-
6.树(入门与进阶)
目录
入门
一、二叉树入门
之前我们实现的符号表中,不难看出,符号表的增删查操作,随着元素个数 N 的增多,其耗时也是线性增多的,时 间复杂度都是O(n), 为了提高运算效率,接下来我们学习树这种数据结构。1.1树的基本定义
树是我们计算机中非常重要的一种数据结构,同时使用树这种数据结构,可以描述现实生活中的很多事物,例如家 谱、单位的组织架构、等等。树是由 n ( n>=1 )个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。把它叫做 “ 树 ” 是因为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。 树具有以下特点:1. 每个结点有零个或多个子结点;2. 没有父结点的结点为根结点;3. 每一个非根结点只有一个父结点;4. 每个结点及其后代结点整体上可以看做是一棵树,称为当前结点的父结点的一个子树;
树具有以下特点:1. 每个结点有零个或多个子结点;2. 没有父结点的结点为根结点;3. 每一个非根结点只有一个父结点;4. 每个结点及其后代结点整体上可以看做是一棵树,称为当前结点的父结点的一个子树;1.2 树的相关术语
结点的度:一个结点含有的子树的个数称为该结点的度;叶结点:度为 0 的结点称为叶结点,也可以叫做终端结点分支结点:度不为 0 的结点称为分支结点,也可以叫做非终端结点结点的层次:从根结点开始,根结点的层次为 1 ,根的直接后继层次为 2 ,以此类推结点的层序编号:将树中的结点,按照从上层到下层,同层从左到右的次序排成一个线性序列,把他们编成连续的自然数。树的度:树中所有结点的度的最大值树的高度 ( 深度 ) :树中结点的最大层次森林:m ( m>=0 )个互不相交的树的集合,将一颗非空树的根结点删去,树就变成一个森林;给森林增加一个统一的根结点,森林就变成一棵树 孩子结点:一个结点的直接后继结点称为该结点的孩子结点双亲结点 ( 父结点 ) :一个结点的直接前驱称为该结点的双亲结点兄弟结点:同一双亲结点的孩子结点间互称兄弟结点
孩子结点:一个结点的直接后继结点称为该结点的孩子结点双亲结点 ( 父结点 ) :一个结点的直接前驱称为该结点的双亲结点兄弟结点:同一双亲结点的孩子结点间互称兄弟结点1.3 二叉树的基本定义
二叉树就是度不超过 2 的树 ( 每个结点最多有两个子结点 ) 满二叉树:一个二叉树,如果每一个层的结点树都达到最大值,则这个二叉树就是满二叉树。
满二叉树:一个二叉树,如果每一个层的结点树都达到最大值,则这个二叉树就是满二叉树。 完全二叉树:叶节点只能出现在最下层和次下层,并且最下面一层的结点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置的二叉树
完全二叉树:叶节点只能出现在最下层和次下层,并且最下面一层的结点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置的二叉树
1.4 二叉查找树的创建
1.4.1二叉树的结点类
根据对图的观察,我们发现二叉树其实就是由一个一个的结点及其之间的关系组成的,按照面向对象的思想,我们设计一个结点类来描述结点这个事物。结点类 API 设计:
代码实现:
- private class Node<Key,Value>{
- //存储键
- public Key key;
- //存储值
- private Value value;
- //记录左子结点
- public Node left;
- //记录右子结点
- public Node right;
- public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right) {
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.left = left;
- this.right = right;
- }
- }
1.4.2 二叉查找树API设计

1.4.3 二叉查找树实现
插入方法 put 实现思想:1. 如果当前树中没有任何一个结点,则直接把新结点当做根结点使用2. 如果当前树不为空,则从根结点开始:2.1 如果新结点的 key 小于当前结点的 key ,则继续找当前结点的左子结点;2.2如果新结点的key 大于当前结点的 key ,则继续找当前结点的右子结点;2.3 如果新结点的 key 等于当前结点的 key ,则树中已经存在这样的结点,替换该结点的 value 值即可。
查询方法get实现思想:
从根节点开始:1. 如果要查询的 key 小于当前结点的 key ,则继续找当前结点的左子结点;2.如果要查询的key 大于当前结点的 key ,则继续找当前结点的右子结点;3.如果要查询的key 等于当前结点的 key ,则树中返回当前结点的 value 。删除方法 delete 实现思想:1. 找到被删除结点;2.找到被删除结点右子树中的最小结点minNode3.删除右子树中的最小结点4. 让被删除结点的左子树称为最小结点 minNode 的左子树,让被删除结点的右子树称为最小结点 minNode 的右子 树5. 让被删除结点的父节点指向最小结点 minNode

 代码:
代码: - //二叉树代码
- public class BinaryTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
- //记录根结点
- private Node root;
- //记录树中元素的个数
- private int N;
- //获取树中元素的个数
- public int size() {
- return N;
- }
- //向树中添加元素key-value
- public void put(Key key, Value value) {
- root = put(root, key, value);
- }
- //向指定的树x中添加key-value,并返回添加元素后新的树
- private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value) {
- if (x == null) {
- //个数+1
- N++;
- return new Node(key, value, null, null);
- }
- int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
- if (cmp > 0) {
- //新结点的key大于当前结点的key,继续找当前结点的右子结点
- x.right = put(x.right, key, value);
- } else if (cmp < 0) {
- //新结点的key小于当前结点的key,继续找当前结点的左子结点
- x.left = put(x.left, key, value);
- } else {
- //新结点的key等于当前结点的key,把当前结点的value进行替换
- x.value = value;
- }
- return x;
- }
- //查询树中指定key对应的value
- public Value get(Key key) {
- return get(root, key);
- }
- //从指定的树x中,查找key对应的值
- public Value get(Node x, Key key) {
- if (x == null) {
- return null;
- }
- int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
- if (cmp > 0) {
- //如果要查询的key大于当前结点的key,则继续找当前结点的右子结点;
- return get(x.right, key);
- } else if (cmp < 0) {
- //如果要查询的key小于当前结点的key,则继续找当前结点的左子结点;
- return get(x.left, key);
- } else {
- //如果要查询的key等于当前结点的key,则树中返回当前结点的value。
- return x.value;
- }
- }
- //删除树中key对应的value
- public void delete(Key key) {
- root = delete(root, key);
- }
- //删除指定树x中的key对应的value,并返回删除后的新树
- public Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
- if (x == null) {
- return null;
- }
- int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
- if (cmp > 0) {
- //新结点的key大于当前结点的key,继续找当前结点的右子结点
- x.right = delete(x.right, key);
- } else if (cmp < 0) {
- //新结点的key小于当前结点的key,继续找当前结点的左子结点
- x.left = delete(x.left, key);
- } else {
- //新结点的key等于当前结点的key,当前x就是要删除的结点
- //1.如果当前结点的右子树不存在,则直接返回当前结点的左子结点
- if (x.right == null) {
- return x.left;
- }
- //2.如果当前结点的左子树不存在,则直接返回当前结点的右子结点
- if (x.left == null) {
- return x.right;
- }
- //3.当前结点的左右子树都存在
- //3.1找到右子树中最小的结点
- Node minNode = x.right;
- while (minNode.left != null) {
- minNode = minNode.left;
- }
- //3.2删除右子树中最小的结点
- Node n = x.right;
- while (n.left != null) {
- if (n.left.left == null) {
- n.left = null;
- } else {
- n = n.left;
- }
- }
- //3.3让被删除结点的左子树称为最小结点minNode的左子树,让被删除结点的右子树称为最小结点
- minNode的右子树
- minNode.left = x.left;
- minNode.right = x.right;
- //3.4让被删除结点的父节点指向最小结点minNode
- x = minNode;
- //个数-1
- N--;
- }
- return x;
- }
- private class Node {
- //存储键
- public Key key;
- //存储值
- private Value value;
- //记录左子结点
- public Node left;
- //记录右子结点
- public Node right;
- public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right) {
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.left = left;
- this.right = right;
- }
- }
- }
- //测试代码
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- BinaryTree<Integer, String> bt = new BinaryTree<>();
- bt.put(4, "二哈");
- bt.put(1, "张三");
- bt.put(3, "李四");
- bt.put(5, "王五");
- System.out.println(bt.size());
- bt.put(1,"老三");
- System.out.println(bt.get(1));
- System.out.println(bt.size());
- bt.delete(1);
- System.out.println(bt.size());
- }
- }
1.4.4 二叉查找树其他便捷方法
1.4.4.1 查找二叉树中最小的键
在某些情况下,我们需要查找出树中存储所有元素的键的最小值,比如我们的树中存储的是学生的排名和姓名数据,那么需要查找出排名最低是多少名?这里我们设计如下两个方法来完成:
- //找出整个树中最小的键
- public Key min(){
- return min(root).key;
- }
- //找出指定树x中最小的键所在的结点
- private Node min(Node x){
- if (x.left!=null){
- return min(x.left);
- }else{
- return x;
- }
- }
1.4.4.2 查找二叉树中最大的键
在某些情况下,我们需要查找出树中存储所有元素的键的最大值,比如比如我们的树中存储的是学生的成绩和学生 的姓名,那么需要查找出最高的分数是多少?这里我们同样设计两个方法来完成:public Key max() 找出树中最大的键
public Node max(Node x) 找出指定树x中,最大键所在的结点- //找出整个树中最大的键
- public Key max(){
- return max(root).key;
- }
- //找出指定树x中最大键所在的结点
- public Node max(Node x){
- if (x.right!=null){
- return max(x.right);
- }else{
- return x;
- }
- }
1.5 二叉树的基础遍历
很多情况下,我们可能需要像遍历数组数组一样,遍历树,从而拿出树中存储的每一个元素,由于树状结构和线性 结构不一样,它没有办法从头开始依次向后遍历,所以存在如何遍历,也就是按照什么样的搜索路径 进行遍历的问题。 我们把树简单的画作上图中的样子,由一个根节点、一个左子树、一个右子树组成,那么按照根节点什么时候被访问我们可以把二叉树的遍历分为以下三种方式: 1.前序遍历;先访问根结点,然后再访问左子树,最后访问右子树2. 中序遍历;先访问左子树,中间访问根节点,最后访问右子树3.后序遍历;先访问左子树,再访问右子树,最后访问根节点如果我们分别对下面的树使用三种遍历方式进行遍历,得到的结果如下:
我们把树简单的画作上图中的样子,由一个根节点、一个左子树、一个右子树组成,那么按照根节点什么时候被访问我们可以把二叉树的遍历分为以下三种方式: 1.前序遍历;先访问根结点,然后再访问左子树,最后访问右子树2. 中序遍历;先访问左子树,中间访问根节点,最后访问右子树3.后序遍历;先访问左子树,再访问右子树,最后访问根节点如果我们分别对下面的树使用三种遍历方式进行遍历,得到的结果如下:
1.5.1 前序遍历
我们在 4.4 中创建的树上,添加前序遍历的 API :public QueuepreErgodic() :使用前序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键private void preErgodic(Node x,Queuekeys) :使用前序遍历,把指定树 x 中的所有键放入到 keys 队列中实现过程中,我们通过前序遍历,把 , 把每个结点的键取出,放入到队列中返回即可。实现步骤:1. 把当前结点的 key 放入到队列中 ;2. 找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树3. 找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树代码:- //使用前序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键
- public Queue<Key> preErgodic(){
- Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
- preErgodic(root,keys);
- return keys;
- }
- //使用前序遍历,把指定树x中的所有键放入到keys队列中
- private void preErgodic(Node x,Queue<Key> keys){
- if (x==null){
- return;
- }
- //1.把当前结点的key放入到队列中;
- keys.enqueue(x.key);
- //2.找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树
- if (x.left!=null){
- preErgodic(x.left,keys);
- }
- //3.找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树
- if (x.right!=null){
- preErgodic(x.right,keys);
- }
- }
- //测试代码
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- BinaryTree<String, String> bt = new BinaryTree<>();
- bt.put("E", "5");
- bt.put("B", "2");
- bt.put("G", "7");
- bt.put("A", "1");
- bt.put("D", "4");
- bt.put("F", "6");
- bt.put("H", "8");
- bt.put("C", "3");
- Queue<String> queue = bt.preErgodic();
- for (String key : queue) {
- System.out.println(key+"="+bt.get(key));
- }
- }
- }
1.5.2 中序遍历
我们在 4.4 中创建的树上,添加前序遍历的 API :public QueuemidErgodic() :使用中序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键private void midErgodic(Node x,Queuekeys) :使用中序遍历,把指定树 x 中的所有键放入到 keys 队列中实现步骤:1. 找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树2. 把当前结点的 key 放入到队列中 ;3. 找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树代码- //使用中序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键
- public Queue<Key> midErgodic(){
- Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
- midErgodic(root,keys);
- return keys;
- }
- //使用中序遍历,把指定树x中的所有键放入到keys队列中
- private void midErgodic(Node x,Queue<Key> keys){
- if (x==null){
- return;
- }
- //1.找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树
- if (x.left!=null){
- midErgodic(x.left,keys);
- }
- //2.把当前结点的key放入到队列中;
- keys.enqueue(x.key);
- //3.找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树
- if (x.right!=null){
- midErgodic(x.right,keys);
- }
- }
- //测试代码
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- BinaryTree<String, String> bt = new BinaryTree<>();
- bt.put("E", "5");
- bt.put("B", "2");
- bt.put("G", "7");
- bt.put("A", "1");
- bt.put("D", "4");
- bt.put("F", "6");
- bt.put("H", "8");
- bt.put("C", "3");
- Queue<String> queue = bt.midErgodic();
- for (String key : queue) {
- System.out.println(key+"="+bt.get(key));
- }
- }
- }
1.5.3 后序遍历
我们在4.4中创建的树上,添加前序遍历的API:
public Queue
afterErgodic():使用后序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键 private void afterErgodic(Node x,Queue
keys):使用后序遍历,把指定树 x中的所有键放入到keys队列中实现步骤:
1.找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树
2.找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树
3. 把当前结点的 key 放入到队列中 ;代码:- //使用后序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键
- public Queue<Key> afterErgodic(){
- Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
- afterErgodic(root,keys);
- return keys;
- }
- //使用后序遍历,把指定树x中的所有键放入到keys队列中
- private void afterErgodic(Node x,Queue<Key> keys){
- if (x==null){
- return;
- }
- //1.找到当前结点的左子树,如果不为空,递归遍历左子树
- if (x.left!=null){
- afterErgodic(x.left,keys);
- }
- //2.找到当前结点的右子树,如果不为空,递归遍历右子树
- if (x.right!=null){
- afterErgodic(x.right,keys);
- }
- //3.把当前结点的key放入到队列中;
- keys.enqueue(x.key);
- }
- //测试代码
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- BinaryTree<String, String> bt = new BinaryTree<>();
- bt.put("E", "5");
- bt.put("B", "2");
- bt.put("G", "7");
- bt.put("A", "1");
- bt.put("D", "4");
- bt.put("F", "6");
- bt.put("H", "8");
- bt.put("C", "3");
- Queue<String> queue = bt.afterErgodic();
- for (String key : queue) {
- System.out.println(key+"="+bt.get(key));
- }
- }
- }
1.6 二叉树的层序遍历
所谓的层序遍历,就是从根节点(第一层)开始,依次向下,获取每一层所有结点的值,有二叉树如下: 那么层序遍历的结果是: EBGADFHC我们在 4.4 中创建的树上,添加层序遍历的 API :public Queue
那么层序遍历的结果是: EBGADFHC我们在 4.4 中创建的树上,添加层序遍历的 API :public QueuelayerErgodic() :使用层序遍历,获取整个树中的所有键实现步骤:1. 创建队列,存储每一层的结点;2. 使用循环从队列中弹出一个结点:2.1 获取当前结点的 key ;2.2如果当前结点的左子结点不为空,则把左子结点放入到队列中2.3 如果当前结点的右子结点不为空,则把右子结点放入到队列中 代码:
代码:- //使用层序遍历得到树中所有的键
- public Queue<Key> layerErgodic(){
- Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
- Queue<Node> nodes = new Queue<>();
- nodes.enqueue(root);
- while(!nodes.isEmpty()){
- Node x = nodes.dequeue();
- keys.enqueue(x.key);
- if (x.left!=null){
- nodes.enqueue(x.left);
- }
- if (x.right!=null){
- nodes.enqueue(x.right);
- }
- }
- return keys;
- }
- //测试代码
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- BinaryTree<String, String> bt = new BinaryTree<>();
- bt.put("E", "5");
- bt.put("B", "2");
- bt.put("G", "7");
- bt.put("A", "1");
- bt.put("D", "4");
- bt.put("F", "6");
- bt.put("H", "8");
- bt.put("C", "3");
- Queue<String> queue = bt.layerErgodic();
- for (String key : queue) {
- System.out.println(key+"="+bt.get(key));
- }
- }
- }
1.7 二叉树的最大深度问题
需求:给定一棵树,请计算树的最大深度(树的根节点到最远叶子结点的最长路径上的结点数); 上面这棵树的最大深度为
4
。
实现:我们在 1.4 中创建的树上,添加如下的 API 求最大深度:public int maxDepth() :计算整个树的最大深度private int maxDepth(Node x): 计算指定树 x 的最大深度实现步骤:1. 如果根结点为空,则最大深度为 0 ;2. 计算左子树的最大深度;3. 计算右子树的最大深度;4. 当前树的最大深度 = 左子树的最大深度和右子树的最大深度中的较大者 +1代码:
上面这棵树的最大深度为
4
。
实现:我们在 1.4 中创建的树上,添加如下的 API 求最大深度:public int maxDepth() :计算整个树的最大深度private int maxDepth(Node x): 计算指定树 x 的最大深度实现步骤:1. 如果根结点为空,则最大深度为 0 ;2. 计算左子树的最大深度;3. 计算右子树的最大深度;4. 当前树的最大深度 = 左子树的最大深度和右子树的最大深度中的较大者 +1代码:- //计算整个树的最大深度
- public int maxDepth() {
- return maxDepth(root);
- }
- //计算指定树x的最大深度
- private int maxDepth(Node x) {
- //1.如果根结点为空,则最大深度为0;
- if (x == null) {
- return 0;
- }
- int max = 0;
- int maxL = 0;
- int maxR = 0;
- //2.计算左子树的最大深度;
- if (x.left != null) {
- maxL = maxDepth(x.left);
- }
- //3.计算右子树的最大深度;
- if (x.right != null) {
- maxR = maxDepth(x.right);
- }
- //4.当前树的最大深度=左子树的最大深度和右子树的最大深度中的较大者+1
- max = maxL > maxR ? maxL + 1 : maxR + 1;
- return max;
- }
- //测试代码
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- BinaryTree<String, String> bt = new BinaryTree<>();
- bt.put("E", "5");
- bt.put("B", "2");
- bt.put("G", "7");
- bt.put("A", "1");
- bt.put("D", "4");
- bt.put("F", "6");
- bt.put("H", "8");
- bt.put("C", "3");
- int i = bt.maxDepth();
- System.out.println(i);
- }
- }
1.8 折纸问题
需求:请把一段纸条竖着放在桌子上,然后从纸条的下边向上方对折 1 次,压出折痕后展开。此时 折痕是凹下去的,即折 痕突起的方向指向纸条的背面。如果从纸条的下边向上方连续对折2 次,压出折痕后展开,此时有三条折痕,从上 到下依次是下折痕、下折痕和上折痕。给定一 个输入参数 N ,代表纸条都从下边向上方连续对折 N 次,请从上到下打印所有折痕的方向 例如: N=1 时,打 印: down ; N=2 时,打印: down down up 分析:我们把对折后的纸张翻过来,让粉色朝下,这时把第一次对折产生的折痕看做是根结点,那第二次对折产生的下折 痕就是该结点的左子结点,而第二次对折产生的上折痕就是该结点的右子结点,这样我们就可以使用树型数据结构 来描述对折后产生的折痕。这棵树有这样的特点:1. 根结点为下折痕;2. 每一个结点的左子结点为下折痕;3. 每一个结点的右子结点为上折痕;
分析:我们把对折后的纸张翻过来,让粉色朝下,这时把第一次对折产生的折痕看做是根结点,那第二次对折产生的下折 痕就是该结点的左子结点,而第二次对折产生的上折痕就是该结点的右子结点,这样我们就可以使用树型数据结构 来描述对折后产生的折痕。这棵树有这样的特点:1. 根结点为下折痕;2. 每一个结点的左子结点为下折痕;3. 每一个结点的右子结点为上折痕; 实现步骤:1. 定义结点类2. 构建深度为 N 的折痕树;3. 使用中序遍历,打印出树中所有结点的内容;构建深度为 N 的折痕树:1. 第一次对折,只有一条折痕,创建根结点;2. 如果不是第一次对折,则使用队列保存根结点;3. 循环遍历队列:3.1从队列中拿出一个结点;3.2如果这个结点的左子结点不为空,则把这个左子结点添加到队列中;3.3如果这个结点的右子结点不为空,则把这个右子结点添加到队列中;3.4 判断当前结点的左子结点和右子结点都不为空,如果是,则需要为当前结点创建一个值为 down 的左子结点,一 个值为up 的右子结点。代码:
实现步骤:1. 定义结点类2. 构建深度为 N 的折痕树;3. 使用中序遍历,打印出树中所有结点的内容;构建深度为 N 的折痕树:1. 第一次对折,只有一条折痕,创建根结点;2. 如果不是第一次对折,则使用队列保存根结点;3. 循环遍历队列:3.1从队列中拿出一个结点;3.2如果这个结点的左子结点不为空,则把这个左子结点添加到队列中;3.3如果这个结点的右子结点不为空,则把这个右子结点添加到队列中;3.4 判断当前结点的左子结点和右子结点都不为空,如果是,则需要为当前结点创建一个值为 down 的左子结点,一 个值为up 的右子结点。代码:- public class PaperFolding {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //构建折痕树
- Node tree = createTree(3);
- //遍历折痕树,并打印
- printTree(tree);
- }
- //3.使用中序遍历,打印出树中所有结点的内容;
- private static void printTree(Node tree) {
- if (tree==null){
- return;
- }
- printTree(tree.left);
- System.out.print(tree.item+",");
- printTree(tree.right);
- }
- //2.构建深度为N的折痕树;
- private static Node createTree(int N) {
- Node root = null;
- for (int i = 0; i <N ; i++) {
- if (i==0){
- //1.第一次对折,只有一条折痕,创建根结点;
- root = new Node("down",null,null);
- }else{
- //2.如果不是第一次对折,则使用队列保存根结点;
- Queue<Node> queue = new Queue<>();
- queue.enqueue(root);
- //3.循环遍历队列:
- while(!queue.isEmpty()){
- //3.1从队列中拿出一个结点;
- Node tmp = queue.dequeue();
- //3.2如果这个结点的左子结点不为空,则把这个左子结点添加到队列中;
- if (tmp.left!=null){
- queue.enqueue(tmp.left);
- }
- //3.3如果这个结点的右子结点不为空,则把这个右子结点添加到队列中;
- if (tmp.right!=null){
- queue.enqueue(tmp.right);
- }
- //3.4判断当前结点的左子结点和右子结点都不为空,如果是,则需要为当前结点创建一个
- 值为down的左子结点,一个值为up的右子结点。
- if (tmp.left==null && tmp.right==null){
- tmp.left = new Node("down",null,null);
- tmp.right = new Node("up",null,null);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return root;
- }
- //1.定义结点类
- private static class Node{
- //存储结点元素
- String item;
- //左子结点
- Node left;
- //右子结点
- Node right;
- public Node(String item, Node left, Node right) {
- this.item = item;
- this.left = left;
- this.right = right;
- }
- }
- }
进阶
一、平衡树
之前我们学习过二叉查找树,发现它的查询效率比单纯的链表和数组的查询效率要高很多,大部分情况下,确实是 这样的,但不幸的是,在最坏情况下,二叉查找树的性能还是很糟糕。例如我们依次往二叉查找树中插入 9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1 这 9 个数据,那么最终构造出来的树是长得下面这个样子:
我们会发现,如果我们要查找1这个元素,查找的效率依旧会很低。效率低的原因在于这个树并不平衡,全部是向左边分支,如果我们有一种方法,能够不受插入数据的影响,让生成的树都像完全二叉树那样那么即使在最坏情况下查找的效率依旧会很好。
1.1 2-3查找树
为了保证查找树的平衡性,我们需要一些灵活性,因此在这里我们允许树中的一个结点保存多个键。确切的说,我们将一棵标准的二叉查找树中的结点称为 2- 结点 ( 含有一个键和两条链 ) ,而现在我们引入 3- 结点,它含有两个键和三条链。 2- 结点和 3- 结点中的每条链都对应着其中保存的键所分割产生的一个区间。1.1.1 2-3查找树的定义
一棵2-3查找树要么为空,要么满足满足下面两个要求:
2-结点:
含有一个键 ( 及其对应的值 ) 和两条链,左链接指向 2-3 树中的键都小于该结点,右链接指向的 2-3 树中的键都大于该结点。3-结点:
含有两个键 ( 及其对应的值 ) 和三条链,左链接指向的 2-3 树中的键都小于该结点,中链接指向的 2-3 树中的键都 位于该结点的两个键之间,右链接指向的2-3 树中的键都大于该结点。
1.1.2 查找
将二叉查找树的查找算法一般化我们就能够直接得到 2-3 树的查找算法。要判断一个键是否在树中,我们先将它和 根结点中的键比较。如果它和其中任意一个相等,查找命中;否则我们就根据比较的结果找到指向相应区间的连 接,并在其指向的子树中递归地继续查找。如果这个是空链接,查找未命中。 1.1.3 插入
1.1.3 插入 1.1.3.1 向2-结点中插入新键
往 2-3 树中插入元素和往二叉查找树中插入元素一样,首先要进行查找,然后将节点挂到未找到的节点上。 2-3 树之所以能够保证在最差的情况下的效率的原因在于其插入之后仍然能够保持平衡状态。如果查找后未找到的节点是一个 2- 结点,那么很容易,我们只需要将新的元素放到这个 2- 结点里面使其变成一个 3- 结点即可。但是如果查找的节点结束于一个 3- 结点,那么可能有点麻烦。
1.1.3.2 向一棵只含有一个3-结点的树中插入新键
假设 2-3 树只包含一个 3- 结点,这个结点有两个键,没有空间来插入第三个键了,最自然的方式是我们假设这个结点能存放三个元素,暂时使其变成一个 4- 结点,同时他包含四条链接。然后,我们将这个 4- 结点的中间元素提升,左边的键作为其左子结点,右边的键作为其右子结点。插入完成,变为平衡 2-3 查找树,树的高度从 0 变为 1 。
1.1.3.3 向一个父结点为2-结点的3-结点中插入新键
和上面的情况一样一样,我们也可以将新的元素插入到 3- 结点中,使其成为一个临时的 4- 结点,然后,将该结点中 的中间元素提升到父结点即2- 结点中,使其父结点成为一个 3- 结点,然后将左右结点分别挂在这个 3- 结点的恰当位置。
1.3.1.4 向一个父结点为3-结点的3-结点中插入新键
当我们插入的结点是3-结点的时候,我们将该结点拆分,中间元素提升至父结点,但是此时父结点是一个3-结点, 插入之后,父结点变成了4-结点,然后继续将中间元素提升至其父结点,直至遇到一个父结点是2-结点,然后将其 变为3-结点,不需要继续进行拆分。

1.3.1.5 分解根结点
当插入结点到根结点的路径上全部是 3- 结点的时候,最终我们的根结点会编程一个临时的 4- 结点,此时,就需要将 根结点拆分为两个2- 结点,树的高度加 1 。
1.3.4 2-3树的性质
通过对 2-3 树插入操作的分析,我们发现在插入的时候, 2-3 树需要做一些局部的变换来保持 2-3 树的平衡。一棵完全平衡的 2-3 树具有以下性质:1. 任意空链接到根结点的路径长度都是相等的。2. 4- 结点变换为 3- 结点时,树的高度不会发生变化,只有当根结点是临时的 4- 结点,分解根结点时,树高 +1 。3. 2-3 树与普通二叉查找树最大的区别在于,普通的二叉查找树是自顶向下生长,而 2-3 树是自底向上生长。1.3.5 2-3树的实现
直接实现 2-3 树比较复杂,因为:需要处理不同的结点类型,非常繁琐;需要多次比较操作来将结点下移;需要上移来拆分 4- 结点;拆分 4- 结点的情况有很多种;2-3 查找树实现起来比较复杂,在某些情况插入后的平衡操作可能会使得效率降低。但是 2-3 查找树作为一种比较重要的概念和思路对于我们后面要讲到的红黑树、 B 树和 B+ 树非常重要。1.2 红黑树
我们前面介绍了 2-3 树,可以看到 2-3 树能保证在插入元素之后,树依然保持平衡状态,它的最坏情况下所有子结点都是 2- 结点,树的高度为 lgN, 相比于我们普通的二叉查找树,最坏情况下树的高度为 N ,确实保证了最坏情况下的时间复杂度,但是 2-3 树实现起来过于复杂,所以我们介绍一种 2-3 树思想的简单实现:红黑树。红黑树主要是对 2-3 树进行编码,红黑树背后的基本思想是用标准的二叉查找树 ( 完全由 2- 结点构成 ) 和一些额外的信息 ( 替换 3- 结点 ) 来表示 2-3 树。我们将树中的链接分为两种类型:红链接: 将两个 2- 结点连接起来构成一个 3- 结点; 黑链接: 则是 2-3 树中的普通链接。确切的说,我们将 3- 结点表示为由由一条 左斜 的红色链接 ( 两个 2- 结点其中之一是另一个的左子结点 ) 相连的两个 2- 结点。这种表示法的一个优点是,我们无需修改就可以直接使用标准的二叉查找树的get 方法。
1.2.1 红黑树的定义
红黑树是含有红黑链接并满足下列条件的二叉查找树:1. 红链接均为左链接;2. 没有任何一个结点同时和两条红链接相连;3. 该树是完美黑色平衡的,即任意空链接到根结点的路径上的黑链接数量相同;下面是红黑树与 2-3 树的对应关系:
1.2.2 红黑树结点API
因为每个结点都只会有一条指向自己的链接(从它的父结点指向它),我们可以在之前的 Node 结点中添加一个布 尔类型的变量color 来表示链接的颜色。如果指向它的链接是红色的,那么该变量的值为 true ,如果链接是黑色 的,那么该变量的值为false 。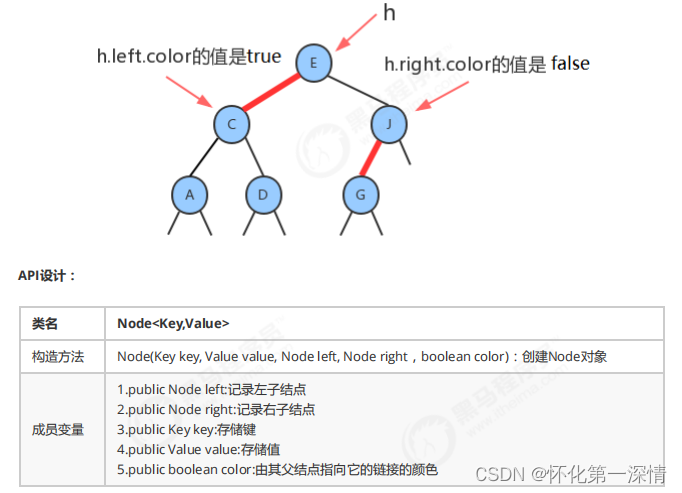
代码:
- private class Node<Key,Value>{
- //存储键
- public Key key;
- //存储值
- private Value value;
- //记录左子结点
- public Node left;
- //记录右子结点
- public Node right;
- //由其父结点指向它的链接的颜色
- public boolean color;
- public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left,Node right,boolean color) {
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.left = left;
- this.right = right;
- this.color = color;
- }
- }
1.2.3 平衡化
在对红黑树进行一些增删改查的操作后,很有可能会出现红色的右链接或者两条连续红色的链接,而这些都不满足红黑树的定义,所以我们需要对这些情况通过旋转进行修复,让红黑树保持平衡。1.2.3.1 左旋当某个结点的左子结点为黑色,右子结点为红色,此时需要左旋。前提: 当前结点为 h ,它的右子结点为 x ;左旋过程:1. 让 x 的左子结点变为 h 的右子结点: h.right=x.left;2. 让 h 成为 x 的左子结点: x.left=h;3. 让 h 的 color 属性变为 x 的 color 属性值: x.color=h.color;4. 让 h 的 color 属性变为 RED : h.color=true;
1.2.3.2 右旋
当某个结点的左子结点是红色,且左子结点的左子结点也是红色,需要右旋
前提: 当前结点为 h ,它的左子结点为 x ;右旋过程:1. 让 x 的右子结点成为 h 的左子结点: h.left = x.right;2. 让 h 成为 x 的右子结点: x.right=h;3. 让 x 的 color 变为 h 的 color 属性值: x.color = h.color;4. 让h 的 color 为 RED ;
1.2.4 向单个2-结点中插入新键
一棵只含有一个键的红黑树只含有一个 2- 结点。插入另一个键后,我们马上就需要将他们旋转。- 如果新键小于当前结点的键,我们只需要新增一个红色结点即可,新的红黑树和单个3-结点完全等价。

- 如果新键大于当前结点的键,那么新增的红色结点将会产生一条红色的右链接,此时我们需要通过左旋,把 红色右链接变成左链接,插入操作才算完成。形成的新的红黑树依然和3-结点等价,其中含有两个键,一条红色链接。

1.2.5 向底部的2-结点插入新键
用和二叉查找树相同的方式向一棵红黑树中插入一个新键,会在树的底部新增一个结点(可以保证有序性),唯一 区别的地方是我们会用红链接将新结点和它的父结点相连。如果它的父结点是一个2- 结点,那么刚才讨论的两种方式仍然适用。
1.2.6 颜色反转
当一个结点的左子结点和右子结点的 color 都为 RED 时,也就是出现了临时的 4- 结点,此时只需要把左子结点和右子 结点的颜色变为BLACK ,同时让当前结点的颜色变为 RED 即可。
1.2.7 向一棵双键树(即一个3-结点)中插入新键
这种情况有可以分为三种子情况:1. 新键大于原树中的两个键


1.2.8 根结点的颜色总是黑色
1.2.9 向树底部的3-结点插入新键
假设在树的底部的一个 3- 结点下加入一个新的结点。前面我们所讲的 3 种情况都会出现。指向新结点的链接可能是 3-结点的右链接(此时我们只需要转换颜色即可),或是左链接 ( 此时我们需要进行右旋转然后再转换 ) ,或是中链 接( 此时需要先左旋转然后再右旋转,最后转换颜色 ) 。颜色转换会使中间结点的颜色变红,相当于将它送入了父结 点。这意味着父结点中继续插入一个新键,我们只需要使用相同的方法解决即可,直到遇到一个2- 结点或者根结点 为止。

1.2.10 红黑树的API设计

1.2.11 红黑树的实现
- //红黑树代码
- public class RedBlackTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
- //根节点
- private Node root;
- //记录树中元素的个数
- private int N;
- //红色链接
- private static final boolean RED = true;
- //黑色链接
- private static final boolean BLACK = false;
- /**
- * 判断当前节点的父指向链接是否为红色
- *
- * @param x
- * @return
- */
- private boolean isRed(Node x) {
- //空结点默认是黑色链接
- if (x == null) {
- return false;
- }
- //非空结点需要判断结点color属性的值
- return x.color == RED;
- }
- /**
- * 左旋转
- *
- * @param h
- * @return
- */
- private Node rotateLeft(Node h) {
- //找出当前结点h的右子结点
- Node hRight = h.right;
- //找出右子结点的左子结点
- Node lhRight = hRight.left;
- //让当前结点h的右子结点的左子结点成为当前结点的右子结点
- h.right = lhRight;
- //让当前结点h称为右子结点的左子结点
- hRight.left = h;
- //让当前结点h的color编程右子结点的color
- hRight.color = h.color;
- //让当前结点h的color变为RED
- h.color = RED;
- //返回当前结点的右子结点
- return hRight;
- }
- /**
- * 右旋
- *
- * @param h
- * @return
- */
- private Node rotateRight(Node h) {
- //找出当前结点h的左子结点
- Node hLeft = h.left;
- //找出当前结点h的左子结点的右子结点
- Node rHleft = hLeft.right;
- //让当前结点h的左子结点的右子结点称为当前结点的左子结点
- h.left = rHleft;
- //让当前结点称为左子结点的右子结点
- hLeft.right = h;
- //让当前结点h的color值称为左子结点的color值
- hLeft.color = h.color;
- //让当前结点h的color变为RED
- h.color = RED;
- //返回当前结点的左子结点
- return hLeft;
- }
- /**
- * 颜色反转,相当于完成拆分4-节点
- *
- * @param h
- */
- private void flipColors(Node h) {
- //当前结点的color属性值变为RED;
- h.color = RED;
- //当前结点的左右子结点的color属性值都变为黑色
- h.left.color = BLACK;
- h.right.color = BLACK;
- }
- /**
- * 在整个树上完成插入操作
- *
- * @param key
- * @param val
- */
- public void put(Key key, Value val) {
- //在root整个树上插入key-val
- root = put(root, key, val);
- //让根结点的颜色变为BLACK
- root.color = BLACK;
- }
- /**
- * 在指定树中,完成插入操作,并返回添加元素后新的树
- *
- * @param h
- * @param key
- * @param val
- */
- private Node put(Node h, Key key, Value val) {
- if (h == null) {
- //标准的插入操作,和父结点用红链接相连
- N++;
- return new Node(key, val, null, null, RED);
- }
- //比较要插入的键和当前结点的键
- int cmp = key.compareTo(h.key);
- if (cmp < 0) {
- //继续寻找左子树插入
- h.left = put(h.left, key, val);
- } else if (cmp > 0) {
- //继续寻找右子树插入
- h.right = put(h.right, key, val);
- } else {
- //已经有相同的结点存在,修改节点的值;
- h.value = val;
- }
- //如果当前结点的右链接是红色,左链接是黑色,需要左旋
- if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) {
- h=rotateLeft(h);
- }
- //如果当前结点的左子结点和左子结点的左子结点都是红色链接,则需要右旋
- if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) {
- h=rotateRight(h);
- }
- //如果当前结点的左链接和右链接都是红色,需要颜色变换
- if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) {
- flipColors(h);
- }
- //返回当前结点
- return h;
- }
- //根据key,从树中找出对应的值
- public Value get(Key key) {
- return get(root, key);
- }
- //从指定的树x中,查找key对应的值
- public Value get(Node x, Key key) {
- //如果当前结点为空,则没有找到,返回null
- if (x == null) {
- return null;
- }
- //比较当前结点的键和key
- int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
- if (cmp < 0) {
- //如果要查询的key小于当前结点的key,则继续找当前结点的左子结点;
- return get(x.left, key);
- } else if (cmp > 0) {
- //如果要查询的key大于当前结点的key,则继续找当前结点的右子结点;
- return get(x.right, key);
- } else {
- //如果要查询的key等于当前结点的key,则树中返回当前结点的value。
- return x.value;
- }
- }
- //获取树中元素的个数
- public int size() {
- return N;
- }
- //结点类
- private class Node {
- //存储键
- public Key key;
- //存储值
- private Value value;
- //记录左子结点
- public Node left;
- //记录右子结点
- public Node right;
- //由其父结点指向它的链接的颜色
- public boolean color;
- public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right, boolean color) {
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.left = left;
- this.right = right;
- this.color = color;
- }
- }
- }
- //测试代码
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- RedBlackTree<Integer, String> bt = new RedBlackTree<>();
- bt.put(4, "二哈");
- bt.put(1, "张三");
- bt.put(3, "李四");
- bt.put(5, "王五");
- System.out.println(bt.size());
- bt.put(1,"老三");
- System.out.println(bt.get(1));
- System.out.println(bt.size());
- }
- }
二、B-树
前面我们已经学习了二叉查找树、 2-3 树以及它的实现红黑树。 2-3 树中,一个结点做多能有两个 key ,它的实现红黑树中使用对链接染色的方式去表达这两个 key 。接下来我们学习另外一种树型结构 B 树,这种数据结构中,一个结点允许多于两个 key 的存在。B 树是一种树状数据结构,它能够存储数据、对其进行排序并允许以 O(logn) 的时间复杂度进行查找、顺序读取、插入和删除等操作。1.1 B树的特性
B 树中允许一个结点中包含多个 key ,可以是 3 个、 4 个、 5 个甚至更多,并不确定,需要看具体的实现。现在我们选 择一个参数M ,来构造一个 B 树,我们可以把它称作是 M 阶的 B 树,那么该树会具有如下特点:- 每个结点最多有M-1个key,并且以升序排列;
- 每个结点最多能有M个子结点;
- 根结点至少有两个子结点;
 在实际应用中 B 树的阶数一般都比较大(通常大于 100 ),所以,即使存储大量的数据, B 树的高度仍然比较小,这样在某些应用场景下,就可以体现出它的优势。
在实际应用中 B 树的阶数一般都比较大(通常大于 100 ),所以,即使存储大量的数据, B 树的高度仍然比较小,这样在某些应用场景下,就可以体现出它的优势。2.2 B树存储数据
若参数 M 选择为 5 ,那么每个结点最多包含 4 个键值对,我们以 5 阶 B 树为例,看看 B 树的数据存储。
2.3 B树在磁盘文件中的应用
在我们的程序中,不可避免的需要通过 IO 操作文件,而我们的文件是存储在磁盘上的。计算机操作磁盘上的文件是 通过文件系统进行操作的,在文件系统中就使用到了B 树这种数据结构。2.3.1 磁盘
磁盘能够保存大量的数据,从 GB 一直到 TB 级,但是他的读取速度比较慢,因为涉及到机器操作读取速度为毫秒级。 磁盘由盘片构成 , 每个盘片有两面,又称为盘面 。盘片中央有一个可以旋转的主轴,他使得盘片以固定的旋转速率旋转,通常是5400rpm 或者是 7200rpm, 一个磁盘中包含了多个这样的盘片并封装在一个密封的容器内 。盘片的每个表面是由一组称为磁道同心圆组成的 ,每个磁道被划分为了一组扇区 ,每个扇区包含相等数量的数据位,通常 是512个子节,扇区之间由一些间隙隔开 , 这些间隙中不存储数据 。
磁盘由盘片构成 , 每个盘片有两面,又称为盘面 。盘片中央有一个可以旋转的主轴,他使得盘片以固定的旋转速率旋转,通常是5400rpm 或者是 7200rpm, 一个磁盘中包含了多个这样的盘片并封装在一个密封的容器内 。盘片的每个表面是由一组称为磁道同心圆组成的 ,每个磁道被划分为了一组扇区 ,每个扇区包含相等数量的数据位,通常 是512个子节,扇区之间由一些间隙隔开 , 这些间隙中不存储数据 。2.3.2 磁盘IO
 磁盘用磁头来读写存储在盘片表面的位,而磁头连接到一个移动臂上,移动臂沿着盘片半径前后移动,可以将磁头定位到任何磁道上,这称之为寻道操作。一旦定位到磁道后,盘片转动,磁道上的每个位经过磁头时,读写磁头就 可以感知到该位的值,也可以修改值。对磁盘的访问时间分为 寻道时间, 旋转时间 ,以及 传送时间 。由于存储介质的特性,磁盘本身存取就比主存慢很多,再加上机械运动耗费,因此为了提高效率,要尽量减少磁盘 I/O,减少读写操作。 为了达到这个目的,磁盘往往不是严格按需读取,而是每次都会预读,即使只需要一个字节,磁盘也会从这个位置开始,顺序向后读取一定长度的数据放入内存。这样做的理论依据是计算机科学中著名的局部性原理:当一个数据被用到时,其附近的数据也通常会马上被使用。由于磁盘顺序读取的效率很高(不需要寻道时间,只需很少的旋转时间),因此预读可以提高I/O 效率页是计算机管理存储器的逻辑块,硬件及操作系统往往将主存和磁盘存储区分割为连续的大小相等的块,每个存储 块称为一页(1024 个字节或其整数倍),预读的长度一般为页的整倍数。主存和磁盘以页为单位交换数据。当程序要读取的数据不在主存中时,会触发一个缺页异常,此时系统会向磁盘发出读盘信号,磁盘会找到数据的起始位置并向后连续读取一页或几页载入内存中,然后异常返回,程序继续运行。文件系统的设计者利用了磁盘预读原理,将一个结点的大小设为等于一个页( 1024 个字节或其整数倍),这样每 个结点只需要一次I/O 就可以完全载入。那么 3 层的 B 树可以容纳 1024*1024*1024 差不多 10 亿个数据,如果换成二 叉查找树,则需要30 层!假定操作系统一次读取一个节点,并且根节点保留在内存中,那么 B 树在 10 亿个数据中查 找目标值,只需要小于3 次硬盘读取就可以找到目标值,但红黑树需要小于 30 次,因此 B 树大大提高了 IO 的操作效率。
磁盘用磁头来读写存储在盘片表面的位,而磁头连接到一个移动臂上,移动臂沿着盘片半径前后移动,可以将磁头定位到任何磁道上,这称之为寻道操作。一旦定位到磁道后,盘片转动,磁道上的每个位经过磁头时,读写磁头就 可以感知到该位的值,也可以修改值。对磁盘的访问时间分为 寻道时间, 旋转时间 ,以及 传送时间 。由于存储介质的特性,磁盘本身存取就比主存慢很多,再加上机械运动耗费,因此为了提高效率,要尽量减少磁盘 I/O,减少读写操作。 为了达到这个目的,磁盘往往不是严格按需读取,而是每次都会预读,即使只需要一个字节,磁盘也会从这个位置开始,顺序向后读取一定长度的数据放入内存。这样做的理论依据是计算机科学中著名的局部性原理:当一个数据被用到时,其附近的数据也通常会马上被使用。由于磁盘顺序读取的效率很高(不需要寻道时间,只需很少的旋转时间),因此预读可以提高I/O 效率页是计算机管理存储器的逻辑块,硬件及操作系统往往将主存和磁盘存储区分割为连续的大小相等的块,每个存储 块称为一页(1024 个字节或其整数倍),预读的长度一般为页的整倍数。主存和磁盘以页为单位交换数据。当程序要读取的数据不在主存中时,会触发一个缺页异常,此时系统会向磁盘发出读盘信号,磁盘会找到数据的起始位置并向后连续读取一页或几页载入内存中,然后异常返回,程序继续运行。文件系统的设计者利用了磁盘预读原理,将一个结点的大小设为等于一个页( 1024 个字节或其整数倍),这样每 个结点只需要一次I/O 就可以完全载入。那么 3 层的 B 树可以容纳 1024*1024*1024 差不多 10 亿个数据,如果换成二 叉查找树,则需要30 层!假定操作系统一次读取一个节点,并且根节点保留在内存中,那么 B 树在 10 亿个数据中查 找目标值,只需要小于3 次硬盘读取就可以找到目标值,但红黑树需要小于 30 次,因此 B 树大大提高了 IO 的操作效率。三、 B+树
B+ 树是对 B 树的一种变形树,它与 B 树的差异在于:1. 非叶结点仅具有索引作用,也就是说,非叶子结点只存储 key ,不存储 value ;2. 树的所有叶结点构成一个有序链表,可以按照 key 排序的次序遍历全部数据。2.1 B+树存储数据
若参数 M 选择为 5 ,那么每个结点最多包含 4 个键值对,我们以 5 阶 B+ 树为例,看看 B+ 树的数据存储。2.2 B+树和B树的对比
B+ 树的优点在于:1. 由于 B+ 树在非叶子结点上不包含真正的数据,只当做索引使用,因此在内存相同的情况下,能够存放更多的key 。 2.B+ 树的叶子结点都是相连的,因此对整棵树的遍历只需要一次线性遍历叶子结点即可。而且由于数据顺序排列并且相连,所以便于区间查找和搜索。而 B 树则需要进行每一层的递归遍历。B 树的优点在于:由于 B 树的每一个节点都包含 key 和 value ,因此我们根据 key 查找 value 时,只需要找到 key 所在的位置,就能找到value ,但 B+ 树只有叶子结点存储数据,索引每一次查找,都必须一次一次,一直找到树的最大深度处,也就是叶子结点的深度,才能找到 value 。3.3 B+树在数据库中的应用
在数据库的操作中,查询操作可以说是最频繁的一种操作,因此在设计数据库时,必须要考虑到查询的效率问题,在很多数据库中,都是用到了 B+ 树来提高查询的效率;在操作数据库时,我们为了提高查询效率,可以基于某张表的某个字段建立索引,就可以提高查询效率,那其实这个索引就是 B+ 树这种数据结构实现的。3.3.1 未建立主键索引查询

执行 select * from user where id=18 ,需要从第一条数据开始,一直查询到第6条,发现id=18,此时才能查询出目标结果,共需要比较6次;

3.3.3 区间查询
执行 select * from user where id>=12 and id<=18 , 如果有了索引,由于 B+ 树的叶子结点形成了一个有序链表,所以我们只需要找到id 为 12 的叶子结点,按照遍历链表的方式顺序往后查即可,效率非常高。 -
相关阅读:
Java.lang.Class类 getField(name)方法有什么功能呢?
SpringBoot项目创建及运行
Redis.conf配置文件说明
Linux内存管理(六):内存模型SPARSEMEM初始化
chatgpt赋能python:Python选择函数
记录Centos7.9 安装mongodb 6.0 过程遇到的坑和解决办法
如何快速将钉钉员工信息同步到飞书
zeek学习笔记(一) —— 环境搭建
QtAV环境配置
Unity-四元数
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_66117547/article/details/127601854
