-
Vue.js -Vuex 全局组件高效的数据通信方案
Vuex 是什么?
Vuex 是 vue 项目中实现
全局的、大范围的数据通信的解决方案作用:
能够方便、高效地实现组件之间的数据通信
使用 Vuex 的好处:
- 数据的
存取一步到位,不需要层层传递 - 数据的
流动非常清晰 - 存储在 Vuex 中的数据都是
响应式的
安装和配置Vuex:
① 安装 Vuex 的依赖包
npm i => npm run serve => npm i vuex@3.6.2 -S
② 创建 store 模块
- 导入Vue 和 Vuex 依赖包
- 把Vuex 安装为 Vue 的插件
- 创建 store 的实例对象
- 向外导出 store 的实例对象

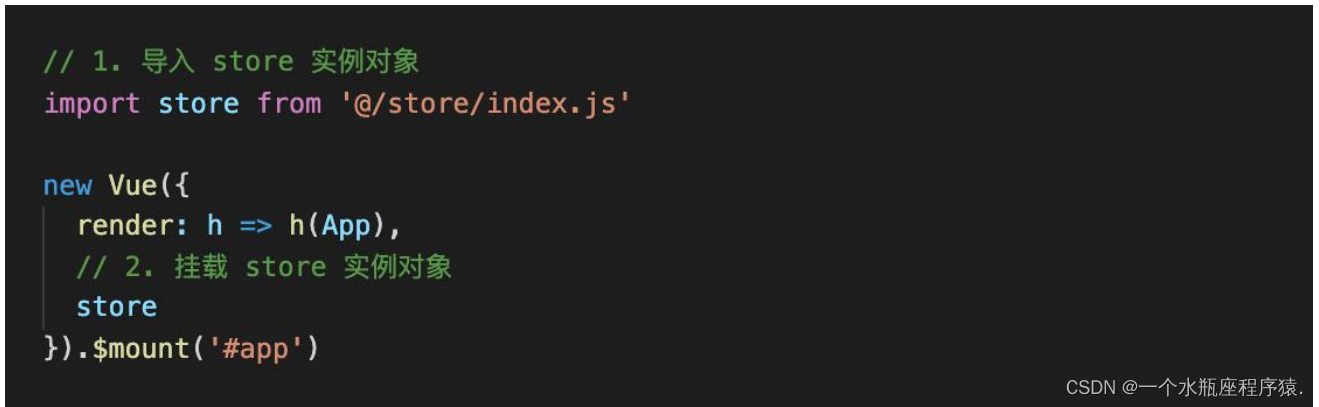
③ 挂载 store 的实例对象到 new Vue() 中去State 的基本使用
state - 定义并使用全局数据
什么是 state ?
state
本质上就是一个对象,用来存储全局的数据的state提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到 store 的 state 中进行存储
state 的使用步骤:
第一种方式:
① 在 Vuex 的
state 选项对象中,定义全局数据② 在组件中通过
this.$store.state.全局数据名称访问全局数据store/index.js
<script> const store = new Vuex.store({ // 在 state 中,定义全局数据 state:{ count: 0 } }) script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Left.vue / Right.vue
<template> <div class="right-container"> <p>count 值:{{$store.state.count}}p> div> template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
第二种方式:
使用
mapState辅助函数 +computed,来获取全局的数据Left.vue
<script> // 1. 导入辅助函数 mapState import { mapState } from 'vuex' // mapState 函数的返回值是一个对象,里面存放的,就是 state 中全局数据的映射 console.log(mapState(['count'])) /* { count:function(){ return this.$store.state.count } } */ export default { name:'left', computed:{ // 2. 将得到的 state 中全局数据的映射,通过扩展运算符,放入 computed 中 // mapState是一个数组,需要使用哪个数据,就在mapState里面写入哪个数据 // ... : 把全局里面的那些数据映射为当前组件的映射属性 // 可以理解为当前count就是我的计算属性 ...mapState(['count']) } } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
mapState 的对象传参格式
当组件 data 中数据和 state 中的全局数据名字冲突的时候,mapState 可以使用对象格式的传参来解决冲突
<script> data(){ return { count:666 } }, computed:{ // 为了解决命名冲突,我们要给 mapState 传一个对象的参数 // mapState({'计算属性的名字':'要访问的全局数据的名字'}) ...mapState({ // 给 count 取了一个名为 ct ct:'count' }) } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
Mutation 的基本使用
mutation - 怎样修改全局数据和严格模式
怎样修改 state 中的数据?
// 实现 +1 功能 addBtn(){ // 直接这样的话,虽然页面上没有任何问题 // 但是 VUe调试工具 监视不到数据的变化,并且不利于数据的统一维护 // 防止这种写法,需要开启 vuex 的严格模式 this.$store.state.count += 1 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
结论:能够直接修改,但是
不推荐原因:会导致
修改来历不明确的问题,不利于调试和 后期的维护开启严格模式
const store = new Vuex.Store({ // 开启 vuex 严格模式 // 开启严格模式之后,直接修改全局数据就会报错,可以防止程序员写垃圾代码 // 但是严格模式性能上有损耗,所以在项目上线之前,要关掉严格模式 strict:true, state:{ count: 0 } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
mutation - 定义和使用 mutation
mutation是什么?
mutation 本质上是 JavaScript
函数,专门用来变更 store 中的数据
特点:想要修改 state 中的数据,就
必须调用 mutation 方法好处:能够确保
修改来源的唯一性,方便调试和后期维护mutation 的使用步骤:
-
在 Vuex 中定义 mutation 方法
const store = new Vuex.Store({ strict:true, state:{ count: 0 }, // mutation:专门用来变更 state 中的数据的 // state 中的数据只允许 mutation 来修改 mutations:{ add(state){ // mutation 函数的第一个参数永远都是 state state.count += 1 } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
-
在组件中,通过
this.$store.commit('mutation中定义的函数名')调用 mutation 方法addBtn(){ // 想要修改全局数据,必须调用 mutation // this.$store.commit('mutations中定义的函数名') this.$store.commit('add') }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
mutation - 给 mutation 函数传参
给 mutation 函数传参
第一种方式:
通过传参可以
提高 mutation 方法的通用性。例如 +1、+2、+3-
index.js
<script> const store = new Vuex.Store({ strict:true, state:{ count: 0 }, mutations:{ add(state,n){ // mutation 函数的第一个参数永远是 state // 第二个参数就是组件中调用的时候,传递过来的参数 state.count += n } } }) script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
-
Left.vue
<script> addBtn(n){ // 通过给 mutation 传参,提高 mutation 函数的通用性 // this.$store.commit('mutation 中定义的函数名',参数) this.$store.commit('add',n) } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
第二种方式:
mapMutations 辅助函数
Vuex 提供了
mapMutations辅助函数,可以方便的把 store 中的mutation方法,映射到当前组件的 methods中import { mapMutations } from 'vuex' console.log(mapMutations(['add'])) /* { add(n){ this.$store.commit('add',n) } }*/ export default { name:'Right', // mapMutaions 辅助函数,必须结合 methods 来使用 methods:{ ...mapMutations(['add']) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
mapMutations 辅助函数对象格式传参,解决命名冲突问题
// 解决命名冲突写法 // ...mapMutations({ 自定义的名字 :'store中全局的mutation的名字' }) ...mapMutations({add2:'add'})- 1
- 2
- 3
Action 的基本使用
Action必须是同步函数- 在项目开发中,为了保证 store 中
状态的每一次变化都是可追踪的,Vuex 规定:mutation 必须是同步函数 - 否则 ,
vue-devtools将无法正常追踪store 中数据的变化,这对大型项目的开发调试是灾难性的

action - 定义并使用 action
action 是什么?
action
本质上就是JavaScript 函数,专门用来处理 Vuex 中的异步操作
action 的使用步骤:
-
在 Vuex 中定义 action 方法
<script> actions:{ addAsync(context){ console.log(context); // context 缩写为 ctx,是 store 的实例对象 // context 永远是 actions 函数的第一个参数 // context 上有commit 函数,用来调用 mutation // 延迟1秒,让 state 中的数据自增 setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('add') },1000) } } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
-
在组件中,通过
this.$store.dispatch('actions中定义的函数名')调用 action 函数<template> <div class="left-container"> <h3>Left 组件h3> <button @click="$store.dispatch('addAsync')">一秒后 -1button> div> template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
给 action 函数传参:
通过传参可以
提高 action 方法的通用性index.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({ mutations:{ add(state,n){ state.count += n; } }, actions:{ // action 函数的第一个参数永远都是 context,也就是 store 实例对象 // 第二个参数,是在组件调用 action 的时候,传递过来的 addAsync(context,n){ setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('add',n) },1000) } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
Left.vue
<template> <div class="left-container"> <button @click="$store.dispatch('addAsync',1)">一秒 + 1button> <button @click="$store.dispatch('addAsync',2)">一秒 + 2button> div> template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
action 接收多个参数:
action 接收多个参数,需要使用对象的格式
Left.vue
<template> <div class="left-container"> <button @click="$store.dispath('addAsync',{n:1,time:1000})">button> <button @click="$store.dispath('addAsync',{n:2,time:2000})">button> div> template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
index.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({ actions:{ // 传多个参数时,第二个参数必须是一个对象 addAsync(context,obj){ setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('add',obj.n) },obj.time) } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
mapActions 辅助函数:
mapActions 辅助函数:
Vuex 提供了
mapActions辅助函数,可以方便的把 store 中的action 方法,映射到当前组件的 methods 中:import { mapActions } from 'vuex' export default { name:'Right', methods:{ // actions 的辅助函数和 mutations 的辅助函数一样,都需要和 methods 配合使用 ...mapActions(['addAsync']) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
mapActions 辅助函数对象格式传参,解决命名冲突问题:
import { mapActions } from 'vuex' export default { name:'Right', methods:{ // 重新命名 ...mapActions({ addAsync2:'addAsync' }) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Getter 的基本使用
getter 是什么?
getter 可以理解为是
Vuex 中的计算属性,它内部依赖于 state 中的数据,state 中的值变化,getter 的值会自动更新getter 的使用步骤:
第一种方式:
- 在 Vuex 中定义 getter 方法
- 在组件中,通过
this.$store.getters.getters中定义的函数名,访问 getter
<script> const store = new Vuex.Store({ state:{ num1:0, num2:0 }, // 使用 getter 定义全局的计算属性 // 某一个值,是依赖于全局的数据动态计算出来 // 这时就用 getters // 第一个值依旧是 state getters:{ sum(state){ // getter 函数的第一个参数是 state // getter 根据全局的数据进行改变 // state 中的值变化,getter 的值会自动更新 return state.num1 + state.num2 } } }) script> <template> <div class="left-container"> <p>全局数据 num1 + num2 = {{$store.getters.sum}}p> div> template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
第二种方式:
mapGetters 辅助函数
Vuex 提供了
mapGetters辅助函数,可以方便的把 store 中的getter,映射到当前组件的 computed 中:<script> import { mapGetters } from 'vuex' // mapGetters 要结合 computed 一起使用 export default { computed:{ // 使用 mapGetters 辅助函数,将全局的 getters 映射到当前组件的 computed 中 // 那边的函数名称,写到这个里面 ...mapGetters(['sum']) } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
mapGetters 辅助函数对象格式传参,解决命名冲突问题
<script> export default { computed:{ // 重新命名 ...mapGetters({ sum2:'sum' }) } } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Module 的基本使用
module - Vuex 中模块的概念
module 是什么?
Vuex 中的 module 表示按照
模块化的开发思想,把有业务关联的数据和方法封装在一起module 就是 Vuex 中的模块化
module 的使用场景
- 当一个项目的
页面数量很少,逻辑功能简单的情况下,是完全可以不使用 module 模块的 - 但是当一个项目的
页面数量很多,逻辑功能复杂的情况下,所有的全局数据、方法都集中在了一起,会导致Vuex 的结构混乱,不利于现阶段的开发和后期的维护,那么此时就需要使用模块来管理全局的数据和方法

定义和注册模块
-
定义模块:
每个模块都是
彼此独立的,都可以拥有自己的 state、mutaions、actions、getters 节点:一个模块都是一个 js 文件
例如:计数器模块 count.js // 计数器模块 export default { // 当前模块的数据 // 函数的形式为了解决: // 模块被多次注册,并开启命名空间时,公用同一份数据 state(){ return {} }, // 当前模块修改 state 数据的函数 mutaions: {} // 当前模块的异步操作 actions: {} // 当前模块的计算属性 getters: {} }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
-
注册模块:
// 1. 导入模块 import moduleCount from './count.js' import moduleTask from './task.js' const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { // 2.注册模块 // 语法:模块注册的名称 : 导入的名称 // 将来访问模块里的数据的时候,要用到这个模块注册的名称 count:moduleCount, task:moduleTask } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
module - 为模块开启命名空间
namespaced(命名空间)
namespaced(命名空间)可以解决不同模块之间成员名称冲突的问题。- 在实际开发中,建议为每个 module 模块都可以命名空间
未开启命名空间:
<script> showBtn() { // 调用 vuex 中的 mutation 函数 // 没有开启命名空间,两个模块的 mutation 都会被调用 // 执行顺序就是注册时的顺序 this.$store.commit('show') } script> <script> mutations:{ show(){ console.log('调用了组件中的 show 方法') } } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
未开启命名空间,那么会默认打印所有模块中对应的show方法
开启命名空间
在
定义模块时,只需在模块中声明namespaced:true选项,即可为当前模块开启命名空间// 结论:在 vuex 中,只要拆分了模块,那么就要为模块开启命名空间 // namespaced:true export default { namespaced:true, state:{}, mutations:{}, actions:{}, getters:{} }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
通过模块的
注册名称访问模块下的成员当模块启用了 namespaced:true 之后,模块就有了自己的
命名空间。访问时要加上模块的注册名称才能访问到示例代码:
showBtn(){ // 开启命名空间后,要使用下面的语法,调用 mutation 函数 // this.$store.commit('模块的注册名称 / 模块下的mutation函数名') this.$store.commit('count/show') }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
module - 在组件中访问模块内 state 的两种方式
方式一:通过
this.$store.state.模块注册名称.要访问的数据<template> <div class="left-container"> <h3>Left 组件h3> <p>count的值:{{this.$store.state.count.num}}p> div> template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
方法二:通过
mapState 辅助函数<template> <div class="right-container"> <p>count的值:{{num}}p> div> template> <script> import {mapState} from 'vuex' export default { computed:{ // 没拆分模块之前,访问 state 的方式 ...mapState(['num']) // 拆分模块之后,访问 state 的方式 // ...mapState('模块的注册名称',['要访问的数据的名称']) ...mapState('count',['num']) } } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
module - 在组件中调用内 mutation 的两种方式
在count 模块中定义一个 mutation
示例代码:count.js
export default { namespaced:true, // 开启命名空间,用于隔离模块 state(){ return { num: 0 } }, mutations: { // 改变 state 中的值 add(state,n){ state.num += n } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
方法一:通过
this.$store.commit('组件的注册名称 / 要调用的mutation函数名称',参数)<template> <div class="left-container"> <h3>Left 组件h3> <button class="btn btn-primary" @click="$store.commit('count/add')">+1button> div> template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
方法二:通过
mapMutations 辅助函数<template> <div class="right-container"> <button class="btn btn-warning" @click="add(-1)">-1button> div> template> <script> import { mapMutations } from 'vuex' export default { methods:{ // ...mapMutations('模块的注册名称',['要调用的mutation函数名称']) ...mapMutations('count',['add']) } } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 数据的
-
相关阅读:
等级保护测评需要多长时间 ?
GZ035 5G组网与运维赛题第10套
【Linux篇】磁盘lvm管理(PV,VG,LV,PE)
I Pa?sWorD(2023icpc网络预选赛)
Spring Data JPA系列5:让IDEA自动帮你写JPA实体定义代码
kafka入门03——简单实战
Android入门第19天-Android里的RatingBar的使用
[Firefox/快捷键] 禁用Ctrl-W快捷键
机器人强化学习——第一人称 VS 第三人称
每日练习------定义一个N*N二维数组,从键盘上输入值,找出每行中最大值组成一个一维数组并输出;
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_60353088/article/details/127738178
