-
Java面向对象编程(四)
目录
一、子类对象实例化过程
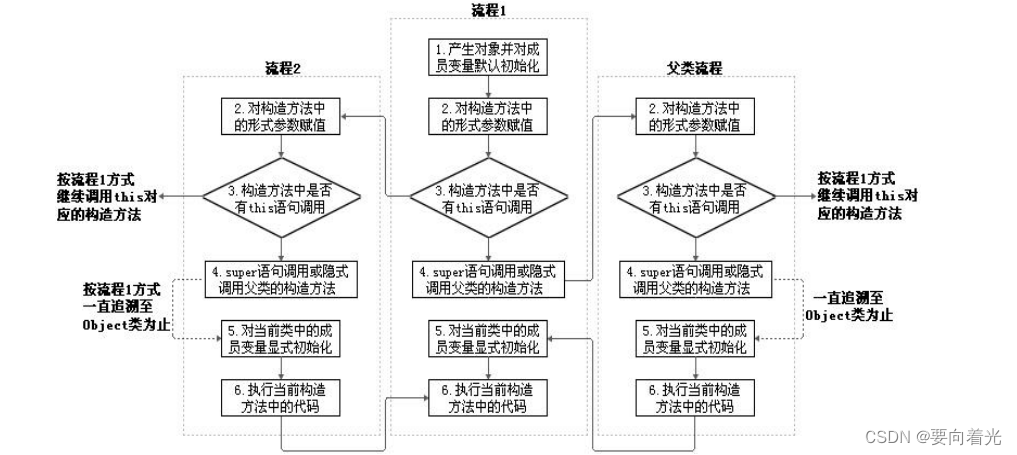
1、从结果上来看(继承性)
- 子类继承父类以后就获取了父类中声明的属性和方法
- 创建子类的对象时会在堆空间中加载所有父类中声明的属性
2、从过程上来看
- 当我们通过子类的构造器创建子类的对象时,一定会直接或间接的调用其父类的构造器,进而调用父类的父类的构造器,直到调用到java.lang.Object类中的空参的构造器上为止,正因为加载过了所有父类中的结构,所以才可以看到内存中有父类中声明的结构,子类中的对象才可以考虑进行调用
注意:虽然创建子类对象时调用了父类的构造器,但自始至终只创建了一个子类对象,即为new的子类对象
二、多态性
多态性是面向对象的重要概念。多态性在java中的体现为:父类的引用指向子类的对象(向上转型 upcasting)
多态性的使用前提
1、要有类的继承关系
2、要有方法的重写
多态的使用
java引用变量有两个类型:编译时类型和运行时类型。编译时类型由声明该变量时使用的类型决定,运行时类型有由际赋给该变量的对象决定。当编译时类型和运行时类型不一致时,就出现了多态性。
有了对象的多态性以后,在编译期,只能调用父类中声明的方法,但在运行期,实际执行的是子类重写父类的方法。(虚拟方法的调用)
注意:对象的多态性,只适用于方法,不适用于属性
如果一个引用类型变量声明为父类的类型,但实际引用的是子类的对象,那么该变量就不能再访问子类中添加的属性和方法。即有了对象的多态性后,在内存中实际上是加载了子类的属性和方法的,但是由于变量声明的是父类类型,导致编译时只能调用父类中声明的方法和属性,子类特有的属性和方法不能调用。
多态应用举例
方法声明的形参类型为父类类型,可以使用子类的对象作为实参调用该方法
- public class Test {
- public void method(Person e) {
- // ……
- e.getInfo();
- }
- public static void main(Stirng args[]) {
- Test t = new Test();
- Student m = new Student();
- t.method(m); // 子类的对象m传送给父类类型的参数e
- }
- }
虚方法的调用
正常方法调用
Person e =new Person();
e.getInfo();
Student s=new Student();
s.getIfo();
虚方法的调用
子类中定义了与父类中同名同参数的方法,在多态的情况下 ,将此时的父类的方法称为虚拟方法。父类根据付给他的不同的子类对象,动态地调用属于子类的方法。这样的方法调用在编译期是无法确定的。
Person e =new Student();
e.getInfo();
编译时类型和运行时类型
编译是e为Person类型,而方法的调用是在运行时确定的,所以调用的是Student类的getInfo()方法(动态绑定)
因此,我们说多态是运行时行为。
对象类型转换(Casting)
如果想让子类对象可以使用自己类中的属性及方法时,就要对带对象进行强制类型转换,java对象的强制类型转换称为造型。
说明:
1、从子类到父类的类型可以进行自动转换
2、从父类到子类的类型转换必须是通过(强制类型转换)实现
3、无继承关系的引用类型间的转换是非法的
4、在造型前可以使用instanceof操作符测试一个对象的类型
instanceof操作符
如果子类想继续使用为了避免在向下转型之前出项classCastExecption的异常,我们可以在向下转型之前,先进性instanceof判断,一旦返回true,就进行向下转型,如果返回false,则不进行向下转型。
x instanceof A
检验是否为类A的对象,返回值为boolean型
要求x所属的类于类A必须是子类和父类的关系,否则编译报错(必须存在继承)
如果x属于类A的子类B,x instanceof A 的值也为true
instanceof练习
建立InstanceTest 类,在类中定义方法 method(Person e);
在method中:
(1)根据e的类型调用相应类的getInfo()方法。
(2)根据e的类型执行:
如果e为Person类的对象,输出: “a person”;
如果e为Student类的对象,输出: “a student” “a person ”
如果e为Graduate类的对象,输出: “a graduated student” “a student” “a person”
- public class InstanceTest {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- InstanceTest test =new InstanceTest();
- test.method(new Person());
- System.out.println("------------");
- test.method(new Student());
- System.out.println("------------");
- test.method(new Graduate());
- }
- public void method(Person e) {
- String info = e.getInfo();
- System.out.println(info);
- if(e instanceof Graduate) {
- System.out.println("a garduated student"+"\na student"+"\na person");
- }else if(e instanceof Student) {
- System.out.println("a student"+"\na person");
- }else {
- System.out.println("a person");
- }
- }
- }
- class Person{
- protected String name="person";
- protected int age=50;
- public String getInfo() {
- return "Name:"+name+"\n"+"age:"+age;
- }
- }
- class Student extends Person{
- protected String school="pku";
- public String getInfo() {
- return "Name:"+name+"\nage:"+age
- +"\nschool"+school;
- }
- }
- class Graduate extends Student{
- public String major="IT";
- public String getInfo() {
- return "Name:"+name+"\nage:"+age
- +"\nschool"+school+"\nmajor"+major;
- }
- }
运行结果如下:

多态练习
定义三个类,父类GeometricObject代表几何形状,子类Circle代表圆形,MyRectangle代表矩形。 定义一个测试类GeometricTest,编写equalsArea方法测试两个对象的面积是否相等(注意方法的参 数类型,利用动态绑定技术),编写displayGeometricObject方法显示对象的面积(注意方法的参 数类型,利用动态绑定技术)。

- public class GeometricTest {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- GeometricTest geo=new GeometricTest();
- //测试面积是否相等
- geo.equalArea(new Circle(2.5,"red",2.5),new Circle(2.6,"red",2.5));
- //分别显示圆和对象的面积
- geo.displayGeometricObject(new Circle(2.5,"red",2.5),new MyRectangle(2, 2, "blue", 2));
- }
- /**
- * 测试两个对象的面积是否相等 动态绑定
- */
- public void equalArea(GeometricObject cir,GeometricObject rec) {
- if(cir.findArea()==rec.findArea()) {
- System.out.println("两对象面积相等");
- }else {
- System.out.println("两对象面积不相等");
- }
- }
- /***
- * 显示对象面积 动态绑定
- */
- public void displayGeometricObject(GeometricObject cir,GeometricObject rec) {
- System.out.println("圆形的面积是:"+cir.findArea());
- System.out.println("矩形的面积是:"+rec.findArea());
- }
- }
- /**
- * 几何形状
- * @author light
- * 父类
- *
- */
- class GeometricObject{
- protected String color;
- protected double weight;
- protected GeometricObject(String color,double weight) {
- this.color=color;
- this.weight=weight;
- }
- public String getColor() {
- return color;
- }
- public void setColor(String color) {
- this.color = color;
- }
- public double getWeight() {
- return weight;
- }
- public void setWeight(double weight) {
- this.weight = weight;
- }
- public double findArea() {
- return 0.0;
- }
- }
- /**
- * 圆形
- * @author light
- * 继承于GeometricObject类
- *
- */
- class Circle extends GeometricObject{
- private double radius;
- public Circle(double radius,String color,double weight) {
- super(color, weight);
- this.radius=radius;
- }
- public double getRadius() {
- return radius;
- }
- public void setRadius(double radius) {
- this.radius = radius;
- }
- /**
- * @Override 圆形类重写父类返回面积方法
- */
- public double findArea() {
- return getRadius()*getRadius()*Math.PI;
- }
- }
- /**
- * 矩形
- * @author light
- * 继承于GeometricObject类
- *
- */
- class MyRectangle extends GeometricObject{
- private double width;
- private double height;
- public MyRectangle(double width,double height,String color,double weight) {
- super(color,weight);
- this.width=width;
- this.height=height;
- }
- public double getWidth() {
- return width;
- }
- public void setWidth(double width) {
- this.width = width;
- }
- public double getHeight() {
- return height;
- }
- public void setHeight(double height) {
- this.height = height;
- }
- /**
- * @Override 矩形类重写父类返回面积方法
- */
- public double findArea() {
- return getHeight()*getWidth();
- }
- }
运行结果如下:

-
相关阅读:
uni-app 5小时快速入门 2 创建uni-app工程(上)
LSTM和GRU
gradle安装配置
Redis高可用的主从复制、哨兵、cluster集群
JDK中内嵌JS引擎介绍及使用
Python 组合序号
初识数据库Mysql
sqlmap基本使用方法
PHP笔记-解决网站CDN加速后图片出现跨越问题
时间复杂度和空间复杂度
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zssxcj/article/details/127531829
