-
(十)Mybatis之动态SQL
上一篇:(九)MyBatis查询语句的返回值类型
下一篇:(十一)MyBatis的高级映射及延迟加载环境
数据库:汽车表t_car
引⼊依赖:mysql驱动依赖、mybatis依赖、logback依赖、junit依赖。
引入配置文件:jdbc.properties、mybatis-config.xml、logback.xml
pojo类:Car
SqlSession工具类:SqlSessionUtil
都可以复制之前的动态SQL前言
有些业务的SQL语句也要进行动态拼接
例如批量删除delete from t_car where id in(1,2,3,4,5,6,......这里是动态的,根据用户选择的id,值就不同);- 1
又例如多条件查询
select * from t_car where 条件1 and 条件2 and 条件n.....;- 1
一般在SQL映射文件,我们是把SQL语句写死的,要想完成这些功能业务,就需要学习动态SQL。
if标签
if标签:sql语句是否拼接
- test属性:true,表示拼接,false,表示不拼接
想要动态肯定不能单纯true|false,可以写一个表达式,只要表达式结果为true就拼接,false就不拼接,类似于java当中的if语句- 当参数是单个简单类型参数时
- 当没有使用@Param注解时,可以填写arg0、arg1…或param1、param2…
- 当使用了@Param注解时,可以填写注解的参数名,或param1、param2…
- 当参数是一个pojo类时,就只能填写pojo类的属性名了
- 当参数是单个简单类型参数时
注意:test属性使用表达式时,想要进行’与‘运算,不能使用&&,因为与xml文件冲突了,mybatis提供了一个and代替&&
if标签里面写的是sql语句业务需求:多条件查询。条件可能包括:品牌(brand)、指导价格(guide_price)、汽车类型(car_type)
创建CarMapper接口,添加方法,使用@Param增强可读性public interface CarMapper { /** * 多条件查询,使用if标签 * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiCondition(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
创建CarMapper.xml映射文件进行配置
<select id="selectByMultiCondition" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car where <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> and guide_price > #{guidePrice} </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> and car_type = #{carType} </if> </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
测试程序,假设都不为null
@Test public void testSelectByMultiCondition(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); //假设都不为null List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("奔驰",2.0,"新能源"); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

查询语句正常,能够查询select * from t_car where brand like "%"?"%" and guide_price > ? and car_type = ?- 1
假设都为null
@Test public void testSelectByMultiCondition(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); //假设都不为null //Listcars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("奔驰",2.0,"新能源"); //假设都为空 List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("",null,""); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
出现异常

发现都为null的情况下,查询语句是这样的select * from t_car where- 1
明显是错误的,不应该只有where,怎么解决,都为null的情况下我们需要在让这个语句查询所有,所以要让where后面的条件恒成立
所以映射文件进行如下改动<select id="selectByMultiCondition" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car <!-- 如果下面if标签都不成立,则这个sql语句就变成:select * from t_car where 会出错 所以需要加个 1=1,表示恒成立 --> where 1=1 <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> and guide_price > #{guidePrice} </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> and car_type = #{carType} </if> </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
再次运行测试程序,查询成功

测试部分为null@Test public void testSelectByMultiCondition(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); //假设都不为null //Listcars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("奔驰",2.0,"新能源"); //假设都为空 //Listcars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("",null,""); //假设部分为空 List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiCondition("奔驰",null,"新能源"); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13

发现出异常,sql语句是这样子的select * from t_car where 1=1 brand like "%"?"%" and car_type = ?- 1
在恒成立条件和第一条查询条件之间没有用关键字衔接,需要修改
映射文件修改如下<select id="selectByMultiCondition" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car <!-- 如果下面if标签都不成立,则这个sql语句就变成:select * from t_car where 会出错 所以需要加个 1=1,表示恒成立 --> where 1=1 <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> <!-- 假设这个不为空,则sql语句就会变成select * from t_car where 1=1 brand like "%"#{brand}"%",也会出错 所以需要加个and --> and brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> and guide_price > #{guidePrice} </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> and car_type = #{carType} </if> </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
再次运行,运行成功

where标签
where标签:专门负责动态生成where子句的,让where子句更加动态智能。
作用:- 所有条件都为空时,where标签保证不会生成where子句。
- 自动去除某些条件前面多余的and或or。
注意:如果and或or写在语句后面,where标签不会自动去除
继续使用if标签的业务需求
接口添加方法:/** * 多条件查询,使用where标签 * @param brand * @param guidePrice * @param carType * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiConditionWithWhere(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
映射文件配置
<select id="selectByMultiConditionWithWhere" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car <where> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> and brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> and guide_price > #{guidePrice} </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> and car_type = #{carType} </if> </where> </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
测试程序
@Test public void testSelectByMultiConditionWithWhere(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); //假设都不为null List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("奔驰",2.0,"新能源"); //假设都为空 //Listcars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("",null,""); //假设部分为空 //Listcars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("",2.0,""); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
测试都不为null

发现查询语句,自动去除了第一个条件语句前面的andselect * from t_car WHERE brand like "%"?"%" and guide_price > ? and car_type = ?- 1
测试都为null
发现查询语句不会生成where关键字

测试部分为null
自动去除and

trim标签
trim标签:动态添加/删除语句,可以解决where标签不能去除后缀的问题
- prefix:在trim标签中的语句前添加内容(加前缀)
- suffix:在trim标签中的语句后添加内容(加后缀)
- prefixOverrides:前缀覆盖掉(去掉前缀)
- suffixOverrides:后缀覆盖掉(去掉后缀)
延用if标签业务需求
接口添加方法:/** * 多条件查询,使用trim标签 * @param brand * @param guidePrice * @param carType * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiConditionWithTrim(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
映射文件配置,这次使用后缀形式:
<select id="selectByMultiConditionWithTrim" resultType="Car"> select * from t_car <!--and|or :表示and或者or都去除--> <trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and|or"> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" and </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> guide_price > #{guidePrice} and </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> car_type = #{carType} </if> </trim> </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
测试程序
@Test public void testSelectByMultiConditionWithTrim(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); //假设都不为null List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithTrim("奔驰",2.0,"新能源"); //假设都为空 //Listcars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithTrim("",null,""); //假设部分为空 //Listcars = mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithTrim("",2.0,""); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
测试都不为null
自动添加where

测试都为null
不会生成where关键字
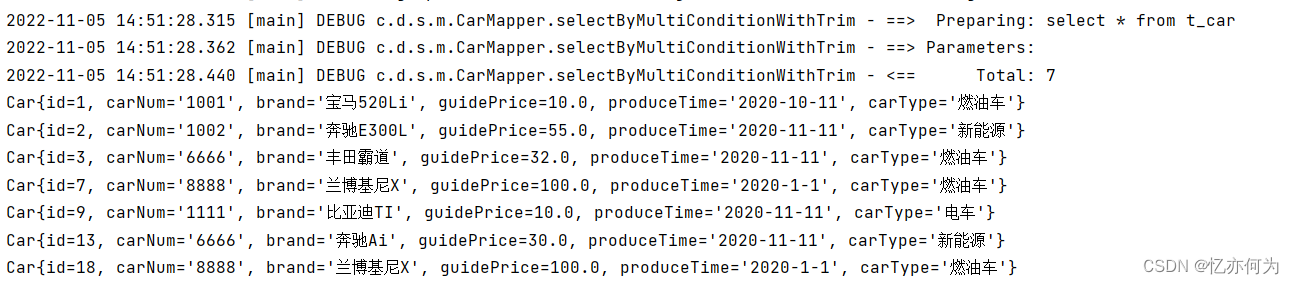
测试部分为null
去除后缀and

set标签
主要使用在update语句当中,用来生成set关键字,同时去掉最后多余的“,”
比如我们只更新提交的不为空的字段,如果提交的数据是空或者"",那么这个字段我们将不更新。
正常的sql语句是这样子的update t_car set car_num = #{carNum}, brand = #{brand}, guide_price = #{guidePrice}, produce_time = #{produceTime}, car_type = #{carType} where id = #{id}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
不够灵活,提交的数据如果为null,也会更新到数据库里面,我们不希望这样,所以要使用set标签进行动态更新
两种进行对比
接口中添加方法:/** * 通过id更新 * @param car * @return */ int updateById(Car car); /** * 通过id更新,使用set标签 * @param car * @return */ int updateBySet(Car car);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
映射文件配置:
<!--没有使用set标签--> <update id="updateById"> update t_car set car_num = #{carNum}, brand = #{brand}, guide_price = #{guidePrice}, produce_time = #{produceTime}, car_type = #{carType} where id = #{id} </update> <!--使用set标签--> <update id="updateBySet"> update t_car <set> <if test="carNum != null and carNum != ''">car_num = #{carNum},</if> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''">brand = #{brand},</if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''">guide_price = #{guidePrice},</if> <if test="produceTime != null and produceTime != ''">produce_time = #{produceTime},</if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''">car_type = #{carType}</if> </set> where id = #{id} </update>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
测试程序
@Test public void testUpdateById(){ //没有使用set标签 SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); int i = mapper.updateById(new Car(7L,null,null,null,null,"燃油车")); session.commit(); System.out.println(i); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); } @Test public void testupdateBySet(){ //使用set标签 SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); int i = mapper.updateBySet(new Car(7L,"2222",null,null,null,"新能源")); session.commit(); System.out.println(i); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
运行前数据

运行没有set标签的测试程序


运行有set标签的测试程序


9其他字段都变成null了,而7只变了编号和汽车类型,没有set的标签,发现运行是把null都赋值上去,而有set标签,发现把null值过滤掉了
choose when otherwise 组合标签
这三个标签是在⼀起使用的:
<choose> <when></when> <when></when> <when></when> <otherwise></otherwise> </choose>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
等同于java当中的if…else if…else
if(){ }else if(){ }else if(){ }else if(){ }else{ }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
只有⼀个分⽀会被选择!!!!
业务需求:先根据品牌查询,如果没有提供品牌,再根据指导价格查询,如果没有提供指导价格,就根据类型查询。
接口添加方法
List<Car> selectByChoose(@Param("brand") String brand,@Param("guidePrice")Double guidePrice,@Param("carType")String carType);- 1
映射文件配置
<select id="selectByChoose" resultType="car"> select * from t_car <where> <choose> <when test="brand != null and brand != ''"> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </when> <when test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> guide_price > #{guidePrice} </when> <otherwise> car_type = #{carType} </otherwise> </choose> </where> </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
测试程序
@Test public void testSelectByChoose(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); //假设都不为null List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose("奔驰",2.0,"新能源"); //假设都为空 //Listcars = mapper.selectByChoose("",null,""); //假设部分为空 //Listcars = mapper.selectByChoose("兰博基尼",2.0,""); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
测试都不为null效果
发现只传一个值,说明只走第一条

测试都为null
发现走最后一个条件,也就是java里面的else

测试部分为null
发现只走第一个条件,第二个条件不走

foreach标签
foreach标签循环数组或集合,动态⽣成sql
-
collection属性:必须,指定数组或集合
-
item属性:代表数组或集合中的元素,相当于迭代属性
-
separator属性:分隔符
-
open属性:foreach标签中所有内容的以什么开始
-
close属性:foreach标签中所有内容的以什么结束
如果参数是数组的话,底层会弄一个map集合 如果没有使用@Param注解,则map存储方式是: map.put("array",数组); map.put("arg0",数组); 如果使用@Param注解,则map存储方式是: map.put("注解名",数组); map.put("param1",数组);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
批量删除,使用in关键字
业务需求:批量删除,使用in关键字
接口添加方法:/** * 批量删除,使用in关键字,使用foreach标签 * @return */ int deleteByIds(@Param("ids")Long[] ids);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
映射文件配置:
<delete id="deleteByIds"> delete from t_car where id in <foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")"> #{id} </foreach> </delete>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
测试程序:
@Test public void testDeleteByIds(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); int i = mapper.deleteByIds(new Long[]{9L,13L,18L}); System.out.println(i); session.commit(); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
测试前数据

运行后数据

批量删除,使用or关键字
业务需求:批量删除,使用or关键字
接口添加方法:/** * 批量删除,使用or关键字,使用foreach标签 * @param ids * @return */ int deleteByIds2(@Param("ids")Long[] ids);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
映射文件配置:
<delete id="deleteByIds2"> delete from t_car where <foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="or"> id = #{id} </foreach> </delete>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
@Test public void testDeleteByIds2(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); int i = mapper.deleteByIds2(new Long[]{2L,3L,7L}); System.out.println(i); session.commit(); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
测试前数据

运行后数据

批量插入
业务需求:批量新增数据
接口添加方法:/** * 批量插入,使用foreach标签 * @param cars * @return */ int insertBatch(@Param("cars") List<Car> cars);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
映射文件配置:
<insert id="insertBatch"> insert into t_car values <foreach collection="cars" item="car" separator=","> (null ,#{car.carNum},#{car.brand},#{car.guidePrice},#{car.produceTime},#{car.carType}) </foreach> </insert>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
测试程序:
@Test public void testInsertBatch(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Car> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Car(null,"111","帕萨特1",10.0,"2020-11-11","燃油车")); list.add(new Car(null,"222","帕萨特2",20.0,"2020-11-11","燃油车")); list.add(new Car(null,"333","帕萨特3",30.0,"2020-11-11","燃油车")); int i = mapper.insertBatch(list); System.out.println(i); session.commit(); SqlSessionUtil.close(session); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
运行后:

sql标签与include标签
sql标签⽤来声明sql片段,id属性:sql标签的唯一标识
include标签⽤来将声明的sql片段包含到某个sql语句当中,refid属性:写sql标签的id
作用:代码复用。易维护。业务需求:有两个查询语句,根据id查询和根据car_num查询,又不想让用户看到id字段和car_num字段
接口添加方法:
List<Car> selectById(Long id); List<Car> selectBycarNum(String carNum);- 1
- 2
映射文件配置:
<sql id="carsql"> brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type </sql> <select id="selectById" resultType="car"> select <include refid="carsql" /> from t_car where id = #{id} </select> <select id="selectBycarNum" resultType="car"> select <include refid="carsql" /> from t_car where car_num = #{carNum} </select>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
测试程序
@Test public void testSelectBy(){ SqlSession session = SqlSessionUtil.getSession(); CarMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CarMapper.class); List<Car> cars = mapper.selectById(26L); cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); List<Car> cars1 = mapper.selectBycarNum("1001"); cars1.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

-
相关阅读:
Unity3D URP 仿蜘蛛侠风格化Bloom&AO
【面试】对CSS预处理器的理解及与原生CSS的区别
[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM建筑材料采购管理系统(程序+LW)
基于JSP的民宿酒店预约管理系统【数据库设计、源码、开题报告】
k8s运维面试
[github配置] 远程访问仓库以及问题解决
基于SSM+小程序民宿短租管理系统(民宿1)
运维的进阶:用它解决90%以上问题
Linux中in、ls、tree、clear的用法
100天精通Python(基础篇)——第8天:字符串的三种定义
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45832694/article/details/127702750