-
回溯算法的应用
模板
void backtracking(参数) { if (终止条件) { 存放结果; return; } for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) { 处理节点; backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归 回溯,撤销处理结果 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
1. 组合
题目描述
给定两个整数
n和k,返回范围[1, n]中所有可能的k个数的组合。你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:n = 4, k = 2 输出: [ [2,4], [3,4], [2,3], [1,2], [1,3], [1,4], ]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
代码
class Solution { //定义路径 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); //返回结果 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { combineHelper(n, k, 1); return res; } /** * 每次从集合中选取元素,可选择的范围随着选择的进行而收缩,调整可选择的范围,就是要靠startIndex * @param startIndex 用来记录本层递归的中,集合从哪里开始遍历(集合就是[1,...,n] )。 */ private void combineHelper(int n, int k, int startIndex){ //设置终止条件:收集完节点就可以 if(path.size() == k){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } //回溯中的循环遍历 for(int i = startIndex;i <= n;i++){ //加入到路径 path.add(i); combineHelper(n, k, i + 1); path.removeLast(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
代码优化(剪枝)
class Solution { //定义路径 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); //返回结果 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { combineHelper(n, k, 1); return res; } /** * 每次从集合中选取元素,可选择的范围随着选择的进行而收缩,调整可选择的范围,就是要靠startIndex * @param startIndex 用来记录本层递归的中,集合从哪里开始遍历(集合就是[1,...,n] )。 */ private void combineHelper(int n, int k, int startIndex){ //设置终止条件:收集完节点就可以 if(path.size() == k){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } //回溯中的循环遍历 /* 此处可以优化,回溯算法的优化大都在控制单层循环的次数上 n - (k - path.size()) + 1:表示可以向下递归所需的最小剩余数组长度 例如:n = 4,k = 4 只有1234,所以当 startIndex = 2,只能遍历到234 */ for(int i = startIndex;i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1;i++){ //加入到路径 path.add(i); combineHelper(n, k, i + 1); path.removeLast(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
2. 组合之和
1. 组合之和(1)
题目描述
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7 输出:[[2,2,3],[7]] 解释: 2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。 7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。 仅有这两种组合。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
代码
class Solution { //创建结果集 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); //路径 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); //记录和 int sum = 0; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { //创建数组 int n = candidates.length; combinationSumHelp(candidates, target, 0, n); return res; } public void combinationSumHelp(int[] candidates, int target,int startIndex,int n){ // 减枝 if (sum > target) { return; } //结束条件 if(sum == target){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for(int i = startIndex;i < n;i++){ path.add(candidates[i]); sum += candidates[i]; //由于元素可以无限制被取,所以不用i + 1 combinationSumHelp(candidates, target, i, n); sum -= candidates[i]; path.removeLast(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
2. 组合之和(2)
题目描述
给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
注意:解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8, 输出: [ [1,1,6], [1,2,5], [1,7], [2,6] ]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
代码
class Solution { //创建结果集 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); //路径 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); //记录和 int sum = 0; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) { //创建数组 int n = candidates.length; //为了将重复的数字都放到一起,所以先进行排序 Arrays.sort(candidates); combinationSumHelp(candidates, target, 0, n); return res; } public void combinationSumHelp(int[] candidates, int target,int startIndex,int n){ // // 减枝 // if (sum > target) { // return; // } //结束条件 if(sum == target){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } //sum + candidates[i] <= target:可以避免单层不必要的遍历,加在这里效率较高,和下面代码效果类似 /* // // 减枝 // if (sum > target) { // return; // } */ for(int i = startIndex;i < n && sum + candidates[i] <= target;i++){ //正确剔除重复解的办法 //跳过同一树层使用过的元素 if ( i > startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] ) { continue; } path.add(candidates[i]); sum += candidates[i]; //i + 1:取不同元素 combinationSumHelp(candidates, target, i + 1, n); sum -= candidates[i]; path.removeLast(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
3. 组合之和(3)
题目描述
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合,且满足下列条件:
只使用数字1到9
每个数字 最多使用一次
返回 所有可能的有效组合的列表 。该列表不能包含相同的组合两次,组合可以以任何顺序返回。示例 1:
输入: k = 3, n = 7 输出: [[1,2,4]] 解释: 1 + 2 + 4 = 7 没有其他符合的组合了。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
代码
class Solution { //定义路径 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); //返回结果 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); //记录和 int sum = 0; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) { combineHelper(n, k, 1); return res; } /** * 每次从集合中选取元素,可选择的范围随着选择的进行而收缩,调整可选择的范围,就是要靠startIndex * @param startIndex 用来记录本层递归的中,集合从哪里开始遍历(集合就是[1,...,n] )。 */ private void combineHelper(int n, int k, int startIndex){ // 减枝 if (sum > n) { return; } //设置终止条件:收集完节点就可以 if(path.size() == k){ if(sum == n) res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } //回溯中的循环遍历 /* 此处可以优化,回溯算法的优化大都在控制单层循环的次数上 n - (k - path.size()) + 1:表示可以向下递归所需的最小剩余数组长度 例如:n = 4,k = 4 只有1234,所以当 startIndex = 2,只能遍历到234 */ for(int i = startIndex;i <= 9 - (k - path.size()) + 1;i++){ //加入到路径 sum += i; path.add(i); combineHelper(n, k, i + 1); path.removeLast(); sum -= i; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
4. 总结
- 三种组合之和的回溯代码模板类似
- 主要是对求取结果集去重**(去重之前应该先排序)**以及回溯过程剪枝
3. 子集问题
1. 分割回文串
题目描述
给你一个字符串
s,请你将s分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回s所有可能的分割方案。回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。示例 1:
输入:s = "aab" 输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]- 1
- 2
代码
class Solution { //结果集 List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>(); //栈 Deque<String> stack = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<String>> partition(String s) { int n = s.length(); partitionHelp(s, 0, n); return res; } public void partitionHelp(String s,int startIndex,int n){ //终止条件,如果起始位置大于s的大小,说明找到了一组分割方案 if(startIndex >= n){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(stack)); return; } //单层循环 for(int i = startIndex;i < n;i++){ //判断是不是回文串 if(isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)){ String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1); stack.addLast(str); }else{ continue; } //起始位置后移,保证不重复 partitionHelp(s, i + 1, n); stack.removeLast(); } } //判断是否是回文串 private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int startIndex, int end) { for (int i = startIndex, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) { if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) { return false; } } return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
2. 复原 IP 地址
题目描述
有效 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 ‘.’ 分隔。
例如:“0.1.2.201” 和 “192.168.1.1” 是 有效 IP 地址,但是 “0.011.255.245”、“192.168.1.312” 和 “192.168@1.1” 是 无效 IP 地址。
给定一个只包含数字的字符串 s ,用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能的有效 IP 地址,这些地址可以通过在 s 中插入 ‘.’ 来形成。你 不能 重新排序或删除 s 中的任何数字。你可以按 任何 顺序返回答案。代码
class Solution { //定义路径 LinkedList<String> stack = new LinkedList<>(); //返回结果 List<String> res = new ArrayList<>(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) { int n = s.length(); restoreIpAddressesHelp(s, 0, n); return res; } public void restoreIpAddressesHelp(String s,int startIndex,int n){ //终止条件,如果起始位置大于s的大小,说明找到了一组分割方案 if(startIndex >= n){ if(stack.size() == 4){ sb.append(stack.get(0)); sb.append("."); sb.append(stack.get(1)); sb.append("."); sb.append(stack.get(2)); sb.append("."); sb.append(stack.get(3)); res.add(sb.substring(0, sb.length())); sb.delete(0,sb.length()); } return; } //单层循环 for(int i = startIndex;i < n && stack.size() <= 4;i++){ String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1); //判断数字是不是符合要求 if(isValid(str)){ stack.add(str); }else{ continue; } //起始位置后移,保证不重复 restoreIpAddressesHelp(s, i + 1, n); stack.removeLast(); } } //判断是否是是 0-255 private boolean isValid(String str) { if(str.charAt(0) == '0' && str.length() > 1) return false; long num = Long.parseLong(str); if(num >= 0 && num <= 255) return true; else return false; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
3. 子集
题目描述
给你一个整数数组
nums,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]- 1
- 2
代码
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { //空集是所有集合的子集 res.add(new ArrayList(0)); int n = nums.length; subsetsHelp(nums, 0, n); return res; } public void subsetsHelp(int[] nums, int startIndex, int n) { //终止条件:如果起始位置等于nums的大小,说明找到了一组 if(path.size() >= n){//终止条件可不加 也可以为 if (startIndex >= nums.length) return; } for(int i = startIndex;i < n;i++){ path.add(nums[i]); res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); subsetsHelp(nums, i + 1, n); path.removeLast(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
4. 子集II(去重)
题目描述
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中可能包含重复元素,请你返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。返回的解集中,子集可以按 任意顺序 排列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,2] 输出:[[],[1],[1,2],[1,2,2],[2],[2,2]]- 1
- 2
代码
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) { //空集是所有集合的子集 res.add(new ArrayList(0)); //1. 排序 Arrays.sort(nums); int n = nums.length; subsetsWithDupHelp(nums, 0, n); return res; } public void subsetsWithDupHelp(int[] nums, int startIndex, int n) { //终止条件:如果起始位置等于nums的大小,说明找到了一组 if(path.size() >= n){//终止条件可不加 也可以为 if (startIndex >= nums.length) return; } for(int i = startIndex;i < n;i++){ //2. 去除重复元素 if ( i > startIndex && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] ) { continue; } path.add(nums[i]); res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); subsetsWithDupHelp(nums, i + 1, n); path.removeLast(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
4. 全排列
1. 全排列
题目描述
给定一个不含重复数字的数组
nums,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]- 1
- 2
代码
class Solution { //结果集 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); //路径 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); //定义访问数组,记录该元素是否被访问 boolean[] visit; public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { int n = nums.length; visit = new boolean[n]; permuteHelp(nums, n); return res; } public void permuteHelp(int[] nums, int n){ //返回条件:path中收集了n个元素后返回 if(path.size() == n){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ //访问,跳过 if(visit[i]) continue; path.add(nums[i]); visit[i] = true; //回溯 permuteHelp(nums, n); path.removeLast(); visit[i] = false; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
2. 全排列II
题目描述
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列
nums,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2] 输出: [[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
代码
class Solution { //结果集 List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); //路径 LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); //定义访问数组,记录该元素是否被访问 boolean[] visit; public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) { int n = nums.length; visit = new boolean[n]; Arrays.fill(visit, false); Arrays.sort(nums); permuteUniqueHelp(nums, n); return res; } public void permuteUniqueHelp(int[] nums, int n){ //返回条件:path中收集了n个元素后返回 if(path.size() == n){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ // visit[i - 1] == true,说明同⼀树⽀visit[i - 1]使⽤过 // visit[i - 1] == false,说明同⼀树层visit[i - 1]使⽤过 // 如果同⼀树层nums[i - 1]使⽤过则直接跳过 if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && visit[i - 1] == false) { continue; } //如果同⼀树⽀nums[i]没使⽤过开始处理 if (visit[i] == false) { visit[i] = true; path.add(nums[i]); //回溯 permuteUniqueHelp(nums, n); path.removeLast(); visit[i] = false; } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
5. N 皇后问题
题目
按照国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击与之处在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上的棋子。
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将
n个皇后放置在n×n的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。给你一个整数
n,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中
'Q'和'.'分别代表了皇后和空位。示例 1:

输入:n = 4 输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]] 解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。- 1
- 2
- 3
分析

代码
class Solution { //定义返回值 List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) { //回溯棋盘 char[][] chessboard = new char[n][n]; for (char[] c : chessboard) { Arrays.fill(c, '.'); } solveNQueensHelp(n, 0, chessboard); return res; } public void solveNQueensHelp(int n, int row, char[][] chessboard){ //结束条件 if(row == n){ res.add(Array2List(chessboard)); return; } //遍历本层 for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){ if(isValid (row, j, n, chessboard)){ chessboard[row][j] = 'Q'; solveNQueensHelp(n, row + 1, chessboard); chessboard[row][j] = '.'; } } } //将二维数组转化为Listlist = new ArrayList<>() public List Array2List(char[][] chessboard) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (char[] c : chessboard) { list.add(String.copyValueOf(c)); } return list; } //判断棋盘是否符合 public boolean isValid (int row, int col, int n, char[][] chessboard){ // 检查列 for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) { // 相当于剪枝 if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') { return false; } } // 检查45度对角线 for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) { if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') { return false; } } // 检查135度对角线 for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j <= n - 1; i--, j++) { if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') { return false; } } return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
6. 解数独
题目
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
数独的解法需 遵循如下规则:
- 数字
1-9在每一行只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一列只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一个以粗实线分隔的3x3宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
数独部分空格内已填入了数字,空白格用
'.'表示。示例 1:

输入:board = [["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]] 输出:[["5","3","4","6","7","8","9","1","2"],["6","7","2","1","9","5","3","4","8"],["1","9","8","3","4","2","5","6","7"],["8","5","9","7","6","1","4","2","3"],["4","2","6","8","5","3","7","9","1"],["7","1","3","9","2","4","8","5","6"],["9","6","1","5","3","7","2","8","4"],["2","8","7","4","1","9","6","3","5"],["3","4","5","2","8","6","1","7","9"]] 解释:输入的数独如上图所示,唯一有效的解决方案如下所示:- 1
- 2
- 3
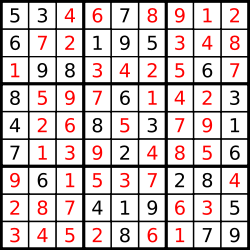
分析

代码
class Solution { public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) { solveSudokuHelper(board); } private boolean solveSudokuHelper(char[][] board){ //「一个for循环遍历棋盘的行,一个for循环遍历棋盘的列, // 一行一列确定下来之后,递归遍历这个位置放9个数字的可能性!」 for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){ // 遍历行 for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++){ // 遍历列 if (board[i][j] != '.'){ // 跳过原始数字 continue; } for (char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++){ // (i, j) 这个位置放k是否合适 if (isValidSudoku(i, j, k, board)){ board[i][j] = k; if (solveSudokuHelper(board)){ // 如果找到合适一组立刻返回 return true; } board[i][j] = '.';//回溯 } } // 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false return false; // 因为如果一行一列确定下来了,这里尝试了9个数都不行,说明这个棋盘找不到解决数独问题的解! // 那么会直接返回, 「这也就是为什么没有终止条件也不会永远填不满棋盘而无限递归下去!」 } } // 遍历完没有返回false,说明找到了合适棋盘位置了 return true; } /** * 判断棋盘是否合法有如下三个维度: * 同行是否重复 * 同列是否重复 * 9宫格里是否重复 */ private boolean isValidSudoku(int row, int col, char val, char[][] board){ // 同行是否重复 for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){ if (board[row][i] == val){ return false; } } // 同列是否重复 for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++){ if (board[j][col] == val){ return false; } } // 9宫格里是否重复 int startRow = (row / 3) * 3; int startCol = (col / 3) * 3; for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3; i++){ for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3; j++){ if (board[i][j] == val){ return false; } } } return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
参考
-
相关阅读:
Hexagon_V65_Programmers_Reference_Manual (51)
365天深度学习训练营-第6周:好莱坞明星识别
读书笔记:从缺陷中学习C++
Streptavidin-Biotin/Biotin-Streptavidin 生物素修饰/标记/偶联链霉亲和素
PHP 变量
深度学习与CV教程(13) | 目标检测 (SSD,YOLO系列)
Python3-提取pdf文件内容的方式,PyPDF2的使用
孩子写作业用台灯好还是不用好?双十一写作业的护眼台灯推荐
shell编程5-函数与正则表达式
Linux引入中saltstack介绍与使用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42130468/article/details/127729086
