的截距
- b = svc.intercept_[0]
- b
- # 9.794733796740164
得到线性方程
- # w1 * x1 + w2 * x2 + b = 0
- # x2 作为y轴,x1作为x轴
- # x2 = -(w1 * x1 + b) / w2
画图
- plt.scatter(data[:,0],data[:,1],c=target)
- x = np.linspace(data[:,0].min(),data[:,0].max(),20)
- y = -(w1 * x + b) / w2
- plt.plot(x,y)

获取支持向量
- svc.support_vectors_
- '''
- array([[-5.79772872, 5.85766345],
- [-4.59471853, 4.94156096]])
- '''
画出支持向量所在直线
- plt.scatter(data[:,0],data[:,1],c=target)
- x = np.linspace(data[:,0].min(),data[:,0].max(),20)
- y = -(w1 * x + b) / w2
- plt.plot(x,y)
- # 画支持向量
- vectors = svc.support_vectors_
- plt.scatter(vectors[:,0],vectors[:,1],c='r',alpha=0.3,s=200)
- # 活出支持向量所在的虚线
- # vectors = array([[-4.64189396, 5.45729366],
- # [-6.04692482, 7.04214351],
- # [-3.63094168, 5.92881411],
- # [-4.74569939, 7.93088232]])
- b1 = -(w1 * vectors[0,0] + w2 * vectors[0,1])
- b2 = -(w1 * vectors[1,0] + w2 * vectors[1,1])
- y1 = -(w1 * x + b1) / w2
- y2 = -(w1 * x + b2) / w2
- plt.plot(x,y1,ls='--')
- plt.plot(x,y2,ls='--')

2、使用多种核函数对iris数据集进行分类
导包
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
- from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
- data,target = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
- data.shape
- # (150, 4)
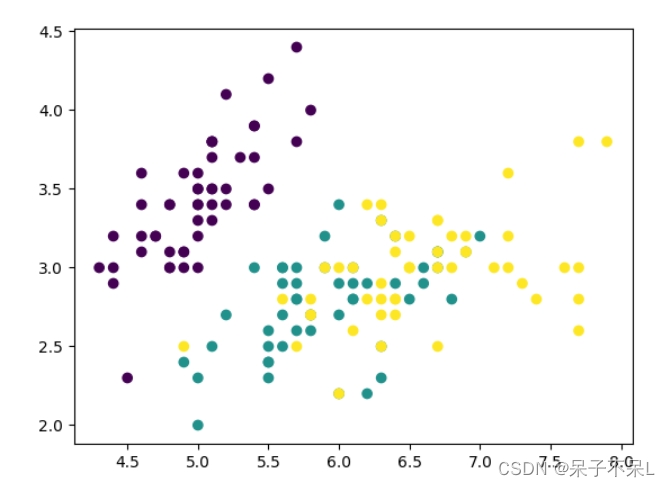
提取数据只提取两个特征,方便画图
- data2 = data[:,:2].copy()
- plt.scatter(data2[:,0],data2[:,1],c=target)
- def get_XY(data2):
- x = np.linspace(data2[:,0].min(),data2[:,0].max(),1000)
- y = np.linspace(data2[:,1].min(),data2[:,1].max(),1000)
- X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y)
- XY = np.c_[X.ravel(),Y.ravel()]
- return X,Y,XY
- X,Y,XY = get_XY(data2)
创建支持向量机的模型:'linear', 'poly'(多项式), 'rbf'(Radial Basis Function:基于半径函数)
- svc_dict = {
- 'linear':SVC(kernel='linear'),
- 'poly':SVC(kernel='poly'),
- 'rbf':SVC(kernel='rbf')
- }
- for i,key in enumerate(svc_dict):
- # 训练
- svc = svc_dict[key]
- svc.fit(data2,target)
- # 预测
- y_pred = svc.predict(XY)
- # 画图
- axes = plt.subplot(1,3,i+1)
- axes.pcolormesh(X,Y,y_pred.reshape(1000,1000),shading='auto')
- axes.scatter(data2[:,0],data2[:,1],c = target,cmap='rainbow')
- axes.set_title(key,fontsize=20)

3、SVM分离坐标点
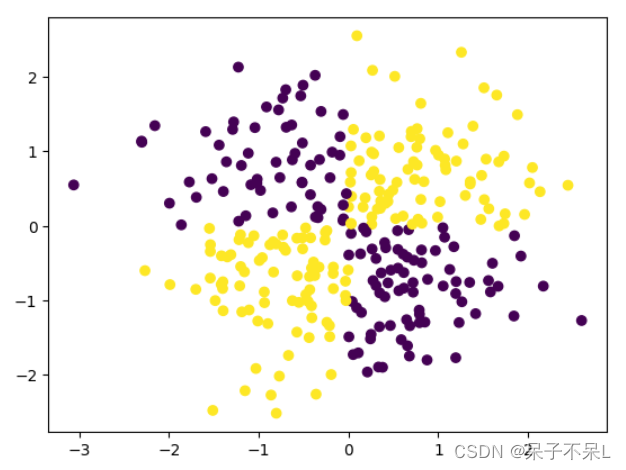
生成随机数据
- data = np.random.randn(300,2)
- data
- plt.scatter(data[:,0],data[:,1])

将1,3象限 和 2,4象限区分颜色
- target = (data[:,0] * data[:,1] > 0) * 1
- target
- # target = 1: 一三象限;target = 0:二四象限
- '''
- array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,
- 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,
- 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0,
- 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0,
- 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0,
- 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1,
- 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0,
- 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1,
- 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
- 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
- 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0,
- 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0,
- 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,
- 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1])
- '''
- plt.scatter(data[:,0],data[:,1],c=target)
使用基于半径核函数
- svc = SVC()
- svc.fit(data,target)
创造一个范围的点以及meshgrid
- def get_XY(data):
- x = np.linspace(data[:,0].min(),data[:,0].max(),1000)
- y = np.linspace(data[:,1].min(),data[:,1].max(),1000)
- X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y)
- XY = np.c_[X.ravel(),Y.ravel()]
- return X,Y,XY
- X,Y,XY = get_XY(data)
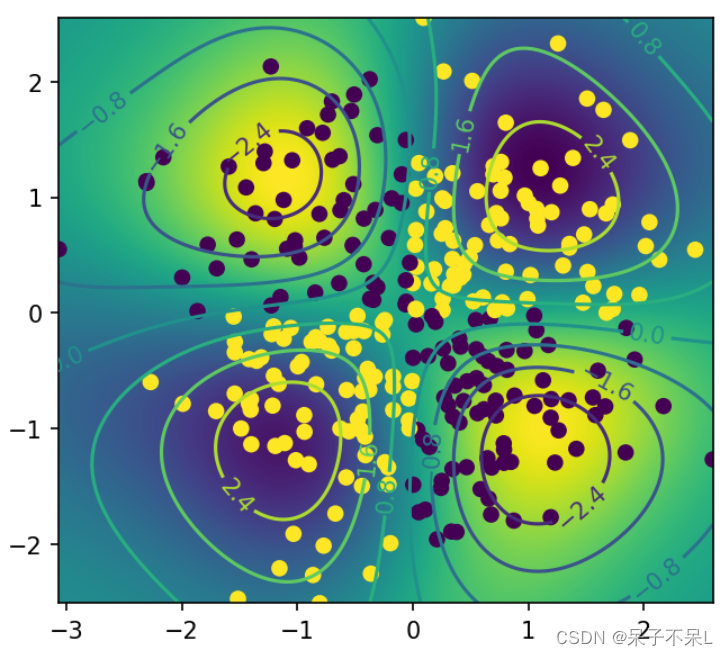
测试点到分离超平面的距离(decision_function)
- distance = svc.decision_function(XY)
- distance
- '''
- array([0.2733806 , 0.27487237, 0.27637551, ..., 0.33516833, 0.33292289,
- 0.33069489])
- '''
把距离当成一个二维的图片
画出图形
- 等高线
- C = plt.contour(X, Y, distance.reshape(1000, 1000))
- plt.figure(figsize=(5,5),dpi=150)
- plt.imshow(distance.reshape(1000,1000),extent=[data[:,0].min(),data[:,0].max(),data[:,1].min(),data[:,1].max()])
- # 等高线
- C = plt.contour(X,Y,distance.reshape(1000,1000))
- plt.clabel(C) # 显示等高线
- plt.scatter(data[:,0],data[:,1],c=target)
4、使用SVM多种核函数进行回归
自定义样本点rand,并且生成sin值
- x = np.random.random(100) * 10
- y = np.sin(x)
- plt.scatter(x, y)

数据加噪
- y[ : : 5] += np.random.randn(20) * 0.2
- plt.scatter(x, y)
提供测试数据
x_test = np.linspace(0, 10, 100).reshape(-1, 1)用不同的核函数预测
- # linear
- linear = SVR(kernel='linear')
- linear.fit(x.reshape(-1, 1), y)
- y_linear = linear.predict(x_test)
- # poly
- poly = SVR(kernel='poly')
- poly.fit(x.reshape(-1, 1), y)
- y_poly = poly.predict(x_test)
- # rbf
- rbf = SVR(kernel='rbf')
- rbf.fit(x.reshape(-1, 1), y)
- y_rbf = rbf.predict(x_test)
- from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
- from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
- # knn
- knn = KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors=5)
- knn.fit(x.reshape(-1, 1), y)
- y_knn = knn.predict(x_test)
- # tree
- tree = DecisionTreeRegressor()
- tree.fit(x.reshape(-1, 1), y)
- y_ = tree.predict(x_test)
绘制图形,观察三种支持向量机内核不同
- plt.scatter(x, y)
- plt.plot(x_test, y_linear, label='Linear')
- plt.plot(x_test, y_poly, label='poly')
- plt.plot(x_test, y_rbf, label='rbf')
- plt.plot(x_test, y_knn, label='knn')
- plt.plot(x_test, y_, label='tree')
- plt.legend()

-
相关阅读:
【Linux】文件权限详解
小程序获取用户手机号
2022.11.8-----leetcode.1684
Java上传文件大小受限怎么解决
一幅长文细学TypeScript(一)——上手
列举一些常用的Webpack配置和插件
C/C++运算优先级
Certificates does not conform to algorithm constraints 解决方案
{} >= {} 返回 true
Java学习笔记:SQLite数据库
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52421831/article/details/127770723
