-
AlexNet学习实现花的种类识别
AlexNet
AlexNet是2012年ISLVRC 2012(ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge)竞赛的冠军网络,分类准确率由传统的 70%+提升到 80%+。它是由Hinton和他的学生Alex Krizhevsky设计的。也是在那年之后,深度学习开始迅速发展。
AlexNet的亮点
1.AlexNet在激活函数上选取了非线性非饱和的relu函数,在训练阶段梯度衰减快慢方面,relu函数比传统神经网络所选取的非线性饱和函数(如sigmoid函数,tanh函数)要快许多。
2.AlexNet在双gpu上运行,每个gpu负责一半网络的运算。
3.采用局部响应归一化(LRN)。对于非饱和函数relu来说,不需要对其输入进行标准化,但Alex等人发现,在relu层加入LRN,可形成某种形式的横向抑制,从而提高网络的泛华能力。
4.池化方式采用overlapping pooling。即池化窗口的大小大于步长,使得每次池化都有重叠的部分。这种重叠的池化方式比传统无重叠的池化方式有着更好的效果,且可以避免过拟合现象的发生。
5.在全连接层的前两层中使用了 Dropout 随机失活神经元操作,以减少过拟合。
Alexnet网络的结构
第一层卷积层
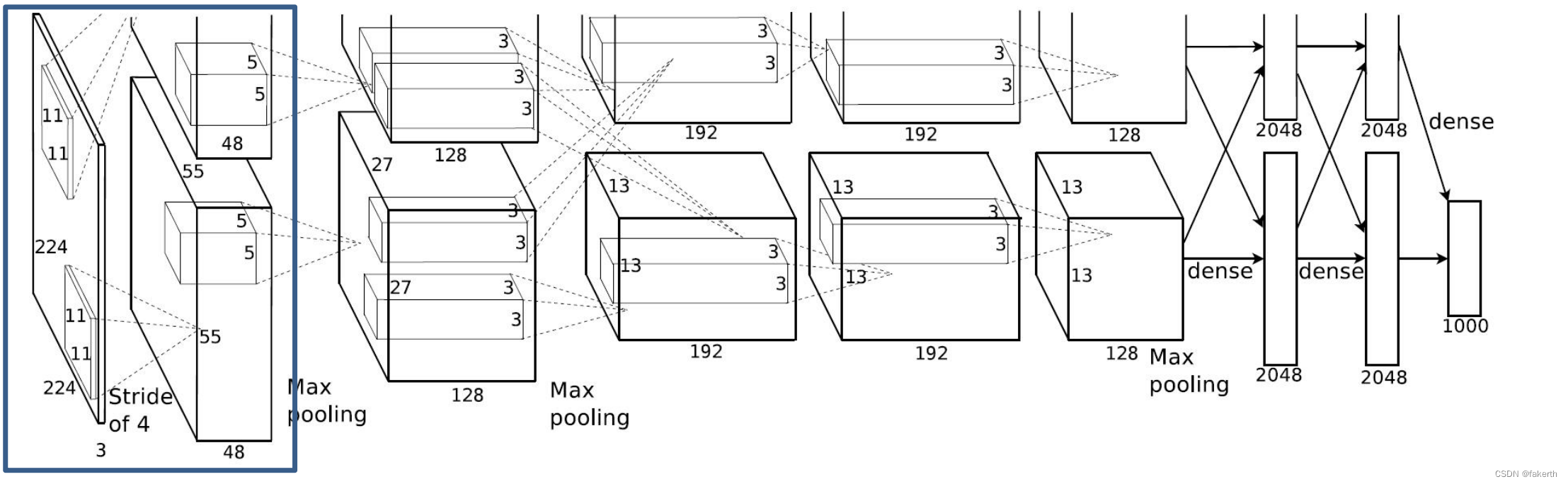
输入图片大小3x224x224,卷积核大小为11,padding[1,2],上面左面补一行0,下面右面补两行0,stride为4,96个卷积核,因为在两个gpu上进行卷积运算,两个卷积运算卷积核数量为48。输出大小为96x55x55,也就是两个48x55x55。
第二层池化层
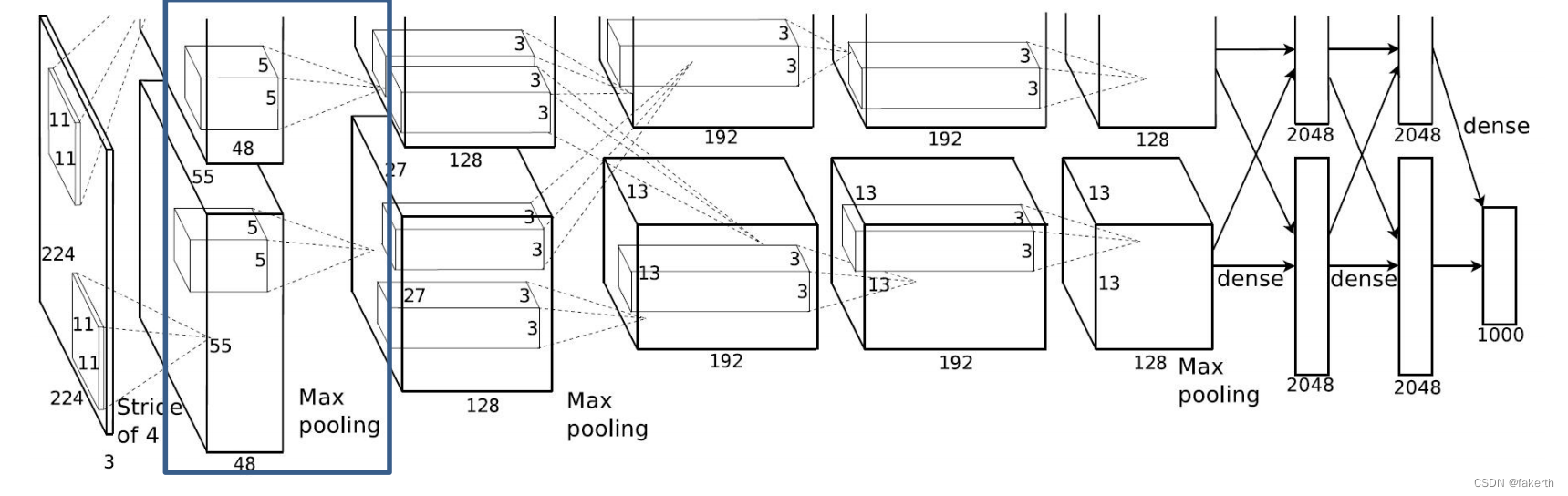
输入为96x55x55,padding为0,按stride为2进行3 × 3的Max池化,输出为96x27x27。
第三层卷积层
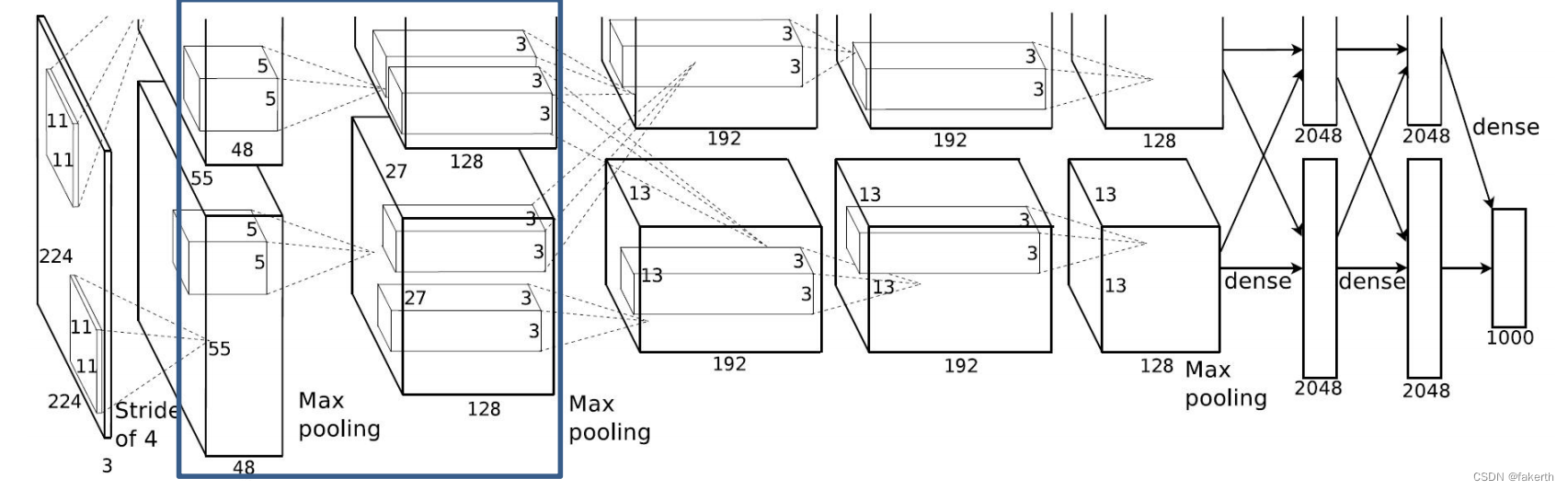
输入为96x27x27,卷积核大小为5,padding[2,2],上下左右各补两行0,stride为1,512个卷积核,因为在两个gpu上进行卷积运算,两个卷积运算卷积核数量为128。输出大小为256x27x27,也就是两个128x27x27。
第四层池化层
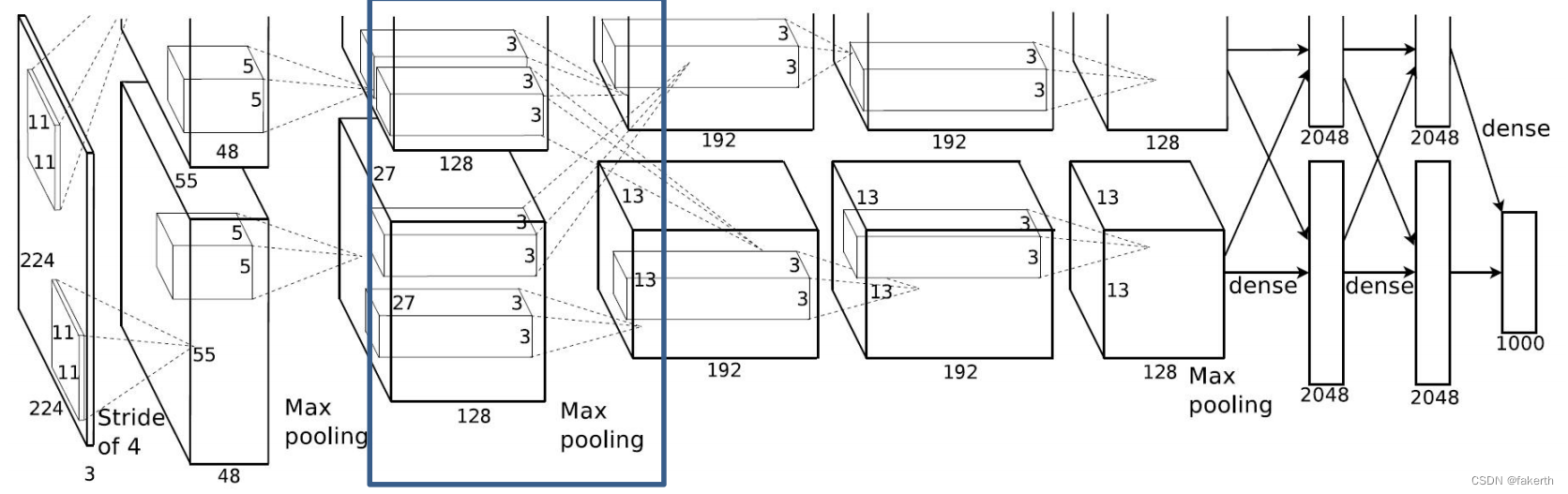
输入为256x27x27,padding为0,按stride为2进行3 × 3的Max池化,输出为256x13x13。
第五层卷积层
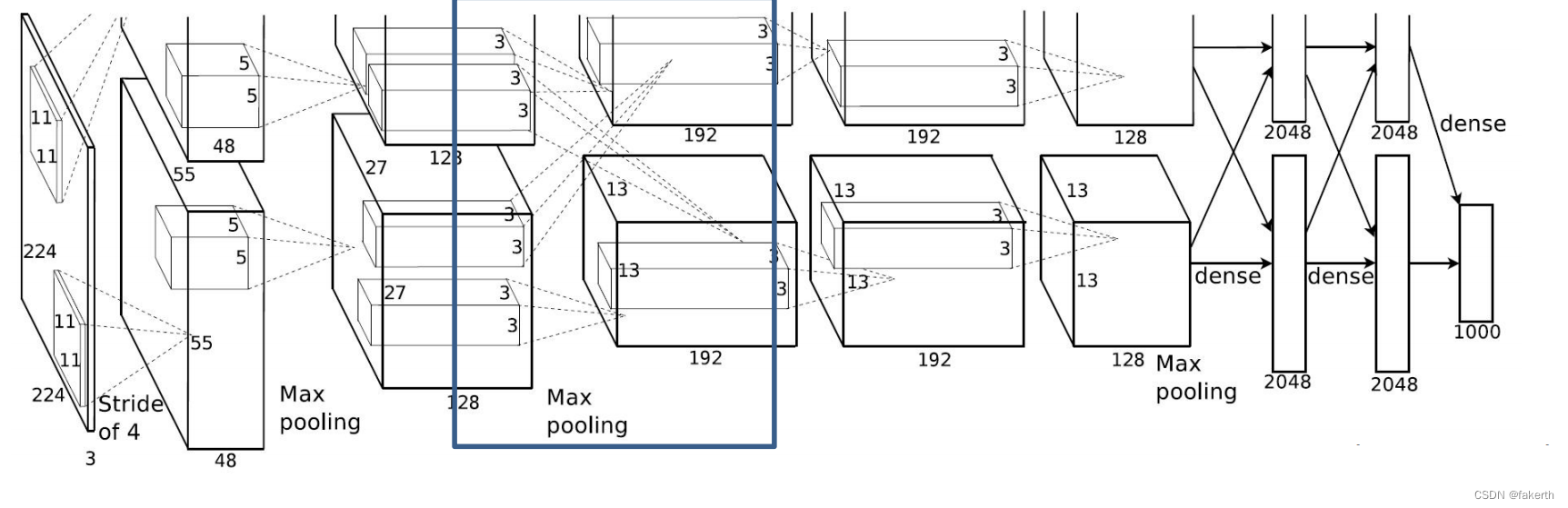
输入为256x13x13,卷积核大小为3,padding[1,1],上下左右各补一行0,stride为1,384个卷积核,因为在两个gpu上进行卷积运算,两个卷积运算卷积核数量为192。输出大小为384x13x13,也就是两个192x13x13。
第六层卷积层
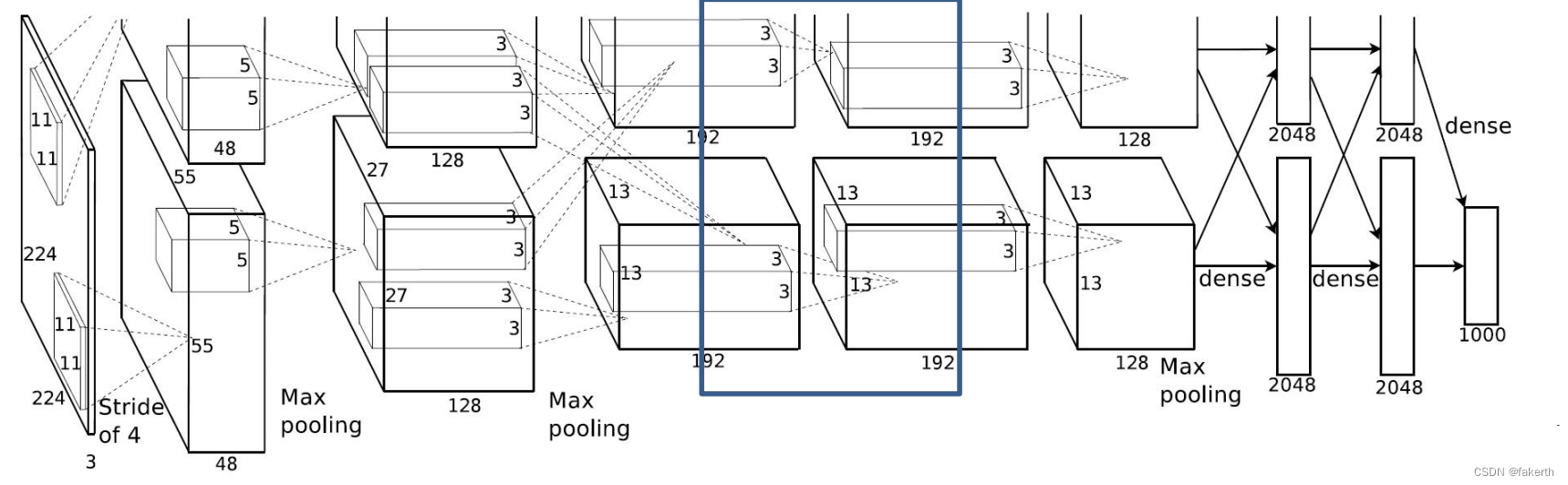
输入为384x13x13,卷积核大小为3,padding[1,1],上下左右各补一行0,stride为1,384个卷积核,因为在两个gpu上进行卷积运算,两个卷积运算卷积核数量为192。输出大小为384x13x13,也就是两个192x13x13。
第七层卷积层
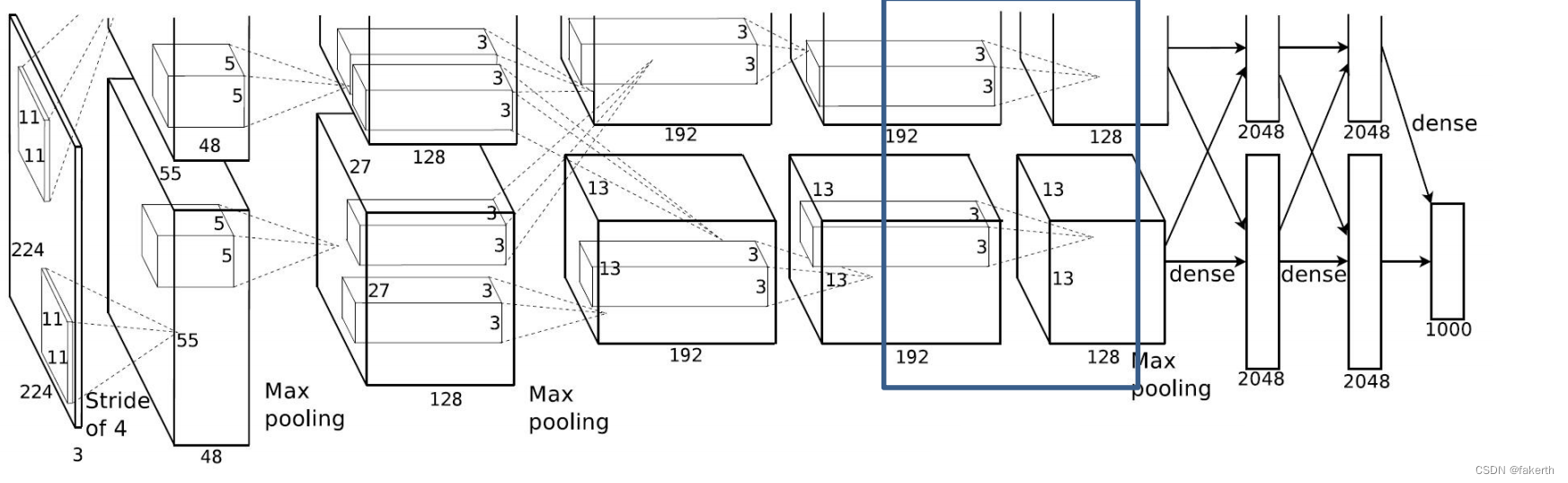
输入为384x13x13,卷积核大小为3,padding[1,1],上下左右各补一行0,stride为1,256个卷积核,因为在两个gpu上进行卷积运算,两个卷积运算卷积核数量为128。输出大小为256x13x13,也就是两个128x13x13。
第八层池化层
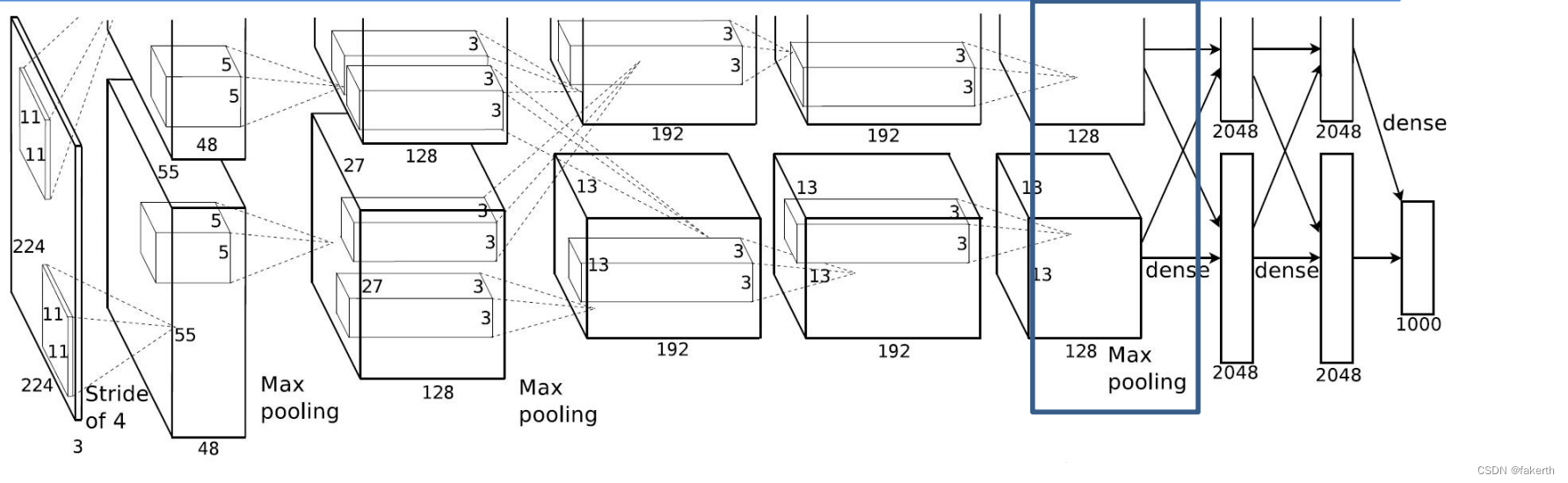
输入为256x13x13,padding为0,按stride为2进行3 × 3的Max池化,输出为256x6x6。
最后三层全连接层
最后三层全连接层输出最后结果。
AlexNet学习实现花的种类识别
1.建立模型
这里我们直接取一半进行卷积运算,第一层卷积层卷积核数量为48,最后的输出数量为我们要辨别的花种类的数量。
import torch.nn as nn import torch class AlexNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, init_weights=False): super(AlexNet, self).__init__() self.features = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(3, 48, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2), # input[3, 224, 224] output[48, 55, 55] nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[48, 27, 27] nn.Conv2d(48, 128, kernel_size=5, padding=2), # output[128, 27, 27] nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[128, 13, 13] nn.Conv2d(128, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[192, 13, 13] nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[192, 13, 13] nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Conv2d(192, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[128, 13, 13] nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[128, 6, 6] ) self.classifier = nn.Sequential( nn.Dropout(p=0.5), nn.Linear(128 * 6 * 6, 2048), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Dropout(p=0.5), nn.Linear(2048, 2048), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Linear(2048, num_classes), ) if init_weights: self._initialize_weights() def forward(self, x): x = self.features(x) x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1) x = self.classifier(x) return x def _initialize_weights(self): for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu') if m.bias is not None: nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01) nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
2.训练模型
数据集我上传到百度网盘里,可自行下载解压到根目录下。
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1291M7EPmVeQnqv9cD1TwcQ?pwd=zo65 提取码:zo65- 1
- 2

我们可以选择gpu训练,如果没有空闲的gpu选择cpu。
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")- 1
图像预处理加上随机截取和翻转,毕竟一张图片是蒲公英,总不能随机截取一下或者反转一下就不是蒲公英了吧,等于扩大了训练集数量。
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
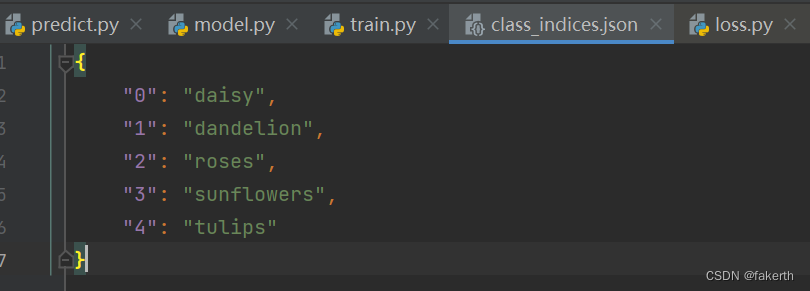
获取花分类名称对应索引,遍历字典将val-key -> key-val,并转成json格式写入文件。
# {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4} flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx # 获取花分类名称对应索引 cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items()) # 遍历字典将val-key -> key-val # write dict into json file json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4) with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file: json_file.write(json_str)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
得到:
完整训练代码如下:
import os import sys import json import torch import torch.nn as nn from torchvision import transforms, datasets, utils import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import torch.optim as optim from tqdm import tqdm from model import AlexNet def main(): device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") print("using {} device.".format(device)) data_transform = { "train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]), "val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)), # cannot 224, must (224, 224) transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])} train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root='./train', transform=data_transform["train"]) train_num = len(train_dataset) # {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4} flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx # 获取花分类名称对应索引 cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items()) # 遍历字典将val-key -> key-val # write dict into json file json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4) with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file: json_file.write(json_str) batch_size = 32 train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=0) validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root='./val', transform=data_transform["val"]) val_num = len(validate_dataset) validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=False, num_workers=0) print("using {} images for training, {} images for validation.".format(train_num, val_num)) # test_data_iter = iter(validate_loader) # test_image, test_label = test_data_iter.next() # # def imshow(img): # img = img / 2 + 0.5 # unnormalize # npimg = img.numpy() # plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0))) # plt.show() # # print(' '.join('%5s' % cla_dict[test_label[j].item()] for j in range(4))) # imshow(utils.make_grid(test_image)) net = AlexNet(num_classes=5, init_weights=True) net.to(device) loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # pata = list(net.parameters()) optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0002) epochs = 10 save_path = './AlexNet.pth' best_acc = 0.0 train_steps = len(train_loader) for epoch in range(epochs): # train net.train() # dropout开启 running_loss = 0.0 train_bar = tqdm(train_loader, file=sys.stdout) for step, data in enumerate(train_bar): images, labels = data optimizer.zero_grad() outputs = net(images.to(device)) loss = loss_function(outputs, labels.to(device)) loss.backward() optimizer.step() # print statistics running_loss += loss.item() train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1, epochs, loss) # validate net.eval() # dropout关闭 acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epoch with torch.no_grad(): val_bar = tqdm(validate_loader, file=sys.stdout) for val_data in val_bar: val_images, val_labels = val_data outputs = net(val_images.to(device)) predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1] acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item() val_accurate = acc / val_num print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' % (epoch + 1, running_loss / train_steps, val_accurate)) if val_accurate > best_acc: best_acc = val_accurate torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path) print('Finished Training') if __name__ == '__main__': main()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
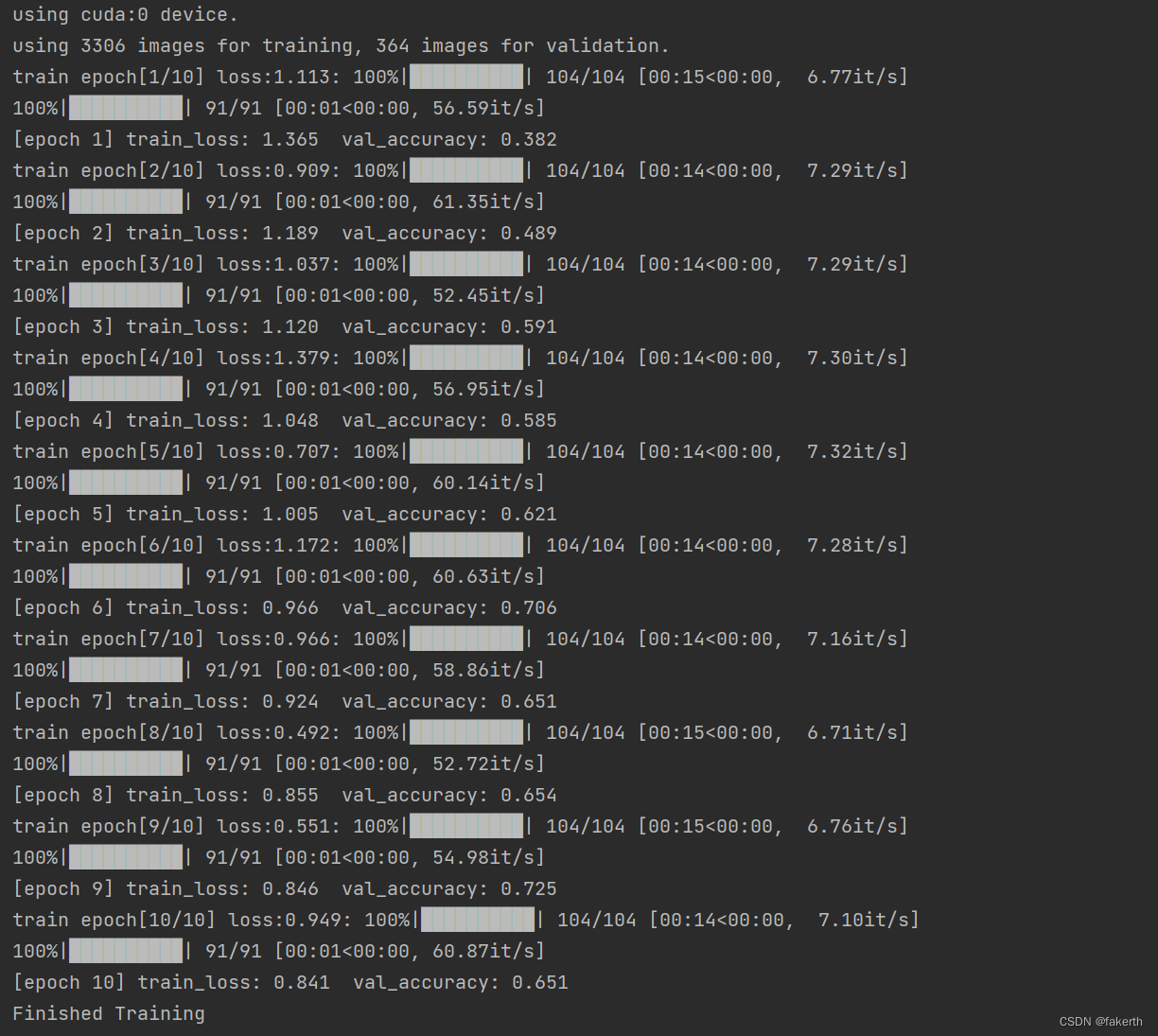
可以看出,最高识别率达到72%。
3.测试泛化能力
去网上找了几张图片,简直恐怖,我都不认识郁金香。
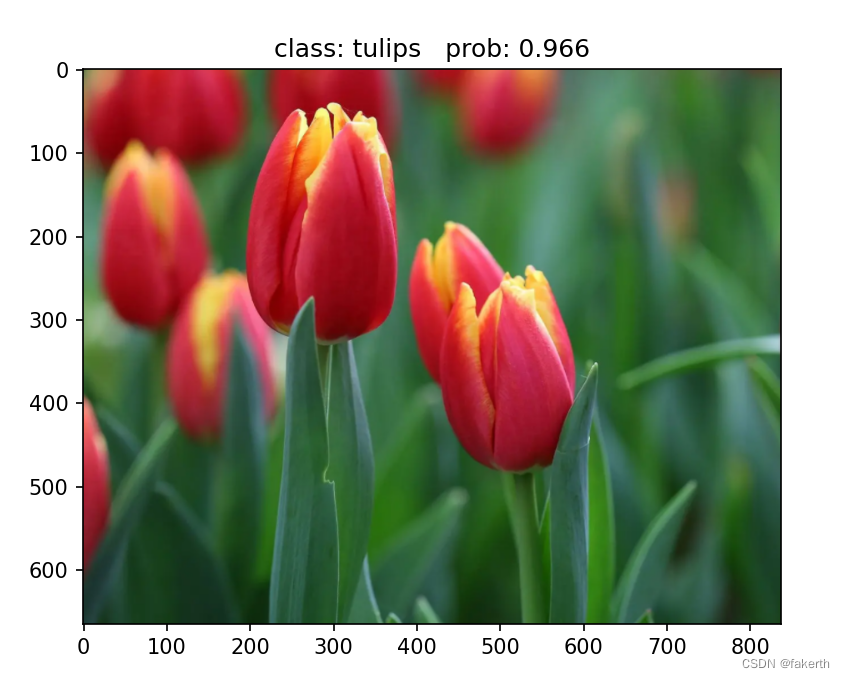
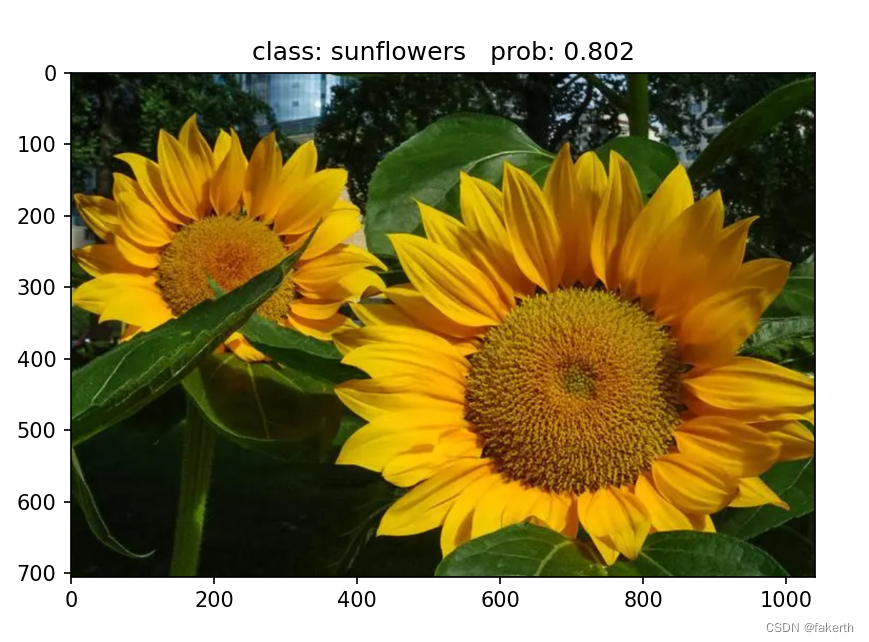
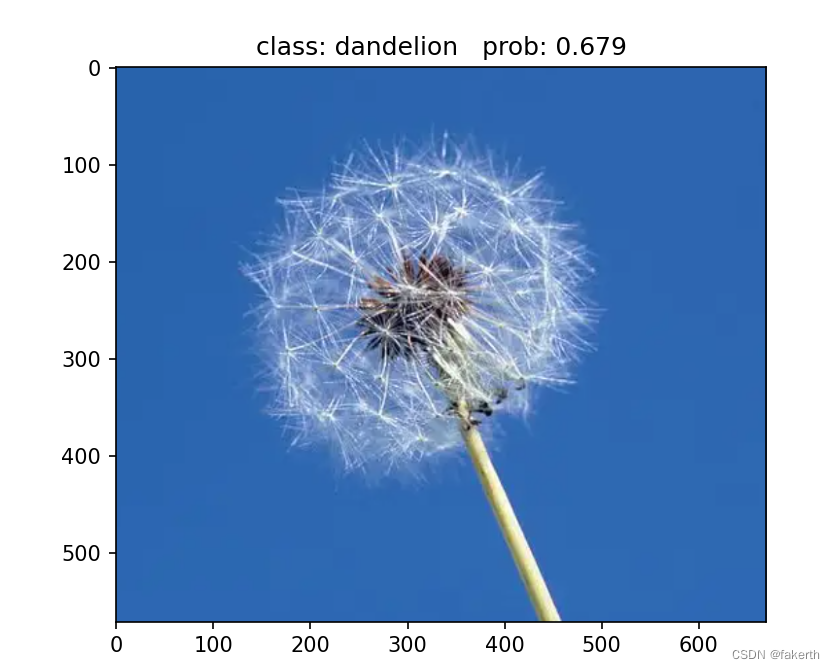


import os import json import torch from PIL import Image from torchvision import transforms import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from model import AlexNet def main(): device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") data_transform = transforms.Compose( [transforms.Resize((224, 224)), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]) # load image img_path = "3.jpg" assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path) img = Image.open(img_path) plt.imshow(img) # [N, C, H, W] img = data_transform(img) # expand batch dimension img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0) # read class_indict json_path = './class_indices.json' assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path) with open(json_path, "r") as f: class_indict = json.load(f) # create model model = AlexNet(num_classes=5).to(device) # load model weights weights_path = "./AlexNet.pth" assert os.path.exists(weights_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(weights_path) model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path)) model.eval() with torch.no_grad(): # predict class output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu() predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0) predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy() print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)], predict[predict_cla].numpy()) plt.title(print_res) for i in range(len(predict)): print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)], predict[i].numpy())) plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': main()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
-
相关阅读:
C语言之mkdtemp()特定占位符:XXXXXX 用法实例(八十五)
PyQt5快速开发与实战 9.4 Matplotlib在PyQt中的应用
Java.lang.Class类 getClasses()方法有什么功能呢?
小白也想搞科研(二)之代码升级
ubuntu------anaconda和openvino安装
axios Post 数据问题
数据库学习之数据类型
较真儿学源码系列-PowerJob启动流程源码分析
Mysql 中如何导出数据?
神经网络有哪些基本功能,常见的神经网络有哪些
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43912621/article/details/127757396
